
Year 476 (CDLXXVI) was a leap year starting on Thursday of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Basiliscus and Armatus. The denomination 476 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.
The 470s decade ran from January 1, 470, to December 31, 479.
The 520s decade ran from January 1, 520, to December 31, 529.
The 570s decade ran from January 1, 570, to December 31, 579.
The 580s decade ran from January 1, 580, to December 31, 589.
The 490s decade ran from January 1, 490, to December 31, 499.
The 480s decade ran from January 1, 480, to December 31, 489.
The 450s decade ran from January 1, 450, to December 31, 459.
Year 524 (DXXIV) was a leap year starting on Monday on the Julian calendar. In the Roman Empire, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Iustinus and Opilio. The denomination 524 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.

Year 584 (DLXXXIV) was a leap year starting on Saturday of the Julian calendar. The denomination 584 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.
Year 585 (DLXXXV) was a common year starting on Monday of the Julian calendar. The denomination 585 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.

Year 474 (CDLXXIV) was a common year starting on Tuesday of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Leo without colleague. The denomination 474 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.

Year 473 (CDLXXIII) was a common year starting on Monday of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Leo without colleague. The denomination 473 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.

Glycerius was Roman emperor of the West from 473 to 474. He served as comes domesticorum during the reign of Olybrius, until Olybrius died in November 472. After a four-month interregnum, Glycerius was proclaimed as emperor in March 473 by Gundobad, the magister militum and power behind the throne. Very few of the events of his reign are known other than that an attempted invasion of Italy by the Visigoths was repelled by local commanders, diverting them to Gaul. Glycerius also prevented an invasion by the Ostrogoths through diplomacy, including a gift of 2,000 solidi.

Year 575 (DLXXV) was a common year starting on Tuesday of the Julian calendar. The denomination 575 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.

Julius Nepos, or simply Nepos, ruled as Roman emperor of the West from 24 June 474 to 28 August 475. After losing power in Italy, Nepos retreated to his home province of Dalmatia, from which he continued to claim the western imperial title, with recognition from the Eastern Roman Empire, until he was murdered in 480. Though Nepos' successor in Italy, Romulus Augustulus, is traditionally deemed the last western Roman emperor, Nepos is regarded by some historians as the true last emperor of the west, being the last widely recognised holder of the position.

Gundobad was King of the Burgundians (473–516), succeeding his father Gundioc of Burgundy. Previous to this, he had been a patrician of the moribund Western Roman Empire in 472–473, three years before its collapse, succeeding his uncle Ricimer. He is perhaps best known today as the probable issuer of the Lex Burgundionum legal codes, which synthesized Roman law with ancient Germanic customs. He was the husband of Caretene.

The Ostrogothic Kingdom, officially the Kingdom of Italy, was a barbarian kingdom established by the Germanic Ostrogoths that controlled Italy and neighbouring areas between 493 and 553. Led by Theodoric the Great, the Ostrogoths killed Odoacer, a Germanic soldier and erstwhile leader of the foederati. Odoacer had previously become the de facto ruler of Italy following his deposition of Romulus Augustulus, the final emperor of the Western Roman Empire, in 476. Under Theodoric, the Ostrogothic kingdom reached its zenith, stretching from modern Southern France in the west to the modern western Serbia in the southeast. Most of the social institutions of the late Western Roman Empire were preserved during his rule. Theodoric called himself Gothorum Romanorumque rex 'King of the Goths and Romans', demonstrating his desire to be a leader for both peoples.
Ovida or Odiva was a late Western Roman general and warlord of likely Gothic origin and the last Roman ruler of Dalmatia. Ovida initially served Julius Nepos, ruler of Roman Dalmatia and later western Roman emperor in Italy from 474 to 475. After being usurped in 475, Nepos continued to claim the imperial title in exile in Dalmatia, supported by the Eastern Roman Empire, but he was murdered by Ovida and another general, Viator, in 480. Upon his death, Ovida became the ruler of Dalmatia, a position he held until he was defeated and killed by Odoacer, the first barbarian King of Italy, in 481 or 482.
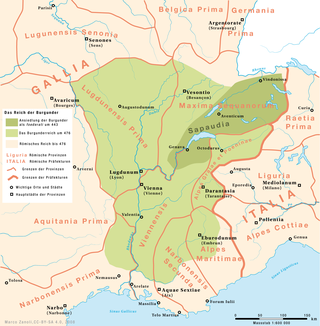
The Kingdom of the Burgundians, or First Kingdom of Burgundy, was established by Germanic Burgundians in the Rhineland and then in eastern Gaul in the 5th century.











