Related Research Articles

The Arkansas Post, formally the Arkansas Post National Memorial, was the first European settlement in the Mississippi Alluvial Plain and present-day U.S. state of Arkansas. In 1686, Henri de Tonti established it on behalf of Louis XIV of France for the purpose of trading with the Quapaw Nation. The French, Spanish, and Americans, who acquired the territory in 1803 with the Louisiana Purchase, considered the site of strategic value. It was the capital of Arkansas from 1819 until 1821 when the territorial government relocated to Little Rock.

Blue Spring Heritage Center is a 33-acre (13 ha) privately owned tourist attraction in the Arkansas Heritage Trails System containing native plants and hardwood trees in a setting of woodlands, meadows, and hillsides. It is located at Highway 62 West, five miles (8 km) west of Eureka Springs, Arkansas, and open daily to the public during warmer months for a fee.

The Nodena site is an archeological site east of Wilson, Arkansas, and northeast of Reverie, Tennessee, in Mississippi County, Arkansas, United States. Around 1400–1650 CE an aboriginal palisaded village existed in the Nodena area on a meander bend of the Mississippi River. The Nodena site was discovered and first documented by Dr. James K. Hampson, archaeologist and owner of the plantation on which the Nodena site is located. Artifacts from this site are on display in the Hampson Museum State Park in Wilson, Arkansas. The Nodena site is the type site for the Nodena phase, believed by many archaeologists to be the province of Pacaha visited by Spanish explorer Hernando de Soto in 1542.

The Eaker site (3MS105) is an archaeological site on Eaker Air Force Base near Blytheville, Arkansas, that was declared a National Historic Landmark in 1996. The site is the largest and most intact Late Mississippian Nodena phase village site within the Central Mississippi Valley, with archaeological evidence indicating a palisaded village some 50 acres (20 ha) in size, with hundreds of structures. The site's major period of occupation was 1350–1450 CE, although evidence of occupation dates back to 600 CE. The site is also hypothesized to have been occupied by the Quapaw prior to a migration further south, after which they made contact with Europeans in the late 17th century.

The Menard–Hodges site (3AR4), is an archaeological site in Arkansas County, Arkansas. It includes two large platform mounds as well as several house mounds. It is the type site for the Menard phase, a protohistoric Mississippian culture group.
Parkin Archeological State Park, also known as Parkin Indian Mound, is an archeological site and state park in Parkin, Cross County, Arkansas. Around 1350–1650 CE an aboriginal palisaded village existed at the site, at the confluence of the St. Francis and Tyronza rivers. Artifacts from this site are on display at the site museum. The Parkin site is the type site for the Parkin phase, an expression of the Mississippian culture from the Late Mississippian period. Many archeologists believe it to be part of the province of Casqui, documented as visited by Spanish explorer Hernando de Soto in 1542. Archeological artifacts from the village of the Parkin people are dated to 1400–1650 CE.
Nady is an unincorporated community in Arkansas County, Arkansas, United States. It is the location of a National Historic Landmark, the Menard–Hodges site. The environs of Nady, at the southern tip of the Little Prairie, are in the portion of Arkansas that saw the earliest European settlement in what is now the state of Arkansas, including Tonty’s 1686 post. The Menard-Hodges archeological site, about one-half mile southwest of Wallace-Menard-Coose Cemetery, along with the adjacent Wallace Bottom archeological site, appear to be the locations of the late 1600s Quapaw village of Osotouy, Tonty’s 1686 Post, and the early to mid-1700s French Arkansas Post.
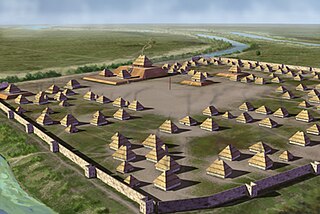
Plum Bayou Mounds Archeological State Park, formerly known as "Toltec Mounds Archeological State Park", also known as Knapp Mounds, Toltec Mounds or Toltec Mounds site, is an archaeological site from the Late Woodland period in Arkansas that protects an 18-mound complex with the tallest surviving prehistoric mounds in Arkansas. The site is on the banks of Mound Lake, an oxbow lake of the Arkansas River. It was occupied by its original inhabitants from the 7th to the 11th century. The site is designated as a National Historic Landmark.
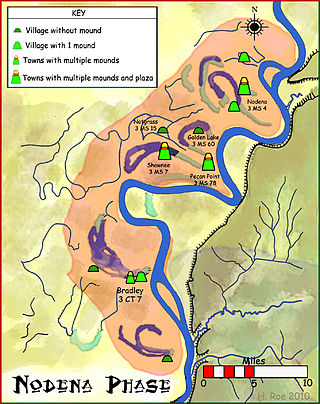
The Nodena phase is an archaeological phase in eastern Arkansas and southeastern Missouri of the Late Mississippian culture which dates from about 1400–1650 CE. The Nodena phase is known from a collection of villages along the Mississippi River between the Missouri Bootheel and Wapanocca Lake. They practiced extensive maize agriculture and artificial cranial deformation and were members of a continent wide trade and religious network known as the Southeastern Ceremonial Complex, which brought chert, whelk shells, and other exotic goods to the area.
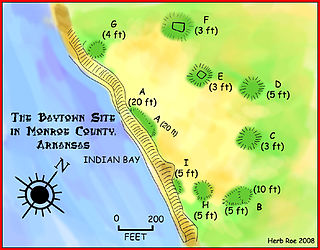
The Baytown Site is a Pre-Columbian Native American archaeological site located on the White River at Indian Bay, in Monroe County, Arkansas. It was first inhabited by peoples of the Baytown culture and later briefly by peoples of the Plum Bayou culture, in a time known as the Late Woodland period. It is considered the type site of the Baytown culture.

