Vertebrate mechanoreceptors
Cutaneous mechanoreceptors
Cutaneous mechanoreceptors respond to mechanical stimuli that result from physical interaction, including pressure and vibration. They are located in the skin, like other cutaneous receptors. They are all innervated by Aβ fibers, except the mechanorecepting free nerve endings, which are innervated by Aδ fibers. Cutaneous mechanoreceptors can be categorized by what kind of sensation they perceive, by the rate of adaptation, and by morphology. Furthermore, each has a different receptive field.[ citation needed ]

By sensation
- The Slowly Adapting type 1 (SA1) mechanoreceptor, with the Merkel corpuscle end-organ (also known as Merkel discs) detect sustained pressure and underlies the perception of form and roughness on the skin. [1] They have small receptive fields and produce sustained responses to static stimulation.[ citation needed ]
- The Slowly Adapting type 2 (SA2) mechanoreceptors, with the Ruffini corpuscle end-organ (also known as the bulbous corpuscles), detect tension deep in the skin and fascia and respond to skin stretch, but have not been closely linked to either proprioceptive or mechanoreceptive roles in perception. [2] They also produce sustained responses to static stimulation, but have large receptive fields.[ citation needed ]
- The Rapidly Adapting (RA) or Meissner corpuscle end-organ mechanoreceptor (also known as the tactile corpuscles) underlies the perception of light touch such as flutter [3] and slip on the skin. [4] It adapts rapidly to changes in texture (vibrations around 50 Hz). They have small receptive fields and produce transient responses to the onset and offset of stimulation.[ citation needed ]
- The Pacinian corpuscle or Vater-Pacinian corpuscles or Lamellar corpuscles [5] in the skin and fascia detect rapid vibrations of about 200–300 Hz. [3] [6] They also produce transient responses, but have large receptive fields.
- Free nerve endings detect touch, pressure, stretching, as well as the tickle and itch sensations. Itch sensations are caused by stimulation of free nerve ending from chemicals. [7]
- Hair follicle receptors called hair root plexuses sense when a hair changes position. Indeed, the most sensitive mechanoreceptors in humans are the hair cells in the cochlea of the inner ear (no relation to the follicular receptors – they are named for the hair-like mechanosensory stereocilia they possess); these receptors transduce sound for the brain. [7]
By rate of adaptation
Cutaneous mechanoreceptors can also be separated into categories based on their rates of adaptation. When a mechanoreceptor receives a stimulus, it begins to fire impulses or action potentials at an elevated frequency (the stronger the stimulus, the higher the frequency). The cell, however, will soon "adapt" to a constant or static stimulus, and the pulses will subside to a normal rate. Receptors that adapt quickly (i.e., quickly return to a normal pulse rate) are referred to as "phasic". Those receptors that are slow to return to their normal firing rate are called tonic. Phasic mechanoreceptors are useful in sensing such things as texture or vibrations, whereas tonic receptors are useful for temperature and proprioception among others.[ citation needed ]
- Slowly adapting: Slowly adapting mechanoreceptors include Merkel and Ruffini corpuscle end-organs, and some free nerve endings.
- Slowly adapting type I mechanoreceptors have multiple Merkel corpuscle end-organs.
- Slowly adapting type II mechanoreceptors have single Ruffini corpuscle end-organs.
- Intermediate adapting: Some free nerve endings are intermediate adapting.
- Rapidly adapting: Rapidly adapting mechanoreceptors include Meissner corpuscle end-organs, Pacinian corpuscle end-organs, hair follicle receptors and some free nerve endings.
- Rapidly adapting type I mechanoreceptors have multiple Meissner corpuscle end-organs.
- Rapidly adapting type II mechanoreceptors (usually called Pacinian) have single Pacinian corpuscle end-organs.
