Charcot–Marie–Tooth disease (CMT) is a hereditary motor and sensory neuropathy of the peripheral nervous system characterized by progressive loss of muscle tissue and touch sensation across various parts of the body. This disease is the most commonly inherited neurological disorder, affecting about one in 2,500 people. It is named after those who classically described it: the Frenchman Jean-Martin Charcot (1825–1893), his pupil Pierre Marie (1853–1940), and the Briton Howard Henry Tooth (1856–1925).

Neurology is the branch of medicine dealing with the diagnosis and treatment of all categories of conditions and disease involving the nervous system, which comprises the brain, the spinal cord and the peripheral nerves. Neurological practice relies heavily on the field of neuroscience, the scientific study of the nervous system.

Neurosurgery or neurological surgery, known in common parlance as brain surgery, is the medical specialty that focuses on the surgical treatment or rehabilitation of disorders which affect any portion of the nervous system including the brain, spinal cord, peripheral nervous system, and cerebrovascular system. Neurosurgery as a medical specialty also includes non-surgical management of some neurological conditions.

Pathology is the study of disease. The word pathology also refers to the study of disease in general, incorporating a wide range of biology research fields and medical practices. However, when used in the context of modern medical treatment, the term is often used in a narrower fashion to refer to processes and tests that fall within the contemporary medical field of "general pathology", an area that includes a number of distinct but inter-related medical specialties that diagnose disease, mostly through analysis of tissue and human cell samples. Idiomatically, "a pathology" may also refer to the predicted or actual progression of particular diseases. The suffix pathy is sometimes used to indicate a state of disease in cases of both physical ailment and psychological conditions. A physician practicing pathology is called a pathologist.

Anatomical pathology (Commonwealth) or anatomic pathology (U.S.) is a medical specialty that is concerned with the diagnosis of disease based on the macroscopic, microscopic, biochemical, immunologic and molecular examination of organs and tissues. Over the 20th century, surgical pathology has evolved tremendously: from historical examination of whole bodies (autopsy) to a more modernized practice, centered on the diagnosis and prognosis of cancer to guide treatment decision-making in oncology. Its modern founder was the Italian scientist Giovanni Battista Morgagni from Forlì.

In neuroanatomy, the optic nerve, also known as the second cranial nerve, cranial nerve II, or simply CN II, is a paired cranial nerve that transmits visual information from the retina to the brain. In humans, the optic nerve is derived from optic stalks during the seventh week of development and is composed of retinal ganglion cell axons and glial cells; it extends from the optic disc to the optic chiasma and continues as the optic tract to the lateral geniculate nucleus, pretectal nuclei, and superior colliculus.

The somatic nervous system (SNS), also known as voluntary nervous system, is a part of the peripheral nervous system (PNS) that links brain and spinal cord to skeletal muscles under conscious control, as well as to sensory receptors in the skin. The other part complementary to the somatic nervous system is the autonomic nervous system (ANS).
Diabetic neuropathy includes various types of nerve damage associated with diabetes mellitus. The most common form, diabetic peripheral neuropathy, affects 30% of all diabetic patients. Symptoms depend on the site of nerve damage and can include motor changes such as weakness; sensory symptoms such as numbness, tingling, or pain; or autonomic changes such as urinary symptoms. These changes are thought to result from a microvascular injury involving small blood vessels that supply nerves. Relatively common conditions which may be associated with diabetic neuropathy include distal symmetric polyneuropathy; third, fourth, or sixth cranial nerve palsy; mononeuropathy; mononeuropathy multiplex; diabetic amyotrophy; and autonomic neuropathy.
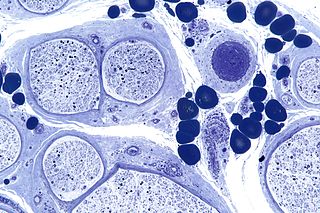
Peripheral neuropathy, often shortened to neuropathy, refers to damage or disease affecting the nerves. Damage to nerves may impair sensation, movement, gland function, and/or organ function depending on which nerve fibers are affected. Neuropathies affecting motor, sensory, or autonomic nerve fibers result in different symptoms. More than one type of fiber may be affected simultaneously. Peripheral neuropathy may be acute or chronic, and may be reversible or permanent.

Polyneuropathy is damage or disease affecting peripheral nerves in roughly the same areas on both sides of the body, featuring weakness, numbness, and burning pain. It usually begins in the hands and feet and may progress to the arms and legs and sometimes to other parts of the body where it may affect the autonomic nervous system. It may be acute or chronic. A number of different disorders may cause polyneuropathy, including diabetes and some types of Guillain–Barré syndrome.

A nerve conduction study (NCS) is a medical diagnostic test commonly used to evaluate the function, especially the ability of electrical conduction, of the motor and sensory nerves of the human body. These tests may be performed by medical specialists such as clinical neurophysiologists, physical therapists, physiatrists, and neurologists who subspecialize in electrodiagnostic medicine. In the United States, neurologists and physiatrists receive training in electrodiagnostic medicine (performing needle electromyography as part of residency training and, in some cases, acquire additional expertise during a fellowship in clinical neurophysiology, electrodiagnostic medicine, or neuromuscular medicine. Outside the US, clinical neurophysiologists learn needle EMG and NCS testing.

