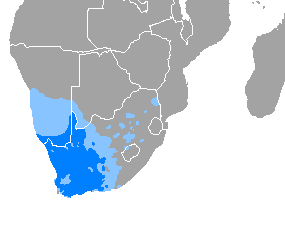
Afrikaans is a West Germanic language that evolved in the Dutch Cape Colony from the Dutch vernacular of Holland proper used by Dutch, French, and German settlers and their slaves. Afrikaans gradually began to develop distinguishing characteristics during the course of the 18th century. Now spoken in South Africa, Namibia and Botswana, Zambia, and Zimbabwe, estimates circa 2010 of the total number of Afrikaans speakers range between 15 and 23 million. Most linguists consider Afrikaans to be a partly creole language.

Bulgarian is an Eastern South Slavic language spoken in Southeast Europe, primarily in Bulgaria. It is the language of the Bulgarians.
A quotation is the repetition of a sentence, phrase, or passage from speech or text that someone has said or written. In oral speech, it is the representation of an utterance that is introduced by a quotative marker, such as a verb of saying. For example: John said: "I saw Mary today". Quotations in oral speech are also signaled by special prosody in addition to quotative markers. In written text, quotations are signaled by quotation marks. Quotations are also used to present well-known statement parts that are explicitly attributed by citation to their original source; such statements are marked with quotation marks.
The Finnish language is spoken by the majority of the population in Finland and by ethnic Finns elsewhere. Unlike the languages spoken in neighbouring countries, such as Swedish and Norwegian, which are North Germanic languages, or Russian, which is a Slavic language, Finnish is a Uralic language of the Finnic languages group. Typologically, Finnish is agglutinative. As in some other Uralic languages, Finnish has vowel harmony, and like other Finnic languages, it has consonant gradation.
Manglish is an informal form of Malaysian English with features of an English-based creole principally used in Malaysia. It is heavily influenced by the dominant languages of the country, Malay, Chinese languages, and Tamil. It is not an official language of Malaysia.
A tag question is a construction in which an interrogative element is added to a declarative or an imperative clause. The resulting speech act comprises an assertion paired with a request for confirmation. For instance, the English tag question "You're John, aren't you?" consists of the declarative clause "You're John" and the interrogative tag "aren't you?"
Dunglish is a popular term for an English spoken with a mixture of Dutch. It is often viewed pejoratively due to certain typical mistakes that native Dutch speakers, particularly those from the Netherlands, make when speaking English. The term is first recorded in 1965, with other colloquial portmanteau words including Denglish, Dutchlish (1986), and Dinglish (2003).
An interrogative clause is a clause whose form is typically associated with question-like meanings. For instance, the English sentence "Is Hannah sick?" has interrogative syntax which distinguishes it from its declarative counterpart "Hannah is sick". Also, the additional question mark closing the statement assures that the reader is informed of the interrogative mood. Interrogative clauses may sometimes be embedded within a phrase, for example: "Paul knows who is sick", where the interrogative clause "who is sick" serves as complement of the embedding verb "know".
This article describes the grammar of Afrikaans, a language spoken in South Africa and Namibia which originated from 17th century Dutch.

Bulgarian grammar is the grammar of the Bulgarian language. Bulgarian is a South Slavic language that evolved from Old Church Slavonic—the written norm for the Slavic languages in the Middle Ages which derived from Proto-Slavic. Bulgarian is also a part of the Balkan sprachbund, which also includes Greek, Macedonian, Romanian, Albanian and the Torlakian dialect of Serbian. It shares with them several grammatical innovations that set it apart from most other Slavic languages, even other South Slavic languages. Among these are a sharp reduction in noun inflections—Bulgarian has lost the noun cases but has developed a definite article, which is suffixed at the end of words. In its verbal system, Bulgarian is set apart from most Slavic languages by the loss of the infinitive, the preservation of most of the complexities of the older conjugation system and the development of a complex evidential system to distinguish between witnessed and several kinds of non-witnessed information.
Anejom̃ or Aneityum is an Oceanic language spoken by 900 people on Aneityum Island, Vanuatu. It is the only indigenous language of Aneityum.

Namibia, despite its scant population, is home to a wide diversity of languages, from multiple language families: Germanic, Bantu, and the various Khoisan families. When Namibia was administered by South Africa, Afrikaans, German, and English enjoyed an equal status as official languages. Upon Namibian independence in 1990, English was enshrined as the nation's sole official language in the constitution of Namibia. German and Afrikaans were stigmatised as relics of the colonial past, while the rising of Mandela's Youth League and the 1951 Defiance Campaign spread English among the masses as the language of the campaign against apartheid.
Yes and no, or word pairs with similar words, are expressions of the affirmative and the negative, respectively, in several languages, including English. Some languages make a distinction between answers to affirmative versus negative questions and may have three-form or four-form systems. English originally used a four-form system up to and including Early Middle English and Modern English has reduced to a two-form system consisting of 'yes' and 'no'. It exists in many facets of communication, such as: eye blink communication, head movements, Morse Code, and sign language. Some languages, such as Latin, do not have yes-no word systems.

Afrikaans is a daughter language of Dutch mainly spoken in South Africa and Namibia; it is a separate standard language rather than a national variety, unlike Netherlands Dutch, Belgian Dutch and Surinamese Dutch. An estimated 90 to 95% of Afrikaans vocabulary is ultimately of Dutch origin, so there are few lexical differences between the two languages, however Afrikaans has a considerably more regular morphology, grammar, and spelling.
In linguistics, grammatical mood is a grammatical feature of verbs, used for signaling modality. That is, it is the use of verbal inflections that allow speakers to express their attitude toward what they are saying. The term is also used more broadly to describe the syntactic expression of modality – that is, the use of verb phrases that do not involve inflection of the verb itself.

Namibia is a multilingual country wherein German is recognised as a national language. While English has been the sole official language of the country since 1990, in many areas of the country, German enjoys official status at a community level.
In linguistics and grammar, affirmation and negation are ways in which grammar encodes positive and negative polarity into verb phrases, clauses, or other utterances. An affirmative (positive) form is used to express the validity or truth of a basic assertion, while a negative form expresses its falsity. For example, the affirmative sentence "Jane is here" asserts that it is true that Jane is currently located near the speaker. Conversely, the negative sentence "Jane is not here" asserts that it is not true that Jane is currently located near the speaker.

The Ibanag language is an Austronesian language spoken by up to 500,000 speakers, most particularly by the Ibanag people, in the Philippines, in the northeastern provinces of Isabela and Cagayan, especially in Tuguegarao, Solana, Abulug, Cabagan, and Ilagan and with overseas immigrants in countries located in the Middle East, United Kingdom and the United States. Most of the speakers can also speak Ilocano, the lingua franca of northern Luzon island. The name Ibanag comes from the prefix I which means 'people of', and bannag, meaning 'river'. It is closely related to Gaddang, Itawis, Agta, Atta, Yogad, Isneg, and Malaweg.

Culture in Namibia is a blend of many different people and its culture and customs have absorbed both African and European elements and fused them into a blend of the two. Although the country is urbanising rapidly, a majority of Namibians still live in rural areas and lead largely impoverished lives. It is among these people, however, that cultural tradition survive most strongly.








