
Malawi, officially the Republic of Malawi, is a landlocked country in Southeastern Africa that was formerly known as Nyasaland. It is bordered by Zambia to the west, Tanzania to the north and northeast, and Mozambique to the east, south and southwest. Malawi spans over 118,484 km2 (45,747 sq mi) and has an estimated population of 19,431,566. Malawi's capital is Lilongwe. Its second-largest is Blantyre, its third-largest is Mzuzu and its fourth-largest is its former capital, Zomba. The name Malawi comes from the Maravi, an old name for the Chewa people who inhabit the area. The country is nicknamed "The Warm Heart of Africa" because of the friendliness of its people.
The History of Malawi covers the area of present-day Malawi. The region was once part of the Maravi Empire. In colonial times, the territory was ruled by the British, under whose control it was known first as British Central Africa and later Nyasaland. It became part of the Federation of Rhodesia and Nyasaland. The country achieved full independence, as Malawi, in 1964. After independence, Malawi was ruled as a one-party state under Hastings Banda until 1994.

Hastings Kamuzu Banda was the prime minister and later president of Malawi from 1964 to 1994.
Music of Malawi has historically been influenced through its triple cultural heritage of British, African, and American music. Malawians have long been travelers and migrant workers, and as a result, their music has spread across the African continent and blended with other music forms. One of the prime historical causes of the Malawian musical melting pot was World War II, when soldiers both brought music to distant lands and also brought them back. By the end of the war, guitar and banjo duos were the most popular type of dance bands. Both instruments were imported. Malawians working in the mines in South Africa and Mozambique also led to fusion and blending in music styles, giving rise to music styles like Kwela.
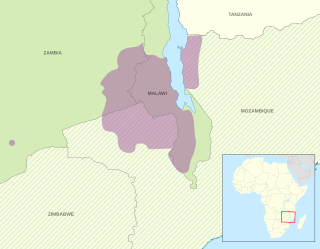
Chewa is a Bantu language spoken in Malawi and a recognised minority in Zambia and Mozambique. The noun class prefix chi- is used for languages, so the language is usually called Chichewa and Chinyanja. In Malawi, the name was officially changed from Chinyanja to Chichewa in 1968 at the insistence of President Hastings Kamuzu Banda, and this is still the name most commonly used in Malawi today. In Zambia, the language is generally known as Nyanja or Cinyanja/Chinyanja '(language) of the lake'.

Blantyre is Malawi's centre of finance and commerce, and its second largest city, with an enumerated 800,264 inhabitants as of 2018. It is sometimes referred to as the commercial and industrial capital of Malawi as opposed to the political capital, Lilongwe. It is the capital of the country's Southern Region as well as the Blantyre District.
The Tumbuka language is a Bantu language which is spoken in Malawi, Zambia, and Tanzania. It is also known as Chitumbuka or Citumbuka — the chi- prefix in front of Tumbuka means "in the manner of", and is understood in this case to mean "the language of the Tumbuka people". Tumbuka belongs to the same language group as Chewa and Sena.

The Chewa are a Bantu ethnic group native to central and southern Africa and the largest ethnic group in Malawi. The Chewa are closely related to people in surrounding regions such as the Tumbuka and Nsenga. They are historically also related to the Bemba, with whom they share a similar origin in the Democratic Republic of the Congo. As with the Nsenga and Tumbuka, a small part of Chewa territory came under the influence of the Ngoni, who were of Zulu or Natal/Transvaal origin. An alternative name, often used interchangeably with Chewa, is Nyanja. Their language is called Chichewa. Internationally, the Chewa are mainly known for their masks and their secret societies, called Nyau, as well as their agricultural techniques.