Neuritis, from the Greek νεῦρον), is inflammation of a nerve or the general inflammation of the peripheral nervous system. Inflammation, and frequently concomitant demyelination, cause impaired transmission of neural signals and leads to aberrant nerve function. Neuritis is often conflated with neuropathy, a broad term describing any disease process which affects the peripheral nervous system. However, neuropathies may be due to either inflammatory or non-inflammatory causes, and the term encompasses any form of damage, degeneration, or dysfunction, while neuritis refers specifically to the inflammatory process.

The sural nerve(L4-S1) is generally considered a pure cutaneous nerve of the posterolateral leg to the lateral ankle. The sural nerve originates from a combination of either the sural communicating branch and medial sural cutaneous nerve, or the lateral sural cutaneous nerve. This group of nerves is termed the sural nerve complex. There are eight documented variations of the sural nerve complex. Once formed the sural nerve takes its course midline posterior to posterolateral around the lateral malleolus. The sural nerve terminates as the lateral dorsal cutaneous nerve.
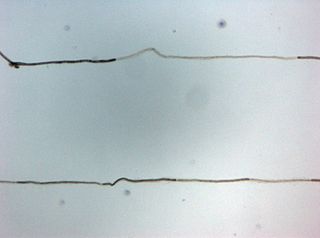
Chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy (CIDP) is an acquired autoimmune disease of the peripheral nervous system characterized by progressive weakness and impaired sensory function in the legs and arms. The disorder is sometimes called chronic relapsing polyneuropathy (CRP) or chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy. CIDP is closely related to Guillain–Barré syndrome and it is considered the chronic counterpart of that acute disease. Its symptoms are also similar to progressive inflammatory neuropathy. It is one of several types of neuropathy.
Small fiber peripheral neuropathy is a type of peripheral neuropathy that occurs from damage to the small unmyelinated and myelinated peripheral nerve fibers. These fibers, categorized as C fibers and small Aδ fibers, are present in skin, peripheral nerves, and organs. The role of these nerves is to innervate some skin sensations and help control autonomic function. It is estimated that 15–20 million people in the United States have some form of peripheral neuropathy.
Hereditary sensory and autonomic neuropathy (HSAN) or hereditary sensory neuropathy (HSN) is a condition used to describe any of the types of this disease which inhibit sensation.
Electrodiagnosis (EDX) is a method of medical diagnosis that obtains information about diseases by passively recording the electrical activity of body parts or by measuring their response to external electrical stimuli. The most widely used methods of recording spontaneous electrical activity are various forms of electrodiagnostic testing (electrography) such as electrocardiography (ECG), electroencephalography (EEG), and electromyography (EMG). Electrodiagnostic medicine is a medical subspecialty of neurology, clinical neurophysiology, cardiology, and physical medicine and rehabilitation. Electrodiagnostic physicians apply electrophysiologic techniques, including needle electromyography and nerve conduction studies to diagnose, evaluate, and treat people with impairments of the neurologic, neuromuscular, and/or muscular systems. The provision of a quality electrodiagnostic medical evaluation requires extensive scientific knowledge that includes anatomy and physiology of the peripheral nerves and muscles, the physics and biology of the electrical signals generated by muscle and nerve, the instrumentation used to process these signals, and techniques for clinical evaluation of diseases of the peripheral nerves and sensory pathways.

Andermann syndrome, also known as agenesis of corpus callosum with neuronopathy (ACCPN), Charlevoix disease and KCC3 axonopathy among other names, is a very rare neurodegenerative genetic disorder that damages the nerves used to control muscles and related to sensation and is often associated with agenesis of the corpus callosum.
Peripheral mononeuropathy is a nerve related disease where a single nerve, that is used to transport messages from the brain to the peripheral body, is diseased or damaged. Peripheral neuropathy is a general term that indicates any disorder of the peripheral nervous system. The name of the disorder itself can be broken down in order to understand this better; peripheral: in regard to peripheral neuropathy, refers to outside of the brain and spinal cord; neuro: means nerve related; -pathy; means disease. Peripheral mononeuropathy is a disorder that links to Peripheral Neuropathy, as it only effects a single peripheral nerve rather than several damaged or diseased nerves throughout the body. Healthy peripheral nerves are able to “carry messages from the brain and spinal cord to muscles, organs, and other body tissues”.
Vasculitic neuropathy is a peripheral neuropathic disease. In a vasculitic neuropathy there is damage to the vessels that supply blood to the nerves. It can be as part of a systemic problem or can exist as a single-organ issue only affecting the peripheral nervous system (PNS). It is diagnosed with the use of electrophysiological testing, blood tests, nerve biopsy and clinical examination. It is a serious medical condition that can cause prolonged morbidity and disability and generally requires treatment. Treatment depends on the type but it is mostly with corticosteroids or immunomodulating therapies.