A Brodmann area is a region of the cerebral cortex, in the human or other primate brain, defined by its cytoarchitecture, or histological structure and organization of cells. The concept was first introduced by the German anatomist Korbinian Brodmann in the early 20th century. Brodmann mapped the human brain based on the varied cellular structure across the cortex and identified 52 distinct regions, which he numbered 1 to 52. These regions, or Brodmann areas, correspond with diverse functions including sensation, motor control, and cognition.

Brodmann area 23 (BA23) is a region in the brain that lies inside the posterior cingulate cortex. It lies between Brodmann area 30 and Brodmann area 31 and is located on the medial wall of the cingulate gyrus between the callosal sulcus and the cingulate sulcus.

The frontal lobe is the largest of the four major lobes of the brain in mammals, and is located at the front of each cerebral hemisphere. It is parted from the parietal lobe by a groove between tissues called the central sulcus and from the temporal lobe by a deeper groove called the lateral sulcus. The most anterior rounded part of the frontal lobe is known as the frontal pole, one of the three poles of the cerebrum.

Brodmann area 44, or BA44, is part of the frontal cortex in the human brain. Situated just anterior to premotor cortex (BA6) and on the lateral surface, inferior to BA9.

Brodmann area 40 (BA40) is part of the parietal cortex in the human brain. The inferior part of BA40 is in the area of the supramarginal gyrus, which lies at the posterior end of the lateral fissure, in the inferior lateral part of the parietal lobe.

The inferior frontal gyrus is the lowest positioned gyrus of the frontal gyri, of the frontal lobe, and is part of the prefrontal cortex.

The middle frontal gyrus makes up about one-third of the frontal lobe of the human brain. (A gyrus is one of the prominent "bumps" or "ridges" on the cerebral cortex.
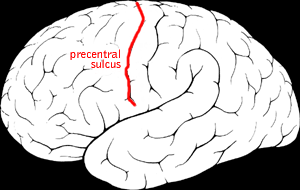
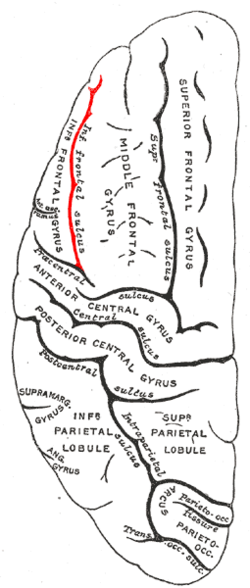
The precentral sulcus is a part of the human brain that lies parallel to, and in front of, the central sulcus. A sulcus is one of the prominent grooves on the surface of the human brain.

The precentral gyrus is a prominent gyrus on the surface of the posterior frontal lobe of the brain. It is the site of the primary motor cortex that in humans is cytoarchitecturally defined as Brodmann area 4.

In neuroanatomy, a gyrus is a ridge on the cerebral cortex. It is generally surrounded by one or more sulci. Gyri and sulci create the folded appearance of the brain in humans and other mammals.

The middle cerebral artery (MCA) is one of the three major paired cerebral arteries that supply blood to the cerebrum. The MCA arises from the internal carotid artery and continues into the lateral sulcus where it then branches and projects to many parts of the lateral cerebral cortex. It also supplies blood to the anterior temporal lobes and the insular cortices.

The lobes of the brain are the four major identifiable regions of the human cerebral cortex, and they comprise the surface of each hemisphere of the cerebrum. The two hemispheres are roughly symmetrical in structure, and are connected by the corpus callosum. Some sources include the insula and limbic lobe but the limbic lobe incorporates parts of the other lobes. The lobes are large areas that are anatomically distinguishable, and are also functionally distinct. Each lobe of the brain has numerous ridges, or gyri, and furrows, sulci that constitute further subzones of the cortex. The expression "lobes of the brain" usually refers only to those of the cerebrum, not to the distinct areas of the cerebellum.

The frontal gyri are six gyri of the frontal lobe in the brain. There are five horizontally oriented, parallel convolutions, of the frontal lobe that are aligned anterior to posterior. Three are visible on the lateral surface of the brain and two are on the inferior surface of the frontal lobe in a region called orbitofrontal cortex. The other main gyrus of the frontal lobe is the precentral gyrus which is vertically oriented, and runs parallel with the precentral sulcus.

Middle temporal gyrus is a gyrus in the brain on the temporal lobe. It is located between the superior temporal gyrus and inferior temporal gyrus. It corresponds largely to Brodmann area 21.

The olfactory tract is a bilateral bundle of afferent nerve fibers from the mitral and tufted cells of the olfactory bulb that connects to several target regions in the brain, including the piriform cortex, amygdala, and entorhinal cortex. It is a narrow white band, triangular on coronal section, the apex being directed upward.
The sensory cortex can refer sometimes to the primary somatosensory cortex, or it can be used as a term for the primary and secondary cortices of the different senses : the visual cortex on the occipital lobes, the auditory cortex on the temporal lobes, the primary olfactory cortex on the uncus of the piriform region of the temporal lobes, the gustatory cortex on the insular lobe, and the primary somatosensory cortex on the anterior parietal lobes. Just posterior to the primary somatosensory cortex lies the somatosensory association cortex or area, which integrates sensory information from the primary somatosensory cortex to construct an understanding of the object being felt. Inferior to the frontal lobes are found the olfactory bulbs, which receive sensory input from the olfactory nerves and route those signals throughout the brain. Not all olfactory information is routed to the olfactory cortex: some neural fibers are routed to the supraorbital region of the frontal lobe, while others are routed directly to limbic structures. The direct limbic connection makes the olfactory sense unique.

The superior frontal sulcus is a sulcus between the superior frontal gyrus and the middle frontal gyrus, that defines the lateral limit of the Superior frontal gyrus.

The inferior or orbital surface of the frontal lobe is concave, and rests on the orbital plate of the frontal bone. It is divided into four orbital gyri by a well-marked H-shaped orbital sulcus. These are named, from their position, the medial, anterior, lateral, and posterior, orbital gyri. The medial orbital gyrus presents a well-marked antero-posterior sulcus, the olfactory sulcus, for the olfactory tract; the portion medial to this is named the straight gyrus, and is continuous with the superior frontal gyrus on the medial surface.

The medial frontal gyrus is a continuation of the superior frontal gyrus from its most anterior border onto the medial surface of the hemisphere. The medial and superior frontal gyri are two of the frontal gyri of the frontal lobe. The portion on the lateral surface of the hemisphere is usually more or less completely subdivided into an upper and a lower part by an antero-posterior sulcus, the paramedial sulcus, which, however, is frequently interrupted by bridging gyri.

The orbital part of inferior frontal gyrus also known as the pars orbitalis is the orbital part of the inferior frontal gyrus.