| Common name | Scientific name and subspecies | Range | Size and ecology | IUCN status and estimated population |
|---|
| West Indian whistling duck  | Dendrocygna arborea
(Linnaeus, 1758) | Cuba, the Cayman Islands, Antigua and Barbuda, Jamaica, Hispaniola (both the Dominican Republic and Haiti), and Puerto Rico.
 | Size: Length of 48 to 58 cm (19 to 23 in). The female weighs from 800 to 1,320 g (1.76 to 2.91 lb) and the male weighs from 760 to 1,240 g (1.68 to 2.73 lb)
Habitat:
Diet: | NT
6,000 - 15,000  [15] [15]
|
|---|
| Wandering whistling duck  | Dendrocygna arcuata
(Horsfield, 1824)
- D. a. arcuata(Horsfield, 1824)
- D. a. australis(Reichenbach, 1850)
- D. a. pygmaea(Mayr, 1945)
| Australia, the Philippines, Borneo, Indonesia, Papua New Guinea, and the Pacific Islands | Size: 54–60 cm in height and weigh on average 750 grams.
Habitat:
Diet: | LC
[16] 
|
|---|
| Black-bellied whistling duck  | Dendrocygna autumnalis
(Linnaeus, 1758)
| southernmost United States, Mexico, and tropical Central to south-central South America
 | Size: Length ranges from 47 to 56 cm (19 to 22 in), body mass from 652 to 1,020 g (1.437 to 2.249 lb), and wingspan ranges from 76 to 94 cm (30 to 37 in).
Habitat:
Diet: | LC
[17] 
|
|---|
| Fulvous whistling duck  | Dendrocygna bicolor
(Vieillot, 1816) | Mexico and South America, the West Indies, the southern United States, sub-Saharan Africa and the Indian subcontinent.
 | Size: 45–53 cm (18–21 in) long; the male weighs 748–1,050 g (26.4–37.0 oz), and the female averages marginally lighter at 712–1,000 g (25.1–35.3 oz)
Habitat:
Diet: | LC
[18] 
|
|---|
| Plumed whistling duck  | Dendrocygna eytoni
(Eyton, 1838) | Australia. | Size: Measuring 42–60 cm (16.5–23.5 in) and weighing around one kilogram (2.2 lb)
Habitat:
Diet: | LC
[19] 
|
|---|
| Spotted whistling duck  | Dendrocygna guttata
(Schlegel, 1866) | Indonesia, New Guinea, Australia and the Philippines | Size: 43–50 cm tall. Males can weigh anywhere from 590g to 650g while females weigh 610g to 860g.
Habitat:
Diet: | LC
6,700 - 17,000 [20] 
|
|---|
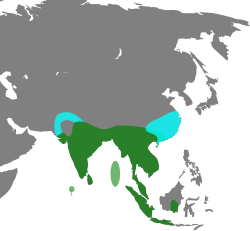
| Lesser whistling duck  | Dendrocygna javanica
(Horsfield, 1821) | Indian subcontinent and Southeast Asia.
 | Size:
Habitat:
Diet: | LC
 [21] [21]
|
|---|
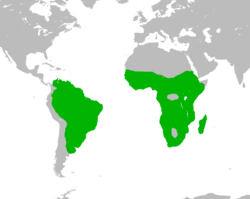
| White-faced whistling duck  | Dendrocygna viduata
(Linnaeus, 1766) | sub-Saharan Africa and much of South America.
 | Size:
Habitat:
Diet: | LC
[22] 
|
|---|















