
Lizard Mound County Park is a county-operated park in the Town of Farmington, Washington County, Wisconsin near the city of West Bend. Established in 1950, it was acquired by Washington County from the state of Wisconsin in 1986. It contains a significant well-preserved effigy mound group.

Shiloh Indian Mounds Site (40HR7) is an archaeological site of the South Appalachian Mississippian culture. It is located beside the Tennessee River on the grounds of the Shiloh National Military Park, in Hardin County of southwestern Tennessee. A National Historic Landmark, it is one of the largest Woodland era sites in the southeastern United States.

The Kolomoki Mounds is one of the largest and earliest Woodland period earthwork mound complexes in the Southeastern United States and is the largest in Georgia. Constructed from 350CE to 600CE, the mound complex is located in southwest Georgia, in present-day Early County near the Chattahoochee River.

An effigy mound is a raised pile of earth built in the shape of a stylized animal, symbol, religious figure, human, or other figure. Effigy mounds were primarily built during the Late Woodland Period.

This is a list of the National Register of Historic Places listings in Dane County, Wisconsin. It aims to provide a comprehensive listing of buildings, sites, structures, districts, and objects in Dane County, Wisconsin listed on the National Register of Historic Places.

The Beattie Park Mound Group is a grouping of Late Woodland period Indian mounds located in downtown Rockford, Illinois, United States.

High Cliff State Park is a 1,187-acre (480 ha) Wisconsin state park near Sherwood, Wisconsin. It is the only state-owned recreation area located on Lake Winnebago. The park got its name from cliffs of the Niagara Escarpment, a land formation east of the shore of Lake Winnebago that stretches north through northeast Wisconsin, Upper Michigan, and Ontario to Niagara Falls and New York State.

Rock Eagle Effigy Mound is an archaeological site in Putnam County, Georgia, U.S. estimated to have been constructed c. 1000 BC to AD 1000. The earthwork was built up of thousands of pieces of quartzite laid in the mounded shape of a large bird. Although it is most often referred to as an eagle, scholars do not know exactly what type of bird the original builders intended to portray. It is listed on the National Register of Historic Places (NRHP) because of its significance. The University of Georgia administers the site. It uses much of the adjoining land for a 4-H camp, with cottages and other buildings, and day and residential environmental education.

Cranberry Creek Archeological District, also known as Cranberry Creek Mound Group, is an ancient American Indian burial mound site from circa AD 100–800 near New Miner, Wisconsin, United States. It is three miles east of Necedah National Wildlife Refuge in Juneau County. It is part of the "effigy mound culture" of native peoples in Wisconsin, who practiced the "respectful burial of their dead".
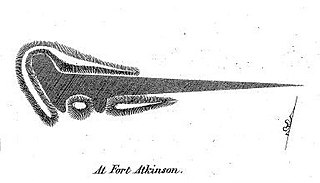
The Panther Intaglio Effigy Mound is a ground depression in Fort Atkinson, Wisconsin. The effigy is a reverse mound: a depression in the shape of a panther or water spirit scooped out by prehistoric Native Americans. In the mid-1800s ten of these reverse effigy mounds were found in Wisconsin, but all except this one have been destroyed. It was added to the National Register of Historic Places in 1970.

The Gee's Slough Group of Indian Mounds, located along the Lemonweir River just outside of New Lisbon, Wisconsin, is listed on the US National Register of Historic Places. The New Lisbon area was a winter gathering place for the Woodland Culture Indians who are considered the ancestors to the Ho-Chunk (Winnebago) tribe.

Grand Mound is a prehistoric burial site in Koochiching County, Minnesota, United States. It is the largest surviving prehistoric structure in the upper Midwest, dating back to 200 BCE. The site was listed as a National Historic Landmark on June 23, 2011.

This is a list of the National Register of Historic Places listings in Madison, Wisconsin.

The Man Mound is a prehistoric humanoid earthwork located in Greenfield, Sauk County, Wisconsin, east of the city of Baraboo. Constructed during the Late Woodland period, the mound is the only surviving anthropomorphic effigy mound in North America. The mound depicts a horned humanoid figure and may have held religious or ceremonial significance to its builders. The mound was preserved as a county park in 1908, listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1978 and designated a National Historic Landmark in 2016.

The Lewis Mound Group (47-Da-74) is a set of prehistoric Native American burial mounds in the village of McFarland, Dane County, Wisconsin, southeast of Madison. Created by late Woodland people overlooking the eastern shore of Lake Waubesa, they include a bear effigy, a hook-shaped mound, and some geometric shapes. They are visible from public trails in Indian Mound Park, which is owned by the village, just west of Indian Mound Middle School. The site was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1984.

Vilas Circle Bear Effigy Mound and the Curtis Mounds are a group of Native American mounds in Madison, Wisconsin. The Bear Effigy Mound is in the public Bear Mound Park, while the Curtis Mounds are on a neighboring residential property. As its name indicates, the Bear Effigy Mound is in the shape of a bear, and is intact except for a section of the bear's leg. The Curtis Mounds were seven linear mounds running down the hill and several conical mounds. Now only parts of one or two linear mounds remain, on private property.

Burrows Park Effigy Mound and Campsite is an archaeological site in Burrows Park in Madison, Wisconsin. The site includes a bird-shaped effigy mound with an 128-foot (39 m) wingspan; it once included a fox-shaped mound as well, though it has been destroyed. The mound was built by Mound Builders during the Late Woodland period, likely between 700 and 1200 A.D. The Mound Builders used effigy mounds as burial sites, and bird-shaped mounds represented sky spirits in their religion; effigies of other animals were used to represent different elements. A 1934 restoration project repaired vandalism to the mound and cleaned up its surroundings.

The Elmside Park Mounds are a group of Native American mounds in Elmside Park in Madison, Wisconsin. The group includes two animal-shaped effigy mounds; while their shapes are inconclusive, they have been described as a lynx and a bear. The mounds were once part of the Oakridge Mound Group, which included three other mounds, but the others were destroyed by home construction. Mound Builder peoples built the mounds in the Late Woodland period, likely between 800 and 1100 A.D., to serve as burial and ceremonial sites. The mounds may be the only remnant of a Late Woodland community on the northeast shore of Lake Monona and are archaeologically significant in the study of Late Woodland civilizations.

The Mills Woods Mound, also known as the Hudson Park Mound, is a Native American mound in Hudson Park in Madison, Wisconsin. It is an animal-shaped effigy mound with a long tail, though the exact animal it represents is unclear. The mound was once part of the large Mills Woods Mound Group, which included roughly thirty mounds of various shapes, but construction destroyed every other mound in the group. The mound group was built during the Late Woodland period, roughly between 800 and 1100 A.D., by a Mound Builder group; the Mound Builders used mounds for burials and ceremonial purposes. The mound is one of less than 60 effigy mounds remaining in Dane County, which once had 289 of the mounds, and has potential archaeological significance for the study of Late Woodland civilizations.

The Pflaum-McWilliams Mound Group, also known as the Edna Taylor Conservancy Mound Group, is a group of Native American mounds in Madison, Wisconsin. Located in the Edna Taylor Conservancy in southeast Madison, the group includes an animal effigy mound and six linear mounds. The linear mounds are unusually long compared to other surviving mounds in the Madison area; the longest is 484 feet (148 m), and several are over 200 feet (61 m) in length. While a number of the linear mounds have been damaged, the group is generally well-preserved. The mounds were built during the Late Woodland period, most likely between 800 and 1100 A.D., and were thought to have been used for ceremonial purposes.






















