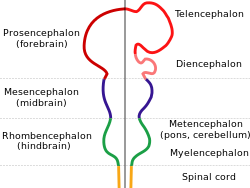| Neuropsychology |
|---|
 |

The human brain anatomical regions are ordered following standard neuroanatomy hierarchies. Functional, connective, and developmental regions are listed in parentheses where appropriate.
Contents
- Hindbrain (rhombencephalon)
- Myelencephalon
- Metencephalon
- Midbrain (mesencephalon)
- Forebrain (prosencephalon)
- Diencephalon
- Telencephalon (cerebrum) Cerebral hemispheres
- Neural pathways
- Motor systems / Descending fibers
- Somatosensory system
- Visual system
- Auditory system
- Nerves
- Neuroendocrine systems
- Neuro vascular systems
- Neurotransmitter pathways
- Dural meningeal system
- Limbic system
- Related topics
- References
- External links