Related Research Articles

The United Kingdom straddles the higher mid-latitudes between 49° and 61°N on the western seaboard of Europe. Since the UK is always in or close to the path of the polar front jet stream, frequent changes in pressure and unsettled weather are typical. Many types of weather can be experienced in a single day.

A period of unusually hot summer weather occurred in the British Isles during the summer of 1976. At the same time, there was a severe drought on the islands of Great Britain and Ireland. It was one of the driest, sunniest and warmest summers (June/July/August) in the 20th century, although the summer of 1995 is now regarded as the driest. Only a few places registered more than half their average summer rainfall. In the Central England temperature record, it was the warmest summer in the series until being surpassed in the 21st century. It was the warmest summer in the Aberdeen area since at least 1864, and the driest summer since 1868 in Glasgow.

The 2006 European heat wave was a period of exceptionally hot weather that arrived at the end of June 2006 in certain European countries. The United Kingdom, France, Belgium, the Netherlands, Luxembourg, Italy, Poland, the Czech Republic, Hungary, Germany and western parts of Russia were most affected.

The British Isles are an archipelago off the northwest coast of Europe, consisting of the islands of Great Britain and Ireland along with smaller surrounding ones. Its position allows dry continental air from Eurasia to meet wetter air from the Atlantic Ocean, which causes the weather to be highly variable, often changing many times during the day. It is defined as a temperate oceanic climate, or Cfb on the Köppen climate classification system. It is significantly warmer than other regions on the same latitude, previously thought to be due to the warmth provided by the Gulf Stream; however, this has been disproven, and most of the mild temperatures have been linked to the Rocky Mountains and the heat storing capabilities of the North Atlantic Ocean. Temperatures do not often switch between great extremes, with warm summers and mild winters.
Malta has a Subtropical-Mediterranean climate according to the Köppen climate classification (Csa), with very mild winters and warm to hot summers. Rain occurs mainly in winter, with summer being generally dry. According to the Troll-Paffen climate classification and the Siegmund/Frankenberg climate classification, Malta lies within the subtropical zone, being at 35ºN latitude.

Estonia lies in the northern part of the temperate climate zone and in the transition zone between maritime and continental climate. Because Estonia is continuously warmed by maritime air influenced by the heat content of the northern Atlantic Ocean, it has a milder climate despite its northern latitude. The Baltic Sea causes differences between the climate of coastal and inland areas.

The 2010 Northern Hemisphere summer heat waves included severe heat waves that impacted most of the United States, Kazakhstan, Mongolia, China, Hong Kong, North Africa and the European continent as a whole, along with parts of Canada, Russia, Indochina, South Korea and Japan during July 29 2010. The first phase of the global heatwaves was caused by a moderate El Niño event, which lasted from June 2009 to May 2010. This lasted only from April 2010 to June 2010 and caused only moderate above-average temperatures in the affected regions, but it also set new record high temperatures for most of the area affected in the Northern Hemisphere.

The 2013 extreme weather events included several all-time temperature records in Northern and Southern Hemisphere. The February extent of snow cover in Eurasia and North America was above average, while the extent of Arctic ice in the same month was 4.5% below the 1981–2010 average. The Northern Hemisphere weather extremes have been linked to the melting of Arctic sea ice, which alters atmospheric circulation in a way that leads to more snow and ice.
The summer of 2014 in Sweden was unusually warm, especially in the northern parts of the country. July was the warmest ever month on record in the north-west.

The 1995 British Isles heatwave occurred between late July and late August. It was part of one of the warmest summers recorded in the UK, and one of the warmest Augusts ever recorded in many locations around the UK, as well as being one of the driest summers ever recorded in the UK; many weather stations recorded the summer of 1995 as drier than, or comparable with, the summer of 1976. Ireland was also widely affected by the heatwave with temperatures reaching over 30 °C (86 °F) in some locations, as well as exceptionally low rainfall throughout the summer.

The 2018 Britain and Ireland heatwave was a period of unusually hot weather that took place in June, July and August. It caused widespread drought, hosepipe bans, crop failures, and a number of wildfires. These wildfires worst affected northern moorland areas around the Greater Manchester region, the largest was at Saddleworth Moor and another was at Winter Hill, together these burned over 14 square miles (36 km2) of land over a period of nearly a month.

The 2018 European drought and heat wave was a period of unusually hot weather that led to record-breaking temperatures and wildfires in many parts of Europe during the spring and summer of 2018. It is part of a larger heat wave affecting the northern hemisphere, caused in part by the jet stream being weaker than usual, allowing hot high-pressure air to linger in the same place. According to the European Drought Observatory, most of the areas affected by drought are across northern and central Europe. According to the World Meteorological Organization, the severe heat waves across the northern hemisphere in the summer of 2018, are linked to climate change in Europe, as well as events of extreme precipitation.
A tropical night is a term used in many European countries to describe days when the temperature does not fall below 20 °C (68.0 °F) during the nighttime. This definition is in use in countries including the United Kingdom, Greece, Republic of Ireland, Spain, Portugal, Denmark, Sweden, Norway, the Netherlands, Germany, Finland, Lithuania, Latvia, Hungary, Romania, Italy, Serbia, and Croatia. In the United States, by contrast, the term sultry nights is used when the temperature does not fall below 27 °C (80.6 °F) in the Gulf and Atlantic states.
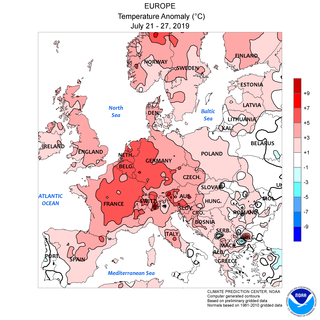
In late June and late July 2019 there were two temporally distinct European heat waves, which set all-time high temperature records in Belgium, France, Germany, Luxembourg, the Netherlands, and the United Kingdom.
The 2021 Britain and Ireland heat wave was a period of unusually hot weather in July 2021 that led to record-breaking temperatures in the UK and Ireland.

