
Linezolid is an antibiotic used for the treatment of infections caused by Gram-positive bacteria that are resistant to other antibiotics. Linezolid is active against most Gram-positive bacteria that cause disease, including streptococci, vancomycin-resistant enterococci (VRE), and methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA). The main uses are infections of the skin and pneumonia although it may be used for a variety of other infections including drug-resistant tuberculosis. It is used either by injection into a vein or by mouth.

Levofloxacin, sold under the brand name Levaquin among others, is a broad-spectrum antibiotic of the fluoroquinolone drug class. It is the left-handed isomer of the medication ofloxacin. It is used to treat a number of bacterial infections including acute bacterial sinusitis, pneumonia, H. pylori, urinary tract infections, Legionnaires' disease, chronic bacterial prostatitis, and some types of gastroenteritis. Along with other antibiotics it may be used to treat tuberculosis, meningitis, or pelvic inflammatory disease. It is available by mouth, intravenously, and in eye drop form.

Ofloxacin is a quinolone antibiotic useful for the treatment of a number of bacterial infections. When taken by mouth or injection into a vein, these include pneumonia, cellulitis, urinary tract infections, prostatitis, plague, and certain types of infectious diarrhea. Other uses, along with other medications, include treating multidrug resistant tuberculosis. An eye drop may be used for a superficial bacterial infection of the eye and an ear drop may be used for otitis media when a hole in the ear drum is present.
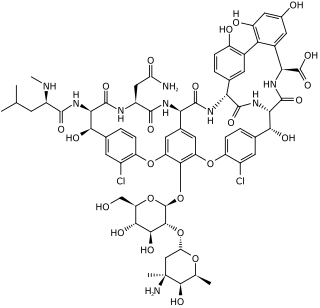
Glycopeptide antibiotics are a class of drugs of microbial origin that are composed of glycosylated cyclic or polycyclic nonribosomal peptides. Significant glycopeptide antibiotics include the anti-infective antibiotics vancomycin, teicoplanin, telavancin, ramoplanin and decaplanin, corbomycin, complestatin and the antitumor antibiotic bleomycin. Vancomycin is used if infection with methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) is suspected.

Tigecycline, sold under the brand name Tygacil, is a tetracycline antibiotic medication for a number of bacterial infections. It is a glycylcycline class drug that is administered intravenously. It was developed in response to the growing rate of antibiotic resistant bacteria such as Staphylococcus aureus, Acinetobacter baumannii, and E. coli. As a tetracycline derivative antibiotic, its structural modifications has expanded its therapeutic activity to include Gram-positive and Gram-negative organisms, including those of multi-drug resistance.
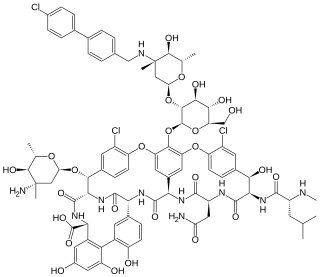
Oritavancin, sold under the brand name Orbactiv among others, is a semisynthetic glycopeptide antibiotic medication for the treatment of serious Gram-positive bacterial infections. Its chemical structure as a lipoglycopeptide is similar to vancomycin.

Cefditoren, also known as cefditoren pivoxil is an antibiotic used to treat infections caused by Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria that are resistant to other antibiotics. It is mainly used for treatment of community acquired pneumonia. It is taken by mouth and is in the cephalosporin family of antibiotics, which is part of the broader beta-lactam group of antibiotics.