By receptive field
Cutaneous mechanoreceptors with small, accurate receptive fields are found in areas needing accurate taction (e.g. the fingertips). In the fingertips and lips, innervation density of slowly adapting type I and rapidly adapting type I mechanoreceptors are greatly increased. These two types of mechanoreceptors have small discrete receptive fields and are thought to underlie most low-threshold use of the fingers in assessing texture, surface slip, and flutter. Mechanoreceptors found in areas of the body with less tactile acuity tend to have larger receptive fields.[ citation needed ]
Lamellar corpuscles
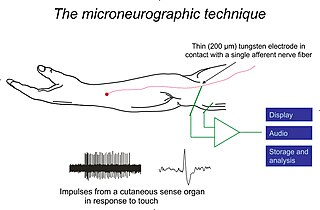
Lamellar corpuscles, or Pacinian corpuscles or Vater-Pacini corpuscle, are deformation or pressure receptors located in the skin and also in various internal organs. [8] Each is connected to a sensory neuron. Because of its relatively large size, a single lamellar corpuscle can be isolated and its properties studied. Mechanical pressure of varying strength and frequency can be applied to the corpuscle by stylus, and the resulting electrical activity detected by electrodes attached to the preparation.[ citation needed ]
Deforming the corpuscle creates a generator potential in the sensory neuron arising within it. This is a graded response: the greater the deformation, the greater the generator potential. If the generator potential reaches threshold, a volley of action potentials (nerve impulses) are triggered at the first node of Ranvier of the sensory neuron.[ citation needed ]
Once threshold is reached, the magnitude of the stimulus is encoded in the frequency of impulses generated in the neuron. So the more massive or rapid the deformation of a single corpuscle, the higher the frequency of nerve impulses generated in its neuron.[ citation needed ]
The optimal sensitivity of a lamellar corpuscle is 250 Hz, the frequency range generated upon finger tips by textures made of features smaller than 200 micrometres. [9]
Ligamentous mechanoreceptors
There are four types of mechanoreceptors embedded in ligaments. As all these types of mechanoreceptors are myelinated, they can rapidly transmit sensory information regarding joint positions to the central nervous system. [10]
- Type I: (small) Low threshold, slow adapting in both static and dynamic settings
- Type II: (medium) Low threshold, rapidly adapting in dynamic settings
- Type III: (large) High threshold, slowly adapting in dynamic settings
- Type IV: (very small) High threshold pain receptors that communicate injury
Type II and Type III mechanoreceptors in particular are believed to be linked to one's sense of proprioception.
Other mechanoreceptors
Other mechanoreceptors than cutaneous ones include the hair cells, which are sensory receptors in the vestibular system of the inner ear, where they contribute to the auditory system and equilibrioception. Baroreceptors are a type of mechanoreceptor sensory neuron that is excited by stretch of the blood vessel. There are also juxtacapillary (J) receptors, which respond to events such as pulmonary edema, pulmonary emboli, pneumonia, and barotrauma.[ citation needed ]
Muscle spindles and the stretch reflex
The knee jerk is the popularly known stretch reflex (involuntary kick of the lower leg) induced by tapping the knee with a rubber-headed hammer. The hammer strikes a tendon that inserts an extensor muscle in the front of the thigh into the lower leg. Tapping the tendon stretches the thigh muscle, which activates stretch receptors within the muscle called muscle spindles. Each muscle spindle consists of sensory nerve endings wrapped around special muscle fibers called intrafusal muscle fibers. Stretching an intrafusal fiber initiates a volley of impulses in the sensory neuron (a I-a neuron) attached to it. The impulses travel along the sensory axon to the spinal cord where they form several kinds of synapses:[ citation needed ]
- Some of the branches of the I-a axons synapse directly with alpha motor neurons. These carry impulses back to the same muscle causing it to contract. The leg straightens.
- Some of the branches of the I-a axons synapse with inhibitory interneurons in the spinal cord. These, in turn, synapse with motor neurons leading back to the antagonistic muscle, a flexor in the back of the thigh. By inhibiting the flexor, these interneurons aid contraction of the extensor.
- Still other branches of the I-a axons synapse with interneurons leading to brain centers, e.g., the cerebellum, that coordinate body movements. [11]
Mechanism of sensation
In somatosensory transduction, the afferent neurons transmit messages through synapses in the dorsal column nuclei, where second-order neurons send the signal to the thalamus and synapse with third-order neurons in the ventrobasal complex. The third-order neurons then send the signal to the somatosensory cortex.[ citation needed ]
More recent work has expanded the role of the cutaneous mechanoreceptors for feedback in fine motor control. [12] Single action potentials from Meissner's corpuscle, Pacinian corpuscle and Ruffini ending afferents are directly linked to muscle activation, whereas Merkel cell-neurite complex activation does not trigger muscle activity. [13]