In 2022, several areas of the world experienced heat waves. Heat waves were especially notable in East Asia, the Indian subcontinent, Australia, western Europe, the United States, and southern South America. 2022 heat waves accounted for record-breaking temperatures and, in some regions, heat-related deaths. Heat waves were worsened by the effects of climate change, and they exacerbated droughts and wildfires.

The 2022 United Kingdom heatwaves were part of several heatwaves across Europe and North Africa. The United Kingdom experienced three heatwaves; the first was for three days in June, the second for three days in July, and the third for six days in August. These were periods of unusually hot weather caused by rising high pressure up from the European continent. There were also more grass fires and wildfires than average, and in August a drought was declared in many regions.
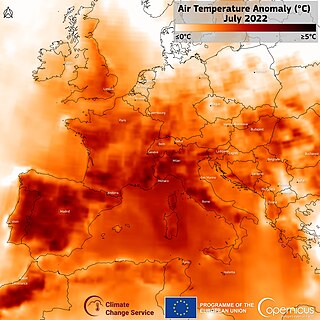
From June to August 2022, persistent heatwaves affected parts of Europe, causing evacuations and killing tens of thousands. These heat waves were the deadliest meteorological events in 2022. The highest temperature recorded was 47.0 °C (116.6 °F) in Pinhão, Portugal, on 14 July.

A number of heat waves began across parts of the northern hemisphere in April 2023, many of which are ongoing. Various heat records have been broken, with July being the hottest month ever recorded.
References
- 1 2 "July finishes in top three sunniest and warmest". Met Office. 5 August 2013. Retrieved 29 October 2013.
- ↑ "Warmest, driest and sunniest summer since 2006". Met Office. 30 August 2013. Retrieved 29 October 2013.
- ↑ "Archived copy" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 2016-10-02. Retrieved 2013-09-02.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link) - ↑ Siddique, Haroon (4 July 2013). "Heatwave to last until mid-July in England and Wales, say forecasters". The Guardian. London. Retrieved 29 October 2013.
- ↑ Carter, Claire (9 July 2013). "Heatwave expected to continue until the weekend". The Telegraph. London: Telegraph Media Group. Archived from the original on 11 July 2013. Retrieved 29 October 2013.
- ↑ Stewart, Linda (9 July 2013). "Temperature soars to 30C in Northern Ireland as heatwave is set to continue". Belfast Telegraph. Independent News & Media. Retrieved 29 October 2013.
- ↑ "Heatwave". Met Office. Retrieved 29 October 2013.
- ↑ "England heatwave alerts issued". BBC News. BBC. 12 July 2013. Retrieved 29 October 2013.
- ↑ Jones, Sam (17 July 2013). "Met Office issues heatwave alert as temperatures pass 30C for fifth day". The Guardian. London. Retrieved 29 October 2013.
- ↑ Morris, Steven (23 July 2013). "Thunderstorms and lightning break British heatwave". The Guardian. London. Retrieved 29 October 2013.
- ↑ Williams, Rob (1 August 2013). "Britain sees hottest August temperatures for ten years as heatwave returns - but just for a day..." . The Independent. London: Independent Print Limited. Archived from the original on 2022-05-01. Retrieved 29 October 2013.
- ↑ Silverman, Rosa (18 July 2013). "Heatwave deaths: 760 lives claimed by hot weather as high temperatures continue". The Telegraph. London: Telegraph Media Group. Archived from the original on 18 July 2013. Retrieved 29 October 2013.
- ↑ Collins, Nick (7 July 2013). "Heatwave prompts surge in ambulance calls". The Telegraph. London: Telegraph Media Group. Archived from the original on 10 July 2013.
- 1 2 Bawden, Tom; Cooper, Charlie (19 July 2013). "Heatwave latest: Spike in A&E admissions, wildfires and melting roads as Britain battles seventh day of 30-plus temperatures" . The Independent. London: Independent Print Limited. Archived from the original on 2022-05-01. Retrieved 29 October 2013.
- ↑ "Lifeboat rescuers record busiest July since 2006". BBC News. BBC. 23 August 2013. Retrieved 29 October 2013.
- ↑ "Heatwave Warning: Danger Of Grass Fires". Sky News. BSkyB. 19 July 2013. Retrieved 29 October 2013.
- ↑ Bannerman, Lucy (20 July 2013). "Heatwave sparks Britain's worst wildfires for years". The Times. London. Retrieved 29 October 2013.(subscription required)
- ↑ "Hot summer helps boost butterflies". BBC Nature. BBC. 16 September 2013. Retrieved 29 October 2013.
- ↑ Philipson, Alice (30 July 2013). "Warm weather sparks jellyfish invasion". The Telegraph. London: Telegraph Media Group. Retrieved 29 October 2013.
- ↑ Dutton, Liam (8 August 2013). "Tens of thousands of fish die in recent heatwave". Channel 4 News. ITN. Retrieved 29 October 2013.
