
Voles are small rodents that are relatives of lemmings and hamsters, but with a stouter body; a longer, hairy tail; a slightly rounder head; smaller eyes and ears; and differently formed molars. They are sometimes known as meadow mice or field mice in North America.

The eastern meadow vole, sometimes called the field mouse or meadow mouse, is a North American vole found in eastern Canada and the United States. Its range extends farther south along the Atlantic coast.

Microtus is a genus of voles found in North America, Europe and northern Asia. The genus name refers to the small ears of these animals. They are stout rodents with short ears, legs and tails. They eat green vegetation such as grasses and sedges in summer, and grains, seeds, root and bark at other times. The genus is also called "meadow voles".

The North American water vole or just water vole is the largest North American vole. It is found in the northwestern United States and southern parts of western Canada. This animal has been historically considered a member of genus Arvicola, but molecular evidence demonstrates that it is more closely related to North American Microtus species. Water voles are on the USDA Forest Service Region 2 sensitive species list because they maintain very small populations and there is high concern that their required habitat may be declining.

The southern bog lemming is a small North American lemming. Its range overlaps with the other species in genus Synaptomys, the northern bog lemming, in southeastern Canada, but extends farther south.

The singing vole, is a medium-sized vole found in northwestern North America, including Alaska and northwestern Canada.

The rock vole, also known as the yellow-nosed vole, is a medium-sized species of vole found in eastern North America.

The prairie vole is a small vole found in central North America.

The short-tailed field vole, short-tailed vole, or simply field vole is a grey-brown vole, around 10 cm in length, with a short tail. It is one of the most common mammals in Europe, with a range extending from the Atlantic coast to Lake Baikal. These voles are found in moist grassy habitats, such as woodland, marsh or on river banks. Although they make shallow burrows, they usually build nests above ground. They are an important food source for owls and some other predators and their population size tends to peak and trough cyclically. Field voles breed prolifically, mainly in summer, but often all year round, even under snow. Females produce up to seven litters a year, each averaging from four to six young which are weaned after about fourteen days. The short-tailed field vole is both widespread and common and is listed as being of "Least Concern" by the IUCN.

The gray-tailed vole also known as the gray-tailed meadow vole or gray-tailed meadow mouse, is a rodent in the genus Microtus of the family Cricetidae. Voles are small mammals, and this species lies roughly in the middle of their size range. First collected in 1895, it is endemic to the Willamette Valley, Oregon, and Clark County, Washington, in the Pacific Northwest region of North America. Historically, they were found in the prairie areas of the Valley and, though many of these areas have been converted for agricultural purposes, these animals remain common. For reasons that remain unclear, vole population densities in any area may fluctuate widely from season to season and year to year. They are preyed upon by owls, hawks, and carnivorous mammals, and their parasites include fleas and ticks. These voles build burrows and complex tunnel networks, which they sometimes share with other burrowing animals. Relatively little is known about their behavior in the wild, because they are elusive and unlikely to enter traps.

The California vole is a type of vole which lives throughout much of California and part of southwestern Oregon. It is also known as the "California meadow mouse", a misnomer as this species is a vole, not a mouse. It averages 172 mm (6.8 in) in length although this length varies greatly between subspecies.
The Afghan vole is a species of rodent in the family Cricetidae. It is found in south-central Asia.
Irenomys tarsalis, also known as the Chilean climbing mouse, Chilean tree mouse, or long-footed irenomys, is a rodent found in Chile, from about 36° to 46°S, and in adjacent Argentina, mainly in forests. It is a large, long-tailed, soft-furred mouse characterized by grooved upper incisors and specialized molars with transverse ridges, divided by deep valleys, which are connected by a transverse ridge along the midline of the molars.
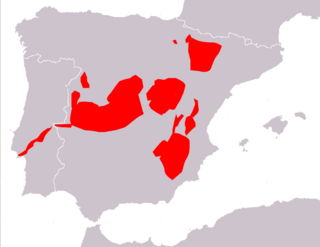
Cabrera's vole is a species of vole native to Spain and Portugal. It is named for Ángel Cabrera, a mammalogist then working at the Museo Nacional de Ciencias Naturales in Madrid. It is the only living member of the subgenus Iberomys, although two fossil species are also known, including M. brecciensis, the likely direct ancestor of the living species.
The Mediterranean pine vole is a species of rodent in the family Cricetidae. It is found in France, Andorra, Portugal, and Spain where it lives in a network of shallow tunnels.

The montane vole is a species of vole native to the western United States and Canada.

The creeping vole, sometimes known as the Oregon meadow mouse, is a small rodent in the family Cricetidae. Ranging across the Pacific Northwest of North America, it is found in forests, grasslands, woodlands, and chaparral environments. The small-tailed, furry, brownish-gray mammal was first described in the scientific literature in 1839, from a specimen collected near the mouth of the Columbia River. The smallest vole in its range, it weighs around 19 g. At birth, they weigh 1.6 g, are naked, pink, unable to open their eyes, and the ear flaps completely cover the ear openings. Although not always common throughout their range, there are no major concerns for their survival as a species.
The Zempoaltépec vole is a species of rodent in the family Cricetidae. The name Microtus is from the Greek word mikros meaning small and otus meaning ear. The name umbrosus could be from the Latin umbros meaning shady. It is rather large and has a long tail when compared with other voles. Its pelage is long and soft. In the upper parts, the hair is uniformly dusky with brown tips and the lower parts a dark grey thinly washed with a reddish yellow color. It is found only in Mexico, in a semi-isolated mountain range southeast of the Cajones River in Mixes district, in Oaxaca.

There are at least 9 large terrestrial mammals, 50 small mammals, and 14 marine mammal species known to occur in Olympic National Park.



















