
The 1952 United States Senate elections was an election for the United States Senate which coincided with the election of Dwight D. Eisenhower to the presidency by a large margin. The 32 Senate seats of Class 1 were contested in regular elections, and three special elections were held to fill vacancies. The Republicans took control of the Senate by managing to make a net gain of two seats. However, Wayne Morse (R-OR) became an independent forcing Republicans to rely on Vice President Richard Nixon's tie-breaking vote, although Republicans maintained a 48–47–1 plurality. Wayne Morse would caucus with the Republicans at the start of Congress’ second session on January 6, 1954 to allow the GOP to remain in control of the Senate. This was the third time, as well as second consecutive, in which a sitting Senate leader lost his seat.

The 1946 United States Senate elections were held November 5, 1946, in the middle of Democratic President Harry S. Truman's first term after Roosevelt's passing. The 32 seats of Class 1 were contested in regular elections, and four special elections were held to fill vacancies. The Republicans took control of the Senate by picking up twelve seats, mostly from the Democrats. This was the first time since 1932 that the Republicans had held the Senate, recovering from a low of 16 seats following the 1936 Senate elections.

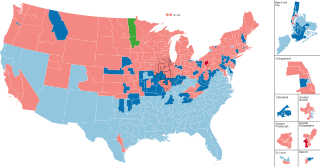
The 1952 United States House of Representatives elections was an election for the United States House of Representatives to elect members to serve in the 83rd United States Congress. They were held for the most part on November 4, 1952, while Maine held theirs on September 8. This was the first election after the congressional reapportionment based on the 1950 census. It also coincided with the election of President Dwight Eisenhower. Eisenhower's Republican Party gained 22 seats from the Democratic Party, gaining a majority of the House. However, the Democrats had almost 250,000 more votes (0.4%) thanks to overwhelming margins in the Solid South, although this election did see the first Republican elected to the House from North Carolina since 1928, and the first Republicans elected from Virginia since 1930. It was also the last election when both major parties increased their share of the popular vote simultaneously, largely due to the disintegration of the American Labor Party and other third parties.
The 1922 United States House of Representatives elections were elections for the United States House of Representatives to elect members to serve in the 68th United States Congress. They were held for the most part on November 7, 1922, though Maine held its on September 11. They occurred in the middle of President Warren G. Harding's term. Just as voters had expressed their distrust of Wilson in 1920, now voters had a chance to express the widespread feeling that Congress had failed to address economic problems, especially the brief but sharp Depression of 1920–1921. Most of the seats that Republicans lost had long been held by Democrats, who now returned with an even stronger base in the major cities.

1916 United States House of Representatives elections were elections for the United States House of Representatives to elect members to serve in the 65th United States Congress. They were held for the most part on November 7, 1916, while Maine held theirs on September 11. They coincided with the re-election of President Woodrow Wilson.

The 1842–43 United States House of Representatives elections were held on various dates in various states between August 1, 1842, and November 8, 1843. Each state set its own date for its elections to the House of Representatives before the first session of the 28th United States Congress convened on December 4, 1843. The exception was Maryland, who held theirs so late that they ran into February 1844. These elections occurred during President John Tyler's term. The congressional reapportionment based on the 1840 United States census unusually decreased the number of House seats, from 242 down to 223.
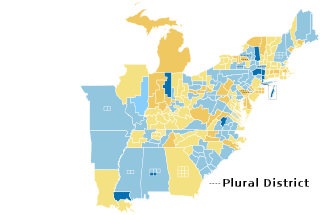
The 1840–41 United States House of Representatives elections were held on various dates in various states between July 6, 1840, and November 2, 1841. Each state set its own date for its elections to the House of Representatives, before or after the first session of the 27th United States Congress convened on May 31, 1841. Elections were held for all 242 seats, representing 26 states.

The 1830–31 United States House of Representatives elections were held on various dates in various states between July 5, 1830, and October 3, 1831. Each state set its own date for its elections to the House of Representatives before the first session of the 22nd United States Congress convened on December 5, 1831. Elections were held for all 213 seats, representing 24 states.

The 1824–25 United States House of Representatives elections were held on various dates in various states between July 7, 1824, and August 30, 1825. Each state set its own date for its elections to the House of Representatives before the first session of the 19th United States Congress convened on December 5, 1825. Elections were held for all 213 seats, representing 24 states.
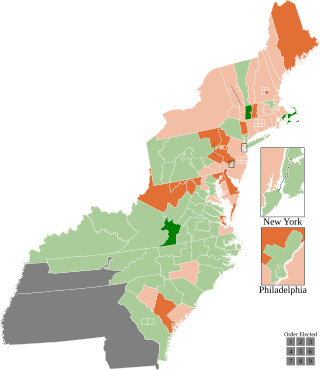
The 1796–97 United States House of Representatives elections took place in the various states took place between August 12, 1796, and October 15, 1797. Each state set its own date for its elections to the House of Representatives. The size of the House increased to 106 seats after Tennessee became the 16th state to join the union. The first session of the 5th United States Congress was convened on May 15, 1797, at the proclamation of the new President of the United States, John Adams. Since Kentucky and Tennessee had not yet voted, they were unrepresented until the second session began on November 13, 1797.

Elections to the United States House of Representatives were held in Pennsylvania on October 13, 1812, for the 13th Congress.
A special election was held in Massachusetts's 1st congressional district on September 5, 1796, and November 21, 1796, to fill a vacancy caused by the resignation of Theodore Sedgwick (F) upon his election to the Senate
A special election was held in Massachusetts's 12th congressional district on five occasions between September 25, 1801, and July 29, 1802, to fill a vacancy left by the resignation of Silas Lee (F) on August 20, 1801, prior to the beginning of the 1st Session of the 7th Congress.
A special election was held in Massachusetts's 10th congressional district to fill a vacancy caused by John Bailey (DR) being declared not eligible for the seat which he had won the previous year on March 24, 1824. The election was held on August 30, 1824, with additional ballots held on November 1 and November 29 due to a majority not being achieved on the first or second ballot.

A special election was held in Kentucky's 5th congressional district on November 6, 1826, to fill a vacancy caused by the death of James Johnson (Jacksonian) on August 14, 1826.

A special election was held in Kentucky's 12th congressional district on November 20, 1826, to fill a vacancy caused by the death of Robert P. Henry (J) on August 25, 1826

A special election was held in Maryland's 2nd congressional district on February 1, 1826, to fill a vacancy caused by the resignation of Joseph Kent (A), who had been elected Governor of Maryland.

A special election was held in North Carolina's 8th congressional district on November 3, 1826, to fill a vacancy caused by the resignation of Willie P. Mangum (J) on March 18, 1826

A special election was held in Ohio's 10th congressional district on October 10, 1826, the same day as the general elections for the 20th Congress, to fill a vacancy caused by the resignation of David Jennings (A) on May 25, 1826.

A special election was held in Virginia's 5th congressional district on January 21, 1826, to fill a vacancy caused by the resignation of John Randolph (J) on December 26, 1825, after being elected to the Senate.
