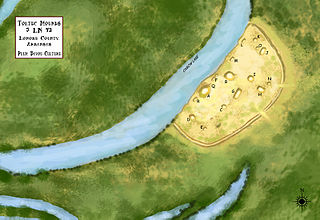
The Coy Site is an archaeological site located next to Indian-Bakers Bayou in Lonoke County, Arkansas. It was inhabited by peoples of the Plum Bayou culture, in a time known as the Late Woodland period. The site was occupied between 700 and 1000 CE. It was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1995.
The Roland Site is an archaeological site located on Dry Lake, an extinct channel of the White River in Arkansas County, Arkansas. It was inhabited intermittently from the beginning of the common era to late prehistoric times, but its most intensive inhabitation was by peoples of the Plum Bayou culture, in a time known as the Late Woodland period.

This is a list of the National Register of Historic Places listings in Ste. Genevieve County, Missouri.

The Illinois Salines, also known as the Saline Springs or Great Salt Springs, is a salt spring site located along the Saline River in Gallatin County, Illinois. The site was a source of salt for Illinois' prehistoric settlers and is now an archaeological site with a large quantity of organic remains. After European settlement of Illinois, the salt springs became part of Illinois' first major industry and were one of the only places in Illinois where slavery was legal after 1818.
The Ross Site designated 3CL401, is a prehistoric archaeological site in Clark County, Arkansas, near the small town of Whelen Springs. The site includes two Native American mounds from the Caddoan culture, which have been dated to AD 1400–1600. It is one of a small number of Caddoan sites in southwestern Arkansas. The site was relatively unscathed until the mid-1980s, having never been plowed over, thus leaving intact potential ground-level features other than the mounds.
The Zebree Homestead is a prehistoric archaeological site in Mississippi County, Arkansas. The site contains evidence of a Late Woodland Period village, and is most significant as oldest known site of the Mississippian culture south of St. Louis. It appears to have been settled from Cahokia around 900 CE, with evidence of habitation and tool work, as well as a c. 1100 CE ditch and palisade.
The Calf Creek site, designated Site 3SE33 by archaeologists, is an important archaeological site near the mouth of Calf Creek where it empties into the Buffalo River in Searcy County, Arkansas. The site exhibits evidence of long-term occupation, spanning several archaeological eras. It contains one of the largest known assemblages of prehistoric material in the Buffalo National River.
The Jones Mill Site, designated by the Smithsonian trinomial 3HS28, is a prehistoric archaeological site near Jones Mill in Hot Spring County, Arkansas. It is a deeply stratified site, with evidence of human habitation in at least three different time periods. It is one of the few documented Archaic sites in the region, with evidence of human activity dating to 3000 BCE. It is located near documented prehistoric stone quarry sites, and finds at the site include extensive stone tool construction artifacts.
The Lake Catherine Quarry is a prehistoric stone quarry in Hot Spring County, Arkansas. The site was used as a source of black novaculite, a relatively rare form of chert. Evidence of Native American quarrying activity at the site includes quarry pits, spoil piles, and a scattered talus slope of rejected materials. The site is untainted by historic quarrying, providing a potentially significant window into prehistoric quarrying methods.
References
- 1 2 "National Register Information System". National Register of Historic Places . National Park Service. July 9, 2010.
- ↑ "Summary description of Bayou Sel". Arkansas Preservation. Archived from the original on August 3, 2014. Retrieved July 26, 2014.