
A heat wave or heatwave, sometimes described as extreme heat, is a period of abnormally hot weather. Definitions vary but are similar. A heat wave is usually measured relative to the usual climate in the area and to normal temperatures for the season. Temperatures that humans from a hotter climate consider normal, can be regarded as a heat wave in a cooler area. This would be the case if the warm temperatures are outside the normal climate pattern for that area. High humidity often occurs during heat waves as well. This is especially the case in oceanic climate countries. Heat waves have become more frequent, and more intense over land, across almost every area on Earth since the 1950s, the increase in frequency and duration being caused by climate change.
The July 1995 Chicago heat wave led to 739 heat-related deaths in Chicago over a period of five days. Most of the victims of the heat wave were elderly poor residents of the city, who did not have air conditioning, or had air conditioning but could not afford to turn it on, and did not open windows or sleep outside for fear of crime. The heat wave also heavily impacted the wider Midwestern region, with additional deaths in both St. Louis, Missouri and Milwaukee, Wisconsin.

The 2003 European heat wave saw the hottest summer recorded in Europe since at least 1540. France was hit especially hard. The heat wave led to health crises in several countries and combined with drought to create a crop shortfall in parts of Southern Europe. The death toll has been estimated at more than 70,000.
The 2007 North American heat wave started at the end of July and lasted into the first weeks of August. It was associated with severe drought over regions of the southeastern United States and parts of the Great Lakes region.

The 2010 Northern Hemisphere summer heat waves included severe heat waves that impacted most of the United States, Kazakhstan, Mongolia, China, Hong Kong, North Africa and the European continent as a whole, along with parts of Canada, Russia, Indochina, South Korea and Japan during July 29, 2010. The first phase of the global heatwaves was caused by a moderate El Niño event, which lasted from June 2009 to May 2010. This lasted only from April 2010 to June 2010 and caused only moderate above-average temperatures in the affected regions, but it also set new record high temperatures for most of the area affected in the Northern Hemisphere.

The 1911 Eastern North America heat wave was an 11-day severe heat wave that killed at least 380 people, though estimates have put the death toll as high as 2,000 people. The heat wave began on July 4, 1911 and didn't cease until July 15. In Nashua, New Hampshire, the temperature peaked at 106 °F (41 °C). In New York City 158 people and 600 horses died.
The 2011 North American heat wave was a deadly summer 2011 heat wave that affected the Southern Plains, the Midwestern United States, Eastern Canada, the Northeastern United States, and much of the Eastern Seaboard, and had Heat index/Humidex readings reaching upwards of 131 °F (55 °C). On a national basis, the heat wave was the hottest in 75 years.

The Summer 2012 North American heat wave was one of the most severe heat waves in modern North American history. It resulted in more than 82 heat-related deaths across the United States and Canada, and an additional twenty-two people died in the resultant June 2012 North American derecho. This long-lived, straight-line wind and its thunderstorms cut electrical power to 3.7 million customers. Over 500,000 were still without power on July 6, as the heat wave continued. Temperatures generally decreased somewhat the week of July 9 in the east, but the high pressure shifted to the west, causing the core of the hot weather to build in the Mountain States and the Southwestern United States shifting eastwards again by mid-July. By early August, the core of the heat remained over the Southern Plains.

The 2013 extreme weather events included several all-time temperature records in Northern and Southern Hemisphere. The February extent of snow cover in Eurasia and North America was above average, while the extent of Arctic ice in the same month was 4.5% below the 1981–2010 average. The Northern Hemisphere weather extremes have been linked to the melting of Arctic sea ice, which alters atmospheric circulation in a way that leads to more snow and ice.

The November 2014 North American cold wave was an extreme weather event that occurred across most of Canada and the contiguous United States, including parts of the Western United States up to western California. One of the first events of the winter, the cold wave was caused by the northward movement of an extremely powerful bomb cyclone associated with Typhoon Nuri's remnant, which shifted the jet stream far northward, creating an omega block pattern. This allowed a piece of the polar vortex to advance southward into the Central and Eastern United States, bringing record-cold temperatures to much of the region. In contrast, Alaska experienced above-average temperatures.
In May 2015, India was struck by a severe heat wave. As of 3 June 2015, it caused the deaths of at least 2,500 people in multiple regions. The heat wave occurred during the Indian dry season, which typically lasts from March to July with peak temperatures in April and May. Although it typically remains hot until late October, Indian monsoons often provide some respite from the heat.
The 2018 North American heat wave affected regions of Canada, where at least 70 deaths in Quebec were heat-related, the United States, where 18 states between Michigan and New Mexico issued heat advisories to a population of over 60 million people, and of Mexico, particularly the northwest and central regions.

The February 13–17, 2021 North American winter storm was a crippling, large and major winter and ice storm that had widespread impacts across the United States, Northern Mexico, and parts of Canada from February 13 to 17, 2021. The storm, unofficially referred to as Winter Storm Uri by the Weather Channel, started out in the Pacific Northwest and quickly moved into the Southern United States, before moving on to the Midwestern and Northeastern United States a couple of days later.

The February 2021 North American cold wave was an extreme weather event that brought record low temperatures to a significant portion of Canada, the United States and parts of northern Mexico during the first two-thirds of February 2021. The cold was caused by a southern migration of the polar vortex, likely caused by a sudden stratospheric warming event that occurred the prior month. Temperatures fell as much as 25–50 °F below average as far south as the Gulf Coast. Severe winter storms also were associated with the bitter cold, which allowed for heavy snowfall and ice accumulations to places as far south as Houston, Texas, and contributing to one of the snowiest winters ever in some areas in the Deep South.

The 2021 Western North America heat wave was an extreme heat wave that affected much of Western North America from late June through mid-July 2021. The heat wave affected Northern California, Idaho, Western Nevada, Oregon, and Washington in the United States, as well as British Columbia, and in its latter phase, Alberta, Manitoba, the Northwest Territories, Saskatchewan, and Yukon, all in Canada. It also affected inland regions of Central and Southern California, Nevada, and Montana, though the temperature anomalies were not as extreme as in the regions farther north.

This page documents notable heat waves worldwide in 2021.
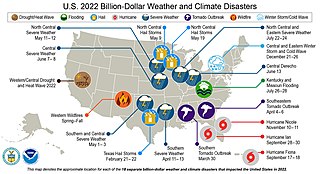
The following is a list of weather events that occurred on Earth in the year 2022. The year began with a La Niña. There were several natural disasters around the world from various types of weather, including blizzards, cold waves, droughts, heat waves, wildfires, floods, tornadoes, and tropical cyclones. The deadliest weather event of the year were the European heat waves, which killed over 26,000 people, 11,000 of which were in France. The costliest weather event of the year was Hurricane Ian, which caused at least $112.9 billion in damages in Florida and Cuba. Another significant weather event was the Pakistan floods, which killed 1,739 people and a total of $14.9 billion in damages.
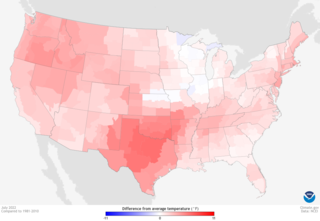
From late spring to late summer heat waves in 2022 smashed many records in North America between May and September of that year. Dozens of temperature records were surpassed in the United States.

From December 21 to 26, 2022, an extratropical cyclone created crippling winter storm conditions, including blizzards, high winds, snowfall, and record cold temperatures across the majority of the United States and parts of Canada. Areas which experienced blizzard conditions included parts of Minnesota, Iowa, Wisconsin, Michigan, Ohio, Pennsylvania, New York and Ontario, with the Buffalo area of New York and the Fort Erie and Kingston areas of Ontario experiencing almost two full days of blizzard/zero-visibility conditions starting from December 23. The cold wave affected all U.S. states from Colorado to the Eastern Seaboard, with effects felt as far south as Miami, Florida. On December 24, 110 million people across 36 states were subject to wind chill alerts.