Islam is the second largest religion in Malawi behind Christianity. Nearly all of Malawi's Muslims adhere to Sunni Islam. Though difficult to assess, according to the CIA Factbook, in 2018 about 13.8% of the country's population was Muslim. Muslim organisations in the country claim a figure of 20-25%. According to the latest census (2018), Muslims make up 13.8% (2,426,754) of the country's population. According to the Malawi Religion Project run by the University of Pennsylvania, in 2010 approximately 25.6% of the population was Muslim, concentrated mostly in the Southern Region.

The United States established diplomatic relations with Malawi in 1964 after Malawi gained independence from the United Kingdom. Malawi's transition from a one-party state to a multi-party democracy significantly strengthened the already cordial U.S. relationship with Malawi. Significant numbers of Malawians study in the United States. The United States has an active Peace Corps program, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Department of Health and Human Servicess, and an Agency for International Development (USAID) mission in Malawi. Both countries have a common history and English language, as they were part of the British Empire.
Tobacco production in Malawi is one of the nation's largest sources of income. As of 2005, Malawi was the twelfth-largest producer of tobacco leaves and the 7th largest global supporter of tobacco leaves. As of 2010, Malawi was the world's leading producer of burley leaf tobacco. With the decline of tobacco farms in the West, interest in Malawi's low-grade, high-nicotine tobacco has increased. Today, Malawian tobacco is found in blends of nearly every cigarette smoked in industrialized nations including the popular and ubiquitous Camel and Marlboro brands. It is the world's most tobacco dependent economy. In 2013 Malawi produced about 133,000 tonnes of tobacco leaf, a reduction from a maximum of 208,000 tonnes in 2009 and although annual production was maintained at similar levels in 2014 and 2015, prices fell steadily from 2013 to 2017, in part because of weakening world demand but also because of declining quality.

Malawian cannabis, particularly the strain known as Malawi Gold, is internationally renowned as one of the finest sativa strains from Africa. According to a World Bank report it is among "the best and finest" marijuana strains in the world, generally regarded as one of the most potent psychoactive pure African sativas. The popularity of this variety has led to such a profound increase in marijuana tourism and economic profit in Malawi that Malawi Gold is listed as one of the three "Big C's" in Malawian exports: chambo, chombe (tea), and chamba (cannabis).
The Mwangwego script is an abugida writing system developed for Malawian languages and other African Bantu languages by linguist Nolence Mwangwego in 1977. It is one of several indigenous scripts invented for local language communities in Africa.
Mass media in Malawi consist of several different types of communications media: television, radio, cinema, newspapers, magazines and Internet-based Web sites. Malawi also has a growing music industry. Media is either privately owned or government owned.
Ezra Jofiya Chadza (1923-1985) or E.J. Chadza, as he signed his books, was a well-known Malawian teacher, author and poet, writing especially in the Chichewa language of Malawi.

Professor Francis P. B. Moto is a Malawian writer, academic, and diplomat. His home is Golomoti in the Dedza District of Malawi. He attended secondary school in Chichiri in Blantyre and was admitted to the University of Malawi in 1972, obtaining a degree in linguistics in 1977.
Willie T. Zingani is a Malawian novelist, poet, playwright and journalist.
Boston Jaston Soko, is a professor at Mzuzu University in the French section of the Faculty of Education's department of Languages and Literature. He has taught in several universities on French language as well as French literature. He has written for over four decades on African literature in French language as well as in English. Prof. Soko is also a chair-person of the Ngoni cultural heritage association known as Mzimba Heritage Association. He coined the name for the Ngoni Cultural Festival which is called "uMthetho". The name was approved by the Executive and His Majesty Inkosi ya Makosi M'mbelwa IV in 2004. Professor Soko's work is much praised and appreciated for contributing to the promotion of the French language in the Republic of Malawi as well as promoting Malawian literature. He "has been very active in research in African Literatures, teaching the African novel of French expression, negritude poetry, and oral literature".
Alfred (“Al”) D. Mtenje is a professor of Linguistics at the University of Malawi. He is known for his work on the prosody of Malawian Bantu languages, as well as for his work in support of language policies promoting the native languages of Malawi.









