Discovery, orbit and physical properties
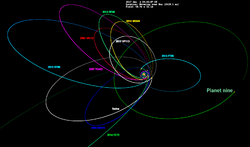
2013 RF98 was discovered by the Dark Energy Survey on September 12, 2013, observing with the 4 m Blanco Telescope from Cerro Tololo Inter-American Observatory. [1] Its orbit is characterized by high eccentricity (0.897), moderate inclination (29.57º) and a semi-major axis of 349 AU. [1] Upon discovery, it was classified as a trans-Neptunian object. Its orbit is relatively well determined; as of January 11, 2017 its orbital solution is based on 51 observations spanning a data-arc of 1092 days. [2] 2013 RF98 has an absolute magnitude of 8.7 which gives a characteristic diameter of 50 to 120 km for an assumed albedo in the range 0.25–0.05. [5]
It came to perihelion (closest approach to the Sun) around October 2009 and was last observed in September 2016. [2] As of October 2016 [update] , it is 36.6 AU from the Sun. Of the seven objects whose aligned orbits suggest the existence of Planet Nine, it is currently the closest to the Sun. It was 18.7 AU from Uranus in 2021. It was in the constellation of Cetus until 2022. It comes to opposition at the start of November.[ year needed ]
2013 RF98's orbit is similar to that of 474640 Alicanto, suggesting that they may have both been thrown onto their current paths by the same body, or that they may have been the same object (single or binary) at one point. Its spectral slope is also similar to that of Alicanto. [4] [6]
2013 RF98's visible spectrum is very different from that of 90377 Sedna. [4] [7] The value of its spectral slope suggests that the surface of this object can have pure methane ices (like in the case of Pluto) and highly processed carbons, including some amorphous silicates. [4]


