The vertebrate cerebrum (brain) is formed by two cerebral hemispheres that are separated by a groove, the longitudinal fissure. The brain can thus be described as being divided into left and right cerebral hemispheres. Each of these hemispheres has an outer layer of grey matter, the cerebral cortex, that is supported by an inner layer of white matter. In eutherian (placental) mammals, the hemispheres are linked by the corpus callosum, a very large bundle of nerve fibers. Smaller commissures, including the anterior commissure, the posterior commissure and the fornix, also join the hemispheres and these are also present in other vertebrates. These commissures transfer information between the two hemispheres to coordinate localized functions.

The occipital lobe is one of the four major lobes of the cerebral cortex in the brain of mammals. The name derives from its position at the back of the head, from the Latin ob, 'behind', and caput, 'head'.

Brodmann area 19, or BA 19, is part of the occipital lobe cortex in the human brain. Along with area 18, it comprises the extrastriate cortex. In humans with normal sight, extrastriate cortex is a visual association area, with feature-extracting, shape recognition, attentional, and multimodal integrating functions.

Brodmann area 37, or BA37, is part of the temporal cortex in the human brain. It contains the fusiform gyrus which in turn contains the fusiform face area, an area important for the recognition of faces.
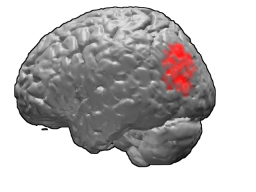
Brodmann area 39, or BA39, is part of the parietal cortex in the human brain. BA39 encompasses the angular gyrus, lying near to the junction of temporal, occipital and parietal lobes.

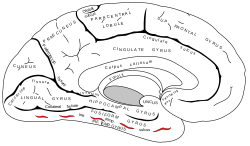
The fusiform gyrus, also known as the lateral occipitotemporal gyrus,is part of the temporal lobe and occipital lobe in Brodmann area 37. The fusiform gyrus is located between the lingual gyrus and parahippocampal gyrus above, and the inferior temporal gyrus below. Though the functionality of the fusiform gyrus is not fully understood, it has been linked with various neural pathways related to recognition. Additionally, it has been linked to various neurological phenomena such as synesthesia, dyslexia, and prosopagnosia.
Parietal is an adjective used predominantly for the parietal lobe and other relevant anatomy

The lateral ventricles are the two largest ventricles of the brain and contain cerebrospinal fluid. Each cerebral hemisphere contains a lateral ventricle, known as the left or right lateral ventricle, respectively.

In biological morphology and anatomy, a sulcus is a furrow or fissure. It may be a groove, natural division, deep furrow, elongated cleft, or tear in the surface of a limb or an organ, most notably on the surface of the brain, but also in the lungs, certain muscles, as well as in bones, and elsewhere. Many sulci are the product of a surface fold or junction, such as in the gums, where they fold around the neck of the tooth.

The middle cerebral artery (MCA) is one of the three major paired cerebral arteries that supply blood to the cerebrum. The MCA arises from the internal carotid artery and continues into the lateral sulcus where it then branches and projects to many parts of the lateral cerebral cortex. It also supplies blood to the anterior temporal lobes and the insