
Porter County is a county in the U.S. state of Indiana. As of 2020, the population was 173,215, making it the 10th most populous county in Indiana. The county seat is Valparaiso. The county is part of Northwest Indiana, as well as the Chicago metropolitan area. Porter County is the site of much of the Indiana Dunes, an area of ecological significance. The Hour Glass Museum in Ogden Dunes documents the region's ecological significance.

Lake County is a county located in the U.S. state of Indiana. In 2020, its population was 498,700, making it Indiana's second-most populous county. The county seat is Crown Point. The county is part of Northwest Indiana and the Chicago metropolitan area, and contains a mix of urban, suburban and rural areas. It is bordered on the north by Lake Michigan and contains a portion of the Indiana Dunes. It includes Marktown, Clayton Mark's planned worker community in East Chicago.

The Calumet River is a system of heavily industrialized rivers and canals in the region between the south side of Chicago, Illinois, and the city of Gary, Indiana. Historically, the Little Calumet River and the Grand Calumet River were one, the former flowing west from Indiana into Illinois, then turning back east to its mouth at Lake Michigan at Marquette Park in Gary. Now the system is part of the Chicago Area Waterway System and through the use of locks flows away from Lake Michigan to the Cal-Sag Channel.

The Watersheds of Indiana consist of six distinct Indiana watershed regions that drain into five major bodies of water.

Indiana Dunes National Park is a United States national park located in northwestern Indiana managed by the National Park Service. It was authorized by Congress in 1966 as the Indiana Dunes National Lakeshore and was redesignated as the nation's 61st national park on February 15, 2019. The park runs for about 20 miles (32 km) along the southern shore of Lake Michigan and covers 15,349 acres (6,212 ha). Along the lakefront, the eastern area is roughly the lake shore south to U.S. 12 or U.S. 20 between Michigan City, Indiana, on the east and the Cleveland-Cliffs steel plant on the west. This area's conservation scheme is enhanced by the older Indiana Dunes State Park. To the west of the steel plant lies West Beach and a small extension south of the steel mill continues west along Salt Creek to Indiana 249. The western area is roughly the shoreline south to U.S. 12 between the Burns Ditch west to Broadway in downtown Gary, Indiana. In addition, there are several outlying areas, including Pinhook Bog, in LaPorte County to the east; the Heron Rookery in Porter County, the center of the park; and the Calumet Prairie State Nature Preserve and the Hobart Prairie Grove, both in Lake County, the western end of the park.

The Kankakee River is a tributary of the Illinois River, approximately 133 miles (214 km) long, in the Central Corn Belt Plains of northwestern Indiana and northeastern Illinois in the United States. At one time, the river drained one of the largest wetlands in North America and furnished a significant portage between the Great Lakes and the Mississippi River. Significantly altered from its original channel, it flows through a primarily rural farming region of reclaimed cropland, south of Lake Michigan.
The Calumet Region is the geographic area drained by the Grand Calumet River and the Little Calumet River of northeastern Illinois and northwestern Indiana in the United States. It is part of the Great Lakes Basin, which eventually reaches the Atlantic Ocean. It is a sub-region of the greater Northwest Indiana region and the even larger Great Lakes region.

Lake Chicago was a prehistoric proglacial lake that is the ancestor of what is now known as Lake Michigan, one of North America's five Great Lakes. Formed about 13,000 years ago and fed by retreating glaciers, it drained south through the Chicago Outlet River.

Northern Indiana is a geographic and cultural region that generally comprises the northern third of the U.S. state of Indiana and borders the states of Illinois to the west, Michigan to the north, and Ohio to the east. Spanning the state's northernmost 26 counties, its main population centers include Northwest Indiana, Michiana, and the Fort Wayne metropolitan area.

The geography of Indiana comprises the physical features of the land and relative location of U.S. State of Indiana. Indiana is in the north-central United States and borders on Lake Michigan. Surrounding states are Michigan to the north and northeast, Illinois to the west, Kentucky to the south, and Ohio to the east. The entire southern boundary is the Ohio River.

The Valparaiso Moraine is a recessional moraine that forms an immense U around the southern Lake Michigan basin in North America. It is a band of hilly terrain composed of glacial till and sand. The Valparaiso Moraine defines part of the continental divide known as the Saint Lawrence River Divide, bounding the Great Lakes Basin. It begins near the border of Wisconsin and Illinois and extends south through Lake, McHenry, Cook, DuPage and Will counties in Illinois, and then turns southeast, going through northwestern Indiana. From this point, the moraine curves northeast through Lake, Porter, and LaPorte counties of Indiana into Michigan. It continues into Michigan as far as Montcalm County.

