Related Research Articles
The field of articulatory phonetics is a subfield of phonetics that studies articulation and ways that humans produce speech. Articulatory phoneticians explain how humans produce speech sounds via the interaction of different physiological structures. Generally, articulatory phonetics is concerned with the transformation of aerodynamic energy into acoustic energy. Aerodynamic energy refers to the airflow through the vocal tract. Its potential form is air pressure; its kinetic form is the actual dynamic airflow. Acoustic energy is variation in the air pressure that can be represented as sound waves, which are then perceived by the human auditory system as sound.
Uvulars are consonants articulated with the back of the tongue against or near the uvula, that is, further back in the mouth than velar consonants. Uvulars may be stops, fricatives, nasals, trills, or approximants, though the IPA does not provide a separate symbol for the approximant, and the symbol for the voiced fricative is used instead. Uvular affricates can certainly be made but are rare: they occur in some southern High-German dialects, as well as in a few African and Native American languages. Uvular consonants are typically incompatible with advanced tongue root, and they often cause retraction of neighboring vowels.

The voiced uvular trill is a type of consonantal sound, used in some spoken languages. The symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet that represents this sound is ⟨ʀ⟩, a small capital version of the Latin letter r. This consonant is one of several collectively called guttural R.
The voiced alveolar fricatives are consonantal sounds. The symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet that represents these sounds depends on whether a sibilant or non-sibilant fricative is being described.

The voiced pharyngeal approximant or fricative is a type of consonantal sound, used in some spoken languages. The symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet that represents this sound is ⟨ʕ⟩, and the equivalent X-SAMPA symbol is ?\. Epiglottals and epiglotto-pharyngeals are often mistakenly taken to be pharyngeal.

The voiced uvular fricative is a type of consonantal sound, used in some spoken languages. The symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet that represents this sound is ⟨ʁ⟩, an inverted small uppercase letter ⟨ʀ⟩, or in broad transcription ⟨r⟩ if rhotic. This consonant is one of the several collectively called guttural R when found in European languages.

The voiced uvular plosive or stop is a type of consonantal sound, used in some spoken languages. The symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet that represents this sound is ⟨ɢ⟩, a small capital version of the Latin letter g, and the equivalent X-SAMPA symbol is G\.

The voiceless pharyngeal fricative is a type of consonantal sound, used in some spoken languages. The symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet that represents this sound is an h-bar, ⟨ħ⟩, and the equivalent X-SAMPA symbol is X\. In the transcription of Arabic, Berber as well as a few other scripts, it is often written ⟨Ḥ⟩, ⟨ḥ⟩.
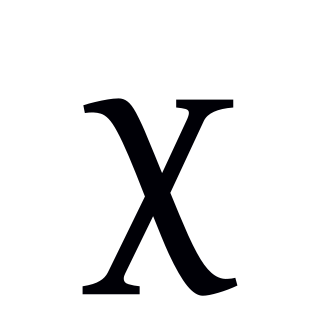
The voiceless uvular fricative is a type of consonantal sound that is used in some spoken languages. The symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet that represents this sound is ⟨χ⟩, the Greek chi. The sound is represented by ⟨x̣⟩ in Americanist phonetic notation. It is sometimes transcribed with ⟨x⟩ in broad transcription.

The open-mid central unrounded vowel, or low-mid central unrounded vowel, is a type of vowel sound, used in some spoken languages. The symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet that represents this sound is ⟨ɜ⟩. The IPA symbol is not the digit ⟨3⟩ or the Cyrillic small letter Ze (з). The symbol is instead a reversed Latinized variant of the lowercase epsilon, ɛ. The value was specified only in 1993; until then, it had been transcribed ⟨ɛ̈⟩.

The open-mid front unrounded vowel, or low-mid front unrounded vowel, is a type of vowel sound used in some spoken languages. The symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet that represents this sound is a Latinized variant of the Greek lowercase epsilon, ⟨ɛ⟩.

