
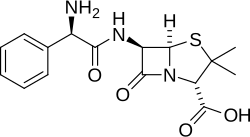
The aminopenicillins are members of the penicillin family that are structural analogs of ampicillin (which is the 2-amino derivative of benzylpenicillin, hence the name). [1] Like other penicillins and beta-lactam antibiotics, they contain a beta-lactam ring that is crucial to its antibacterial activity.[ citation needed ]
In the aminopenicillins the amino group is protonated to give the ammonium derivative, which enhances their uptake through bacterial porin channels. This does not, however, prevent resistance conferred by bacterial beta-lactamases. [2] Members of this family include ampicillin, amoxicillin and bacampicillin. [3]