
Stomiiformes is an order of deep-sea ray-finned fishes of very diverse morphology. It includes, for example, dragonfishes, lightfishes, loosejaws, marine hatchetfishes and viperfishes. The order contains 4 families with more than 50 genera and at least 410 species. As usual for deep-sea fishes, there are few common names for species of the order, but the Stomiiformes as a whole are often called dragonfishes and allies or simply stomiiforms.

The prowfish is a species of scorpaeniform marine fish found in the northern Pacific Ocean. It is the only extant member of the family, Zaproridae. There are 2 extinct species only known with fossil records, Zaprora koreana from the Middle Miocene aged Duho Formation in Pohang, South Korea. Another genus, Araeosteus rothi, is known from the Monterey Formation and the Modelo Formation in Southern California.

The Gonostomatidae are a family of mesopelagic marine fish, commonly named bristlemouths, lightfishes, or anglemouths. It is a relatively small family, containing only eight known genera and 32 species. However, bristlemouths make up for their lack of diversity with relative abundance, numbering in the hundreds of trillions to quadrillions. The genus Cyclothone is thought to be one of the most abundant vertebrate genera in the world.
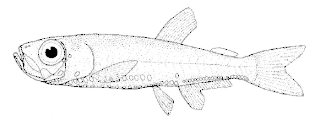
Maurolicus is an oceanic ray-finned fish genus which belongs in the marine hatchetfish family Sternoptychidae. They are commonly known as pearlsides, but the brilliant pearlside is the related Argyripnus iridescens. Occasionally, "bristle-mouth fishes" is used as a common name, but that usually refers to the genus Argyripnus or the family Gonostomatidae.
The Dalatiidae are the family of kitefin sharks of the order Squaliformes. Members of this family are small, under 2 m (6.6 ft) long, and are found worldwide. They have cigar-shaped bodies with narrow heads and rounded snouts. Several species have specialized bioluminescent organs. Though eight genera are in this family, four of them are monotypic.

Dalatias is a genus of kitefin sharks that have lived since the Middle Eocene. It was thought to be a monotypic taxon with the type species, D. licha, considered as the only species until 2022, when Malyshkina and her colleagues described a new Middle Miocene species, D. orientalis. D. orientalis is from the Middle Miocene aged Duho Formation in Pohang, South Korea.
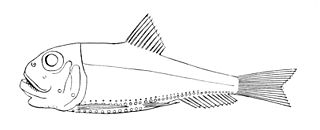
Lightfishes are small stomiiform fishes in the family Phosichthyidae

Chimaera is the type genus of the cartilaginous fish family Chimaeridae.
Vinciguerria poweriae is a species of lightfish belonging to the genus Vinciguerria. They are mostly found in seawater 300–600 metres (1,000–2,000 ft) deep during the day and 50–350 metres (160–1,150 ft) deep at night. They feed on small crustaceans.

Vinciguerria attenuata, commonly known as the slender lightfish, is a small species of ray-finned fish in the family Phosichthyidae, found in deep water in warmer parts of the Atlantic, the Indian and Pacific Oceans.

Cyclothone is a genus containing 13 extant species of bioluminescent fish, commonly known as 'bristlemouths' or 'bristlefishes' due to their shared characteristic of sharp, bristle-like teeth. These fishes typically grow to around 1–3 inches, though some can be larger. They are most commonly found in the mesopelagic zone of the ocean, mostly at depths of over 300 meters, and many species have bioluminescence.

Ichthyococcus are a genus of lightfishes. It is one of seven genera in the family Phosichthyidae.

Coreoperca is a genus of ray-finned fish native to eastern Asia. The members of the genus Coreoperca are known as the oriental perches or eastern perches, freshwater gamefish belonging to the family Sinipercidae. These fish prefer clear, slow-moving currents on the middle reaches of rivers. Eggs are laid in May and June on plants. The eggs and fry are protected by the male.

Gasterosteus is a genus of ray-finned fishes belonging to the family Gasterosteidae, the sticklebacks. These fishes are found in freshwater, brackish water and marine habitats in the Holarctic region.
Stenobrachius is a genus of lanternfishes.

Parotodus, commonly known as the false-toothed mako shark, is an extinct genus of mackerel shark that lived approximately 53 to one million years ago during the Eocene and Pleistocene epochs. Its teeth, which are found worldwide, are often prized by fossil collectors due to their rarity. The scarcity of fossils is because Parotodus likely primarily inhabited open oceans far away from the continents. While the placement of Parotodus with the Lamniformes has been debated, most researchers agree it was probably a member of a now extinct shark clade, either a otodontid or a cardabiodont. In any case, it would have been the last members of either group. While originally being suspected of dying out at the very end of the Pliocene, fossils found in the Waccamaw Formation show that it made it to the Pleistocene.
This list of fossil fishes described in 2019 is a list of new taxa of jawless vertebrates, placoderms, acanthodians, fossil cartilaginous fishes, bony fishes, and other fishes of every kind that were described during the year 2019, as well as other significant discoveries and events related to paleoichthyology that occurred in 2019.
This list of fossil fishes described in 2020 is a list of new taxa of jawless vertebrates, placoderms, acanthodians, fossil cartilaginous fishes, bony fishes, and other fishes of every kind that were described during the year 2020, as well as other significant discoveries and events related to paleoichthyology that occurred in 2020.
This list of fossil fish research presented in 2021 is a list of new taxa of jawless vertebrates, placoderms, acanthodians, fossil cartilaginous fishes, bony fishes, and other fishes that were described during the year, as well as other significant discoveries and events related to paleoichthyology that occurred in 2021.
This list of fossil fish research presented in 2022 is a list of new fossil taxa of jawless vertebrates, placoderms, cartilaginous fishes, bony fishes, and other fishes that were described during the year, as well as other significant discoveries and events related to paleoichthyology that occurred in 2022.












