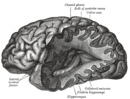
Neurology is a branch of medicine dealing with disorders of the nervous system. Neurology deals with the diagnosis and treatment of all categories of conditions and disease involving the central and peripheral nervous systems, including their coverings, blood vessels, and all effector tissue, such as muscle. Neurological practice relies heavily on the field of neuroscience, the scientific study of the nervous system.

Binswanger's disease, also known as subcortical leukoencephalopathy and subcortical arteriosclerotic encephalopathy (SAE), is a form of small vessel vascular dementia caused by damage to the white brain matter. White matter atrophy can be caused by many circumstances including chronic hypertension as well as old age. This disease is characterized by loss of memory and intellectual function and by changes in mood. These changes encompass what are known as executive functions of the brain. It usually presents between 54 and 66 years of age, and the first symptoms are usually mental deterioration or stroke.
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to neuroscience:
Neuropsychology is a branch of psychology that is concerned with how the brain and the rest of the nervous system influence a person's cognition and behaviors. More importantly, professionals in this branch of psychology often focus on how injuries or illnesses of the brain affect cognitive functions and behaviors.
Cognitive neuropsychology is a branch of cognitive psychology that aims to understand how the structure and function of the brain relates to specific psychological processes. Cognitive psychology is the science that looks at how mental processes are responsible for our cognitive abilities to store and produce new memories, produce language, recognize people and objects, as well as our ability to reason and problem solve. Cognitive neuropsychology places a particular emphasis on studying the cognitive effects of brain injury or neurological illness with a view to inferring models of normal cognitive functioning. Evidence is based on case studies of individual brain damaged patients who show deficits in brain areas and from patients who exhibit double dissociations. Double dissociations involve two patients and two tasks. One patient is impaired at one task but normal on the other, while the other patient is normal on the first task and impaired on the other. For example, patient A would be poor at reading printed words while still being normal at understanding spoken words, while the patient B would be normal at understanding written words and be poor at understanding spoken words. Scientists can interpret this information to explain how there is a single cognitive module for word comprehension. From studies like these, researchers infer that different areas of the brain are highly specialised. Cognitive neuropsychology can be distinguished from cognitive neuroscience, which is also interested in brain damaged patients, but is particularly focused on uncovering the neural mechanisms underlying cognitive processes.

Hypergraphia is a behavioral condition characterized by the intense desire to write or draw. Forms of hypergraphia can vary in writing style and content. It is a symptom associated with temporal lobe changes in epilepsy, which is the cause of the Geschwind syndrome, a mental disorder. Structures that may have an effect on hypergraphia when damaged due to temporal lobe epilepsy are the hippocampus and Wernicke's area. Aside from temporal lobe epilepsy, chemical causes may be responsible for inducing hypergraphia.

Clinical neuropsychology is a sub-field of psychology concerned with the applied science of brain-behaviour relationships. Clinical neuropsychologists use this knowledge in the assessment, diagnosis, treatment, and or rehabilitation of patients across the lifespan with neurological, medical, neurodevelopmental and psychiatric conditions, as well as other cognitive and learning disorders. The branch of neuropsychology associated with children and young people is pediatric neuropsychology.

CarlWernicke was a German physician, anatomist, psychiatrist and neuropathologist. He is known for his influential research into the pathological effects of specific forms of encephalopathy and also the study of receptive aphasia, both of which are commonly associated with Wernicke's name and referred to as Wernicke encephalopathy and Wernicke's aphasia, respectively. His research, along with that of Paul Broca, led to groundbreaking realizations of the localization of brain function, specifically in speech. As such, Wernicke's area has been named after the scientist.
Comparative neuropsychology refers to an approach used for understanding human brain functions. It involves the direct evaluation of clinical neurological populations by employing experimental methods originally developed for use with nonhuman animals.
Semantic dementia (SD), also known as semantic variant primary progressive aphasia (svPPA), is a progressive neurodegenerative disorder characterized by loss of semantic memory in both the verbal and non-verbal domains. However, the most common presenting symptoms are in the verbal domain. SD is one of the three canonical clinical syndromes associated with frontotemporal lobar degeneration (FTLD), with the other two being frontotemporal dementia and progressive nonfluent aphasia. SD is a clinically defined syndrome, but is associated with predominantly temporal lobe atrophy and hence is sometimes called temporal variant FTLD (tvFTLD). SD is one of the three variants of primary progressive aphasia (PPA), which results from neurodegenerative disorders such as FTLD or Alzheimer's disease. It is important to note the distinctions between Alzheimer’s Disease and Semantic dementia with regard to types of memory affected. In general, Alzheimer’s Disease is referred to as disorder affecting mainly episodic memory, defined as the memory related to specific, personal events distinct for each individual. Semantic dementia generally affects semantic memory, which refers to long-term memory that deals with common knowledge and facts.3
Neuropsychiatry is a branch of medicine that deals with mental disorders attributable to diseases of the nervous system. It preceded the current disciplines of psychiatry and neurology, which had common training, however, psychiatry and neurology have subsequently split apart and are typically practiced separately. Nevertheless, neuropsychiatry has become a growing subspecialty of psychiatry and it is also closely related to the fields of neuropsychology and behavioral neurology.

