Myanmar, officially the Republic of the Union of Myanmar and also known as Burma, is a country in Southeast Asia. It is the largest country by area in Mainland Southeast Asia and has a population of about 55 million. It is bordered by Bangladesh and India to its northwest, China to its northeast, Laos and Thailand to its east and southeast, and the Andaman Sea and the Bay of Bengal to its south and southwest. The country's capital city is Naypyidaw, and its largest city is Yangon.
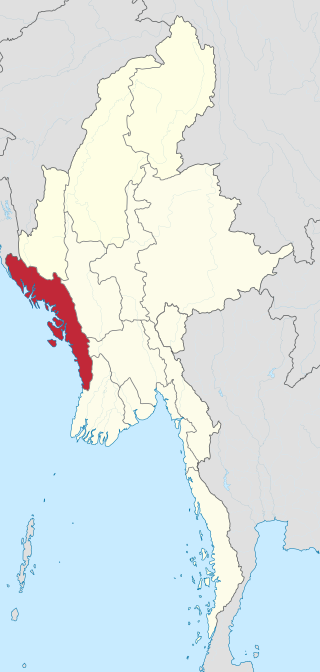
Rakhine State, formerly known as Arakan State, is a state in Myanmar (Burma). Situated on the western coast, it is bordered by Chin State to the north, Magway Region, Bago Region and Ayeyarwady Region to the east, the Bay of Bengal to the west and the Chittagong Division of Bangladesh to the northwest. It is located approximately between latitudes 17°30' north and 21°30' north and longitudes 92°10' east and 94°50' east. The Arakan Mountains or Rakhine Yoma separated Rakhine State from central Burma from North to South. Off the coast of Rakhine State there are some fairly large islands such as Ramree, Cheduba and Myingun. Rakhine State has an area of 36,762 square kilometres (14,194 sq mi) and its capital is Sittwe.

Myanmar is divided into 21 administrative divisions, which include seven regions, seven states, one union territory, one self-administered division, and five self-administered zones.

The Rohingya people are a stateless Indo-Aryan ethnic group who predominantly follow Islam and reside in Rakhine State, Myanmar. Before the Rohingya genocide in 2017, when over 740,000 fled to Bangladesh, an estimated 1.4 million Rohingya lived in Myanmar. Described by journalists and news outlets as one of the most persecuted minorities in the world, the Rohingya are denied citizenship under the 1982 Myanmar nationality law. There are also restrictions on their freedom of movement, access to state education and civil service jobs. The legal conditions faced by the Rohingya in Myanmar have been compared to apartheid by some academics, analysts and political figures, including Nobel laureate Bishop Desmond Tutu, a South African anti-apartheid activist. The most recent mass displacement of Rohingya in 2017 led the International Criminal Court to investigate crimes against humanity, and the International Court of Justice to investigate genocide.
Jinghpaw or Kachin is a Tibeto-Burman language of the Sal branch spoken primarily in Kachin State, Myanmar; Northeast India; and Yunnan, China. The Jinghpaw peoples, a confederation of several ethnic groups who live in the Kachin Hills, are the primary speakers of Jinghpaw language, numbering approximately 625,000 speakers. The term "Kachin language" may refer to the Jinghpaw language or any of the other languages spoken by the Jinghpaw peoples, such as Lisu, Lashi, Rawang, Zaiwa, Lhawo Vo, and Achang. These languages are from distinct branches of the highest level of the Tibeto-Burman family.

Districts are the second-level administrative divisions of Myanmar. They are the subdivisions of the regions and states of Myanmar. According to the Myanmar Information Management Unit (MIMU), as of December 2015, there are 76 districts in Myanmar, which in turn are subdivided into townships, then towns, wards and villages.

Hkamti Township or Khamti Township is a township in Hkamti District in the Sagaing Region of Burma (Myanmar). The principal town is Hkamti. As of 2014 the township had a population of 47,658 people and covered an area of 8,174 square kilometres (3,156 sq mi). The township is dominated by the Chindwin River and its tributaries as well as thickly forested areas. Nearly half the active working population are employed in agriculture, forestry or fishing. The township is a producer of rice and has gold and jade reserves.
Hulaung is an agricultural village near the village of Tonmate in Homalin Township, Hkamti District, in the Sagaing Region of northwestern Myanmar. It is part of the Tonmate village tract.
Tonehein Khondan is a village in Homalin Township, Hkamti District, in the Sagaing Region of northwestern Myanmar. It is part of the Satkaya village tract.
Khonthar is a village in Homalin Township, Hkamti District, in the Sagaing Region of northwestern Myanmar. It is part of the Manhon village tract.
Khondangyi is a village in Homalin Township, Hkamti District, in the Sagaing Region of northwestern Myanmar. It is part of the Khondangyi village tract.
Naungpin is a village in northern Homalin Township, Hkamti District, in the Sagaing Region of northwestern Burma. It is located south of Manpa. It is the principal village of the Naungpin village tract.
Thayagon is a village in northern Homalin Township, Hkamti District, in the Sagaing Region of northwestern Myanmar. It is located on the west bank of the upper Chindwin River about 5 miles (8.0 km) from the Leshi Township border near the major village of Tamanthi It is part of the Tamanthi village tract.
Moklen is an Austronesian language spoken on the western coast of southern Thailand. It is related to but distinct from the Moken language of Myanmar and southern Thailand. Unlike Moken, it is not spoken in Myanmar.

Burmese folk religion refers to the animistic and polytheistic religious worship of nats and ancestors in Myanmar (Burma). Although the beliefs of nats differ across different regions and villages in Burma, there are a handful of beliefs that are universal in Burmese folk religion.

Shwebo is a city in Sagaing Region, Burma, 110 km north-west of Mandalay between the Irrawaddy and the Mu rivers. The city was the origin of the Konbaung Dynasty, established by King Alaungpaya in 1752, that was the dominant political force in Burma after the mid-18th century. It served as Alaungpaya's capital from 1752 to 1760. As of 2021, it has a population of 88,914.

The Rohingya genocide is a series of ongoing persecutions and killings of the Muslim Rohingya people by the military of Myanmar. The genocide has consisted of two phases to date: the first was a military crackdown that occurred from October 2016 to January 2017, and the second has been occurring since August 2017. The crisis forced over a million Rohingya to flee to other countries. Most fled to Bangladesh, resulting in the creation of the world's largest refugee camp, while others escaped to India, Thailand, Malaysia, and other parts of South and Southeast Asia, where they continue to face persecution. Many other countries consider these events ethnic cleansing.

Violent clashes have been ongoing in the northern part of Myanmar's Rakhine State since October 2016. Insurgent attacks by the Arakan Rohingya Salvation Army (ARSA) have led to sectarian violence perpetrated by Myanmar's military and the local Buddhist population against predominantly Muslim Rohingya civilians. The conflict has sparked international outcry and was described as an ethnic cleansing by the United Nations High Commissioner for Human Rights. In August 2017, the situation worsened and hundreds of thousands of refugees fled Myanmar into Bangladesh, with an estimated 500,000 refugees having arrived by 27 September 2017. In January 2019, Arakan Army insurgents raided border police posts in Buthidaung Township, joining the conflict and beginning their military campaign in northern Rakhine State against the Burmese military.

The Myanmar civil war, also called the Burmese Spring Revolution, Burmese civil war or People's Defensive War, is an ongoing civil war following Myanmar's long-running insurgencies, which escalated significantly in response to the 2021 military coup d'état and the subsequent violent crackdown on anti-coup protests. The exiled National Unity Government and major ethnic armed organisations repudiated the 2008 Constitution and called instead for a democratic federal state. Besides engaging this alliance, the SAC also contends with other anti-SAC forces in areas under its control. Hannah Beech of The New York Times observed the insurgents are apportioned into hundreds of armed groups scattered across the country.