This article includes a list of general references, but it lacks sufficient corresponding inline citations .(March 2013) |
| White-faced whistling duck | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Three-note whistling call | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Aves |
| Order: | Anseriformes |
| Family: | Anatidae |
| Genus: | Dendrocygna |
| Species: | D. viduata |
| Binomial name | |
| Dendrocygna viduata (Linnaeus, 1766) | |
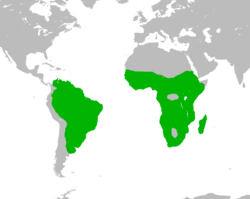 | |
| Range | |
| Synonyms | |
The white-faced whistling duck (Dendrocygna viduata) is a whistling duck that breeds in sub-Saharan Africa and much of South America.
Contents
- Taxonomy
- Description
- Distribution and habitat
- Behaviour and ecology
- Breeding
- Conservation
- Gallery
- References
- Further reading
This species is gregarious, and at favoured sites, the flocks of a thousand or more birds arriving at dawn are an impressive sight. As the name implies, these are noisy birds with a clear three-note whistling call.