The Kankakee Outwash Plain is a flat plain interspersed with sand dunes in the Kankakee River valley in northwestern Indiana and northeastern Illinois of the United States. It is just south of the Valparaiso Moraine and was formed during the Wisconsin Glaciation. As the glacier stopped at the Valparaiso Moraine, its meltwater was carried away to the outwash plain. On the south side of the moraine, where the elevation drops, the meltwaters eroded away valleys, carrying sand and mud with them. As the muddy meltwater reached the valley where the slope lessened, the water slowed, depositing the sand on the outwash plain. This created a smooth, flat, and sandy plain. Before its draining, the Kankakee Marsh, located on the outwash plain, was one of the largest freshwater marshes in the United States.

The Glenwood Shoreline is an ancient shoreline of the precursor to Lake Michigan, Lake Chicago. It is named after the town of Glenwood, Illinois. The shoreline was formed when the lake was higher during the last ice age, while ice blocked the Straits of Mackinac. After the straits were freed, the lake receded and left behind a sand ridge at an elevation of about 640 feet (200 m) where the shore resided. This ridge can be seen clearly in Glenwood, Illinois, Dyer, Indiana, and Schererville, Indiana, all south of Chicago.
The Indiana Dunes are natural sand dunes occurring at the southern end of Lake Michigan in the American State of Indiana. They are known for their ecological significance. Many conservationists have played a role in preserving parts of the Indiana Dunes. The Hour Glass, a museum in Ogden Dunes, showcases some of the ecological import of the Dunes.

The Indiana Dunes comprise ten different habitats. Each provides for a unique combination of plants and animals. The range of the Indiana Dunes varies depending your source. The Indiana Lake Michigan Coastal Program uses the river drainage systems along the shoreline. This expands the area from the areas of lakeshore southward to the edges of the Valparaiso Moraine. This entire region has been dune landscapes since over 114,000 years before present (YBP). Traditionally, the Indiana Dunes area thought of as a narrow area along the shores of Lake Michigan, including the areas of Marquette Park in Gary, Indiana (1920), Indiana Dunes State Park (1926) and Indiana Dunes National Park,. The identified ten habitats can be found in these parks, where they have been preserved, but are also visible throughout the three counties of Northwest Indiana.

The East Arm Little Calumet River, also known as the Little Calumet River East Branch, is a 22.1-mile-long (35.6 km) portion of the Little Calumet River that begins just east of Holmesville, Indiana in New Durham Township in LaPorte County and flows west to Porter County and the Port of Indiana-Burns Waterway.

Salt Creek is a 24.0-mile-long (38.6 km) tributary of the East Arm Little Calumet River that begins south of Valparaiso in Porter County, Indiana and flows north until it joins the East Arm Little Calumet River just before it exits to Lake Michigan via the Port of Indiana-Burns Waterway.
The Shirley Heinze Land Trust, originally known as the Shirley Heinze Environmental Fund, is a 501(c)(3) nonprofit land trust dedicated to the preservation of natural areas in Northwest Indiana. The Heinze Trust manages more than 2,800 acres of protected land in Lake, Porter, LaPorte, St. Joseph, Starke, and Marshall Counties in Indiana. Its preserves include a wide range of dune, wetland, prairie, and forest ecosystems.
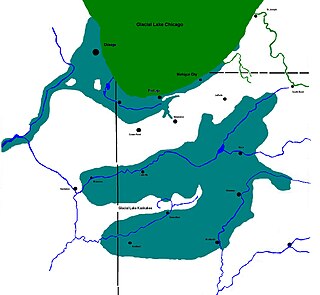
Lake Kankakee formed 14,000 years before present (YBP) in the valley of the Kankakee River. It developed from the outwash of the Michigan Lobe, Saginaw Lobe, and the Huron-Erie Lobe of the Wisconsin glaciation. These three ice sheets formed a basin across Northwestern Indiana. It was a time when the glaciers were receding, but had stopped for a thousand years in these locations. The lake drained about 13,000 YBP, until reaching the level of the Momence Ledge. The outcropping of limestone created an artificial base level, holding water throughout the upper basin, creating the Grand Kankakee Marsh.
The Calumet Aquifer is an aquifer underlying the land at the extreme southern tip of Lake Michigan. It underlies the northern third of Lake County, Indiana and the northern tenth of Porter County, as well as small parts of LaPorte County and Cook County, Illinois. It is notable chiefly for its high levels of contamination by industrial waste from factories and toxic waste dumps in the Calumet Region. It is bordered to the south by Valparaiso Moraine Aquifer, and to the north by Lake Michigan. It is underlain by a Silurian bedrock aquifer complex.



