The open-mid front rounded vowel, or low-mid front rounded vowel, is a type of vowel sound, used in some spoken languages. The symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet that represents the sound is ⟨œ⟩. The symbol œ is a lowercase ligature of the letters o and e. The sound ⟨ɶ⟩, a small capital version of the ⟨Œ⟩ ligature, is used for a distinct vowel sound: the open front rounded vowel.
In phonetics, nasalization is the production of a sound while the velum is lowered, so that some air escapes through the nose during the production of the sound by the mouth. Examples of archetypal nasal sounds include and.

The Sierra Leonean Creole or Krio is an English-based creole language that is lingua franca and de facto national language spoken throughout the West African nation of Sierra Leone. Krio is spoken by 96 percent of the country's population, and it unites the different ethnic groups in the country, especially in their trade and social interaction with each other. Krio is the primary language of communication among Sierra Leoneans at home and abroad, and has also heavily influenced Sierra Leonean English. The language is native to the Sierra Leone Creole people, or Krios, a community of about 104,311 descendants of freed slaves from the West Indies, Canada, United States and the British Empire, and is spoken as a second language by millions of other Sierra Leoneans belonging to the country's indigenous tribes. Krio, along with English, is the official language of Sierra Leone.
Sierra Leonean Americans are an ethnic group of Americans of full or partial Sierra Leonean ancestry. This includes Sierra Leone Creoles whose ancestors were African American Black Loyalists freed after fighting on the side of the British during the American Revolutionary War. Some African Americans trace their roots to indigenous enslaved Sierra Leoneans exported to the United States between the 18th and early 19th century. In particular, the Gullah people of partial Sierra Leonean ancestry, fled their owners and settled in parts of South Carolina, Georgia, and the Sea Islands, where they still retain their cultural heritage. The first wave of Sierra Leoneans to the United States, after the slavery period, was after the Sierra Leone Civil War in the 1990s and early 2000s. According to the American Community Survey, there are 34,161 Sierra Leonean immigrants living in the United States.

Sierra Leone is a multilingual country. English is the official language, and Krio is the most widely spoken language among the different ethnic groups across Sierra Leone.
The voiceless dental non-sibilant affricate is a type of consonantal sound used in some spoken languages. The symbols in the International Phonetic Alphabet that represent this sound are ⟨t͡θ⟩, ⟨t͜θ⟩, ⟨t̪͡θ⟩, and ⟨t̟͡θ⟩.

The Sierra Leone Creole people are an ethnic group of Sierra Leone. The Sierra Leone Creole people are descendants of freed African-American, Afro-Caribbean, and Liberated African slaves who settled in the Western Area of Sierra Leone between 1787 and about 1885. The colony was established by the British, supported by abolitionists, under the Sierra Leone Company as a place for freedmen. The settlers called their new settlement Freetown. Today, the Sierra Leone Creoles are 1.2 percent of the population of Sierra Leone.
The voiced uvular lateral approximant is a type of consonantal sound used in some spoken languages. The symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet that represents this sound is ⟨ʟ̠⟩, and the equivalent X-SAMPA symbol is L\_-. ⟨ʟ̠⟩ may also represent the pharyngeal or epiglottal lateral approximant, a physically possible sound that is not attested in any language. The letter for a back-velar in the Uralic Phonetic Alphabet, ⟨ᴫ⟩, may also be used.
The Gambian Creole people, or Krio or Aku, are a minority ethnic group of Gambia with connections to and roots from the Sierra Leone Creole people. In Gambia the Aku account for about 2% of the population. Some estimates put the figure higher. However, according to the 2013 Gambian Census, the Aku make up 0.5% of the population or around 8,477 people.
References
- ↑ Saidu Bangura, 2015 A Roadmap to Sierra Leone English: A Sociohistorical and Ecological Perspective, Universidad de Las Palmas de Gran Canaria, PhD thesis, p. 124, 222, 232-242.
- ↑ Ladefoged & Maddieson (1996), p. 236.
- ↑ Collins & Mees (2013), p. 199.