Frontal lobe disorder is an impairment of the frontal lobe that occurs due to disease or head trauma. The frontal lobe of the brain plays a key role in higher mental functions such as motivation, planning, social behaviour, and speech production. A frontal lobe syndrome can be caused by a range of conditions including head trauma, tumours, degenerative diseases, neurosurgery and cerebrovascular disease. Frontal lobe impairment can be detected by recognition of typical clinical signs, use of simple screening tests, and specialist neurological testing.
Edith F. Kaplan was an American psychologist. She was a pioneer of neuropsychological tests and did most of her work at the Boston VA Hospital. Kaplan is known for her promotion of clinical neuropsychology as a specialty area in psychology. She examined brain-behavioral relationships in aphasia, apraxia, developmental issues in clinical neuropsychology, as well as normal and abnormal aging. Kaplan helped develop a new method of assessing brain function with neuropsychological assessment, called "The Boston Process Approach."
Autotopagnosia from the Greek a and gnosis, meaning "without knowledge", topos meaning "place", and auto meaning "oneself", autotopagnosia virtually translates to the "lack of knowledge about one's own space," and is clinically described as such.
Geschwind syndrome, also known as Gastaut-Geschwind, is a group of behavioral phenomena evident in some people with temporal lobe epilepsy. It is named for one of the first individuals to categorize the symptoms, Norman Geschwind, who published prolifically on the topic from 1973 to 1984. There is controversy surrounding whether it is a true neuropsychiatric disorder. Temporal lobe epilepsy causes chronic, mild, interictal changes in personality, which slowly intensify over time. Geschwind syndrome includes five primary changes; hypergraphia, hyperreligiosity, atypical sexuality, circumstantiality, and intensified mental life. Not all symptoms must be present for a diagnosis. Only some people with epilepsy or temporal lobe epilepsy show features of Geschwind syndrome.
Norman Geschwind was a pioneering American behavioral neurologist, best known for his exploration of behavioral neurology through disconnection models based on lesion analysis.
Elizabeth Kerr Warrington FRS is a British neuropsychologist specialised in the study of dementia. She holds a PhD in Psychology visual processing and is now an emeritus professor of clinical neuropsychology at the University College London. She formerly worked as the Head of the Department of Neuropsychology at the National Hospital for Neurology and Neurosurgery where she is also a member of the Dementia Research Centre. She was made a Fellow of the Royal Society in 1986.
Clinical neuroscience is a branch of neuroscience that focuses on the scientific study of fundamental mechanisms that underlie diseases and disorders of the brain and central nervous system. It seeks to develop new ways of conceptualizing and diagnosing such disorders and ultimately of developing novel treatments.
The American Neuropsychiatric Association (ANPA) is a non-profit organization of professionals in neuropsychiatry, behavioral neurology and the clinical neurosciences, with over 700 members from around the world. Established in 1988, its mission is to improve the lives of people with disorders at the interface of psychiatry and neurology, with the vision of transforming recognition, understanding and treatment of neuropsychiatric disorders. It founded in 1988 by two academic physicians doubly certified in neurology and psychiatry, Barry S. Fogel and Randolph Schiffer.
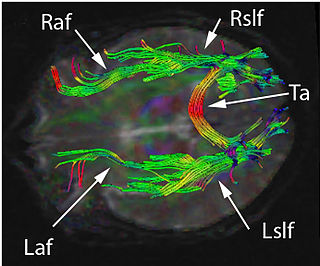
Disconnection syndrome is a general term for a collection of neurological symptoms caused -- via lesions to associational or commissural nerve fibres -- by damage to the white matter axons of communication pathways in the cerebrum, independent of any lesions to the cortex. The behavioral effects of such disconnections are relatively predictable in adults. Disconnection syndromes usually reflect circumstances where regions A and B still have their functional specializations except in domains that depend on the interconnections between the two regions.