A beta-lactam (β-lactam) ring is a four-membered lactam. A lactam is a cyclic amide, and beta-lactams are named so because the nitrogen atom is attached to the β-carbon atom relative to the carbonyl. The simplest β-lactam possible is 2-azetidinone. β-lactams are significant structural units of medicines as manifested in many β-lactam antibiotics. Up to 1970, most β-lactam research was concerned with the penicillin and cephalosporin groups, but since then, a wide variety of structures have been described.

Beta-lactamases (β-lactamases) are enzymes produced by bacteria that provide multi-resistance to beta-lactam antibiotics such as penicillins, cephalosporins, cephamycins, monobactams and carbapenems (ertapenem), although carbapenems are relatively resistant to beta-lactamase. Beta-lactamase provides antibiotic resistance by breaking the antibiotics' structure. These antibiotics all have a common element in their molecular structure: a four-atom ring known as a beta-lactam (β-lactam) ring. Through hydrolysis, the enzyme lactamase breaks the β-lactam ring open, deactivating the molecule's antibacterial properties.
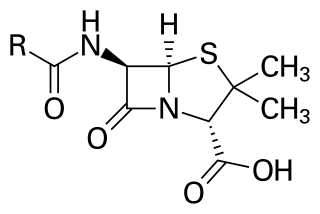
Penicillins are a group of β-lactam antibiotics originally obtained from Penicillium moulds, principally P. chrysogenum and P. rubens. Most penicillins in clinical use are synthesised by P. chrysogenum using deep tank fermentation and then purified. A number of natural penicillins have been discovered, but only two purified compounds are in clinical use: penicillin G and penicillin V. Penicillins were among the first medications to be effective against many bacterial infections caused by staphylococci and streptococci. They are still widely used today for different bacterial infections, though many types of bacteria have developed resistance following extensive use.
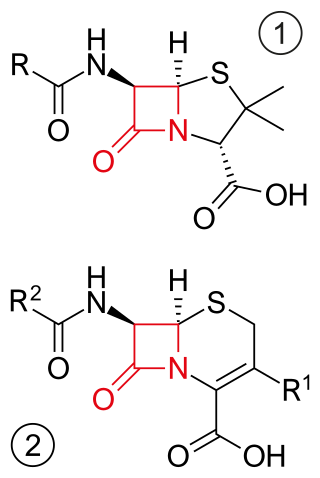
β-lactam antibiotics are antibiotics that contain a beta-lactam ring in their chemical structure. This includes penicillin derivatives (penams), cephalosporins and cephamycins (cephems), monobactams, carbapenems and carbacephems. Most β-lactam antibiotics work by inhibiting cell wall biosynthesis in the bacterial organism and are the most widely used group of antibiotics. Until 2003, when measured by sales, more than half of all commercially available antibiotics in use were β-lactam compounds. The first β-lactam antibiotic discovered, penicillin, was isolated from a strain of Penicillium rubens.

The cephalosporins are a class of β-lactam antibiotics originally derived from the fungus Acremonium, which was previously known as Cephalosporium.
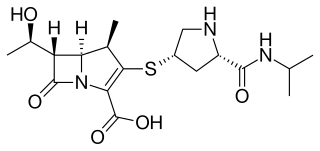
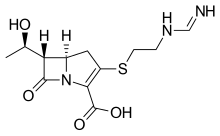
Meropenem, sold under the brand name Merrem among others, is an intravenous carbapenem antibiotic used to treat a variety of bacterial infections. Some of these include meningitis, intra-abdominal infection, pneumonia, sepsis, and anthrax.

Cephems are a sub-group of β-lactam antibiotics including cephalosporins and cephamycins. It is one of the most common 4-membered ring heterocycle. Produced by actinomycetes, cephamycins were found to display antibacterial activity against a wide range of bacteria, including those resistant to penicillin and cephalosporins. The antimicrobial properties of Cephem include the attachment to certain penicillin-binding proteins that are involved in the production of cell walls of bacteria.

Clavulanic acid is a β-lactam drug that functions as a mechanism-based β-lactamase inhibitor. While not effective by itself as an antibiotic, when combined with penicillin-group antibiotics, it can overcome antibiotic resistance in bacteria that secrete β-lactamase, which otherwise inactivates most penicillins.

Piperacillin is a broad-spectrum β-lactam antibiotic of the ureidopenicillin class. The chemical structure of piperacillin and other ureidopenicillins incorporates a polar side chain that enhances penetration into Gram-negative bacteria and reduces susceptibility to cleavage by Gram-negative beta lactamase enzymes. These properties confer activity against the important hospital pathogen Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Thus piperacillin is sometimes referred to as an "anti-pseudomonal penicillin".

Carbapenems are a class of very effective antibiotic agents most commonly used for treatment of severe bacterial infections. This class of antibiotics is usually reserved for known or suspected multidrug-resistant (MDR) bacterial infections. Similar to penicillins and cephalosporins, carbapenems are members of the beta-lactam antibiotics drug class, which kill bacteria by binding to penicillin-binding proteins, thus inhibiting bacterial cell wall synthesis. However, these agents individually exhibit a broader spectrum of activity compared to most cephalosporins and penicillins. Furthermore, carbapenems are typically unaffected by emerging antibiotic resistance, even to other beta-lactams.

Imipenem is a synthetic β-lactam antibiotic belonging to the carbapenems chemical class. developed by Merck scientists Burton Christensen, William Leanza, and Kenneth Wildonger in the mid-1970s. Carbapenems are highly resistant to the β-lactamase enzymes produced by many multiple drug-resistant Gram-negative bacteria, thus playing a key role in the treatment of infections not readily treated with other antibiotics. It is usually administered through intravenous injection.

Temocillin is a β-lactamase-resistant penicillin introduced by Beecham, marketed by Eumedica Pharmaceuticals as Negaban. It is used primarily for the treatment of multiple drug-resistant, Gram-negative bacteria.
It is a 6-methoxy penicillin; it is also a carboxypenicillin.
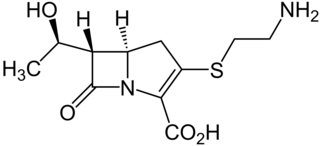
Thienamycin is one of the most potent naturally produced antibiotics known thus far, discovered in Streptomyces cattleya in 1976. Thienamycin has excellent activity against both Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria and is resistant to bacterial β-lactamase enzymes. Thienamycin is a zwitterion at pH 7.

Beta-lactamases are a family of enzymes involved in bacterial resistance to beta-lactam antibiotics. In bacterial resistance to beta-lactam antibiotics, the bacteria have beta-lactamase which degrade the beta-lactam rings, rendering the antibiotic ineffective. However, with beta-lactamase inhibitors, these enzymes on the bacteria are inhibited, thus allowing the antibiotic to take effect. Strategies for combating this form of resistance have included the development of new beta-lactam antibiotics that are more resistant to cleavage and the development of the class of enzyme inhibitors called beta-lactamase inhibitors. Although β-lactamase inhibitors have little antibiotic activity of their own, they prevent bacterial degradation of beta-lactam antibiotics and thus extend the range of bacteria the drugs are effective against.

Isopenicillin N synthase (IPNS) is a non-heme iron protein belonging to the 2-oxoglutarate (2OG)-dependent dioxygenases oxidoreductase family. This enzyme catalyzes the formation of isopenicillin N from δ-(L-α-aminoadipoyl)-L-cysteinyl-D-valine (LLD-ACV).

Dipeptidase 1 (DPEP1), or renal dipeptidase, is a membrane-bound glycoprotein responsible for hydrolyzing dipeptides. It is found in the microsomal fraction of the porcine kidney cortex. It exists as a disulfide-linked homodimer that is glygosylphosphatidylinositol (GPI)-anchored to the renal brush border of the kidney. The active site on each homodimer is made up of a barrel subunit with binuclear zinc ions that are bridged by the Gly125 side-chain located at the bottom of the barrel.
Cephalosporins are a broad class of bactericidal antibiotics that include the β-lactam ring and share a structural similarity and mechanism of action with other β-lactam antibiotics. The cephalosporins have the ability to kill bacteria by inhibiting essential steps in the bacterial cell wall synthesis which in the end results in osmotic lysis and death of the bacterial cell. Cephalosporins are widely used antibiotics because of their clinical efficiency and desirable safety profile.
Carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriaceae (CRE) or carbapenemase-producing Enterobacteriaceae (CPE) are Gram-negative bacteria that are resistant to the carbapenem class of antibiotics, considered the drugs of last resort for such infections. They are resistant because they produce an enzyme called a carbapenemase that disables the drug molecule. The resistance can vary from moderate to severe. Enterobacteriaceae are common commensals and infectious agents. Experts fear CRE as the new "superbug". The bacteria can kill up to half of patients who get bloodstream infections. Tom Frieden, former head of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention has referred to CRE as "nightmare bacteria". Examples of enzymes found in certain types of CRE are KPC and NDM. KPC and NDM are enzymes that break down carbapenems and make them ineffective. Both of these enzymes, as well as the enzyme VIM have also been reported in Pseudomonas.
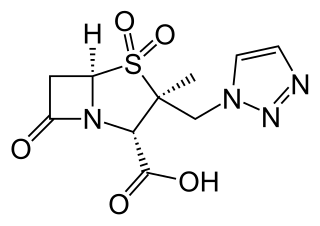
Ceftolozane/tazobactam, sold under the brand name Zerbaxa, is a combination antibiotic medication used for the treatment of complicated urinary tract infections and complicated intra-abdominal infections in adults. Ceftolozane is a cephalosporin antibiotic, developed for the treatment of infections with gram-negative bacteria that are resistant to conventional antibiotics. It was studied for urinary tract infections, intra-abdominal infections and ventilator-associated bacterial pneumonia.

Sulopenem (CP-70,429) is an antibiotic derivative from the carbapenem family, which unlike most related drugs is orally active. It was developed in Japan in the 1990s but has never been approved for medical use, however it has reached Phase III clinical trials on several occasions and continues to be the subject of ongoing research into potential applications, especially in the treatment of multiple drug resistant urinary tract infections.