Ceftobiprole, sold under the brand name Zevtera among others, is a fifth-generation cephalosporin antibacterial used for the treatment of hospital-acquired pneumonia and community-acquired pneumonia. It is marketed by Basilea Pharmaceutica under the brand names Zevtera and Mabelio. Like other cephalosporins, ceftobiprole exerts its antibacterial activity by binding to important penicillin-binding proteins and inhibiting their transpeptidase activity which is essential for the synthesis of bacterial cell walls. Ceftobiprole has high affinity for penicillin-binding protein 2a of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus strains and retains its activity against strains that express divergent mecA gene homologues. Ceftobiprole also binds to penicillin-binding protein 2b in Streptococcus pneumoniae (penicillin-intermediate), to penicillin-binding protein 2x in Streptococcus pneumoniae (penicillin-resistant), and to penicillin-binding protein 5 in Enterococcus faecalis.
Targanta Therapeutics Corporation was a biopharmaceutical company headquartered in Cambridge, Massachusetts. The company also had operations in Indianapolis, Montreal and Toronto. Targanta completed its initial public offering on October 9, 2007 and traded on the Nasdaq market under the symbol: TARG. Targanta was acquired by The Medicines Company in 2009.

Dalbavancin, sold under the brand names Dalvance in the US and Xydalba in the EU among others, is a second-generation lipoglycopeptide antibiotic medication. It belongs to the same class as vancomycin, the most widely used and one of the treatments available to people infected with methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA).

Telavancin is a bactericidal lipoglycopeptide for use in MRSA or other Gram-positive infections. Telavancin is a semi-synthetic derivative of vancomycin.
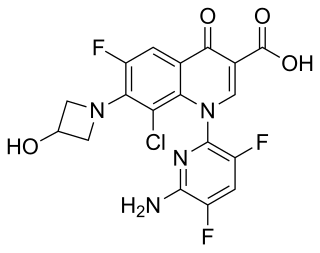
Delafloxacin sold under the brand name Baxdela among others, is a fluoroquinolone antibiotic used to treat acute bacterial skin and skin structure infections.

Tedizolid, sold under the brand name Sivextro is an oxazolidinone-class antibiotic. Tedizolid phosphate is a phosphate ester prodrug of the active compound tedizolid. It was developed by Cubist Pharmaceuticals, following acquisition of Trius Therapeutics, and is marketed for the treatment of acute bacterial skin and skin structure infections.

Ceftaroline fosamil (INN), brand name Teflaro in the US and Zinforo in Europe, is a cephalosporin antibiotic with anti-MRSA activity. Ceftaroline fosamil is a prodrug of ceftaroline. It is active against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) and other Gram-positive bacteria. It retains some activity of later-generation cephalosporins having broad-spectrum activity against Gram-negative bacteria, but its effectiveness is relatively much weaker. It is currently being investigated for community-acquired pneumonia and complicated skin and skin structure infection.
Skin and skin structure infections (SSSIs), also referred to as skin and soft tissue infections (SSTIs), or acute bacterial skin and skin structure infections (ABSSSIs), are infections of skin and associated soft tissues. Historically, the pathogen involved has most frequently been a bacterial species—always, since redescription of SSSIs as ABSSSIs—and as such, these infections require treatment by antibiotics.
Taksta is a front-loaded oral dosing regimen of sodium fusidate under development in the U.S. as an antibiotic for gram-positive infections including drug-resistant strains such as methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus.

Omadacycline, sold under the brand name Nuzyra, is a broad spectrum antibiotic medication belonging to the aminomethylcycline subclass of tetracycline antibiotics. In the United States, it was approved in October 2018, for the treatment of community-acquired bacterial pneumonia and acute skin and skin structure infections.

Ceftazidime/avibactam, sold under the brand name Avycaz among others, is a fixed-dose combination medication composed of ceftazidime, a cephalosporin antibiotic, and avibactam, a β-lactamase inhibitor. It is used to treat complicated intra-abdominal infections, urinary tract infections, and pneumonia. It is only recommended when other options are not appropriate. It is given by infusion into a vein.

Lefamulin, sold under the brand name Xenleta, is an antibiotic medication used it to treat adults with community-acquired bacterial pneumonia. It is taken by mouth or by injection into a vein.
Imipenem/cilastatin/relebactam, sold under the brand name Recarbrio(Merck), is a fixed-dose combination medication used as an antibiotic. In 2019, it was approved for use in the United States for the treatment of complicated urinary tract and complicated intra-abdominal infections. It is administered via intravenous injection.
















