This article needs additional citations for verification .(November 2017) |
| Years |
|---|
| Millennium |
| 1st millennium |
| Centuries |
| Decades |
| Years |
| 293 by topic |
|---|
| Leaders |
| Categories |
| Gregorian calendar | 293 CCXCIII |
| Ab urbe condita | 1046 |
| Assyrian calendar | 5043 |
| Balinese saka calendar | 214–215 |
| Bengali calendar | −301 – −300 |
| Berber calendar | 1243 |
| Buddhist calendar | 837 |
| Burmese calendar | −345 |
| Byzantine calendar | 5801–5802 |
| Chinese calendar | 壬子年 (Water Rat) 2990 or 2783 — to — 癸丑年 (Water Ox) 2991 or 2784 |
| Coptic calendar | 9–10 |
| Discordian calendar | 1459 |
| Ethiopian calendar | 285–286 |
| Hebrew calendar | 4053–4054 |
| Hindu calendars | |
| - Vikram Samvat | 349–350 |
| - Shaka Samvat | 214–215 |
| - Kali Yuga | 3393–3394 |
| Holocene calendar | 10293 |
| Iranian calendar | 329 BP – 328 BP |
| Islamic calendar | 339 BH – 338 BH |
| Javanese calendar | 173–174 |
| Julian calendar | 293 CCXCIII |
| Korean calendar | 2626 |
| Minguo calendar | 1619 before ROC 民前1619年 |
| Nanakshahi calendar | −1175 |
| Seleucid era | 604/605 AG |
| Thai solar calendar | 835–836 |
| Tibetan calendar | ཆུ་ཕོ་བྱི་བ་ལོ་ (male Water-Rat) 419 or 38 or −734 — to — ཆུ་མོ་གླང་ལོ་ (female Water-Ox) 420 or 39 or −733 |
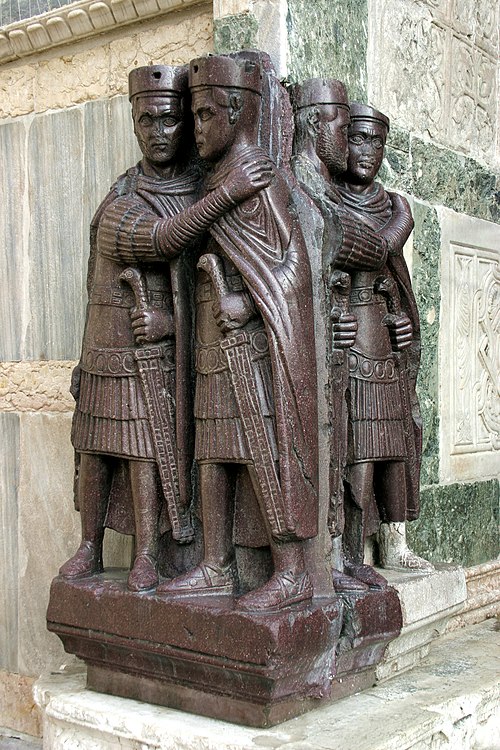

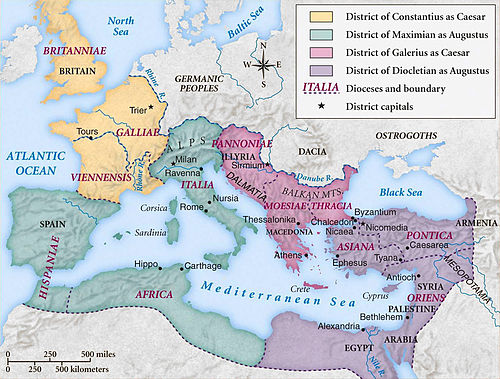
Year 293 ( CCXCIII ) was a common year starting on Sunday of the Julian calendar. In the Roman Empire, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Diocletian and Maximian (or, less frequently, year 1046 Ab urbe condita ). The denomination 293 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.