| Brodmann area 38 | |
|---|---|
 | |
 | |
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | area temporopolaris |
| NeuroLex ID | birnlex_1771 |
| FMA | 68635 |
| Anatomical terms of neuroanatomy | |
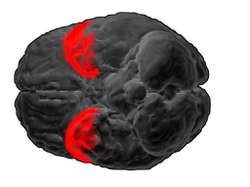
Brodmann area 38, also BA38 or temporopolar area 38 (H), is part of the temporal cortex in the human brain. BA 38 is at the anterior end of the temporal lobe, known as the temporal pole.
Contents
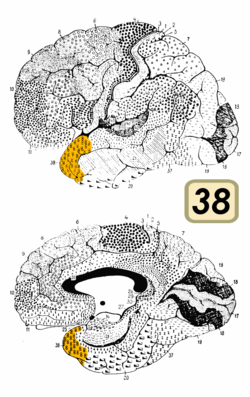
BA38 is a subdivision of the cytoarchitecturally defined temporal region of cerebral cortex. It is located primarily in the most rostral portions of the superior temporal gyrus and the middle temporal gyrus. Cytoarchitecturally it is bounded caudally by the inferior temporal area 20, the middle temporal area 21, the superior temporal area 22 and the ectorhinal area 36. [1]
The temporal pole is a paralimbic region involved in high level semantic representation and socio-emotional processing. The uncinate fasciculus provides a direct bidirectional path to the orbitofrontal cortex, allowing mnemonic representations stored in the temporal pole to bias decision making in the frontal lobe. The temporal pole appears to be a convergence zone where concepts (also known as semantic memories) that are stored in the ventral anterior temporal lobe are imbued with emotional significance and personal meaning. [2] In addition, concepts of individual people, abstracted away from the perceptual representations, are stored in a “face patch” in the temporal pole. This face patch is found in both non-human primates and humans. [3] This relates to early work showing that damage to the temporal pole can cause an amnestic prosopagnosia in which recognition of familiar faces is lost. [3]
Bilateral damage to the temporal poles, though rare, can cause dramatic changes in personality. Klüver-Bucy syndrome involves damage to the greater temporal pole as well as the amygdala. In this disorder, people and animals demonstrate fearlessness, hypersexuality, and hyperorality. [2]
This area is among the earliest affected by Alzheimer's disease, frontotemporal dementia, frontotemporal lobar degeneration, and is commonly involved at the start of temporal lobe seizures. [4]
Cytoarchitectonic and chemoarchitectonic studies find that it contains at least seven subareas, one of which, "TG", is unique to humans. [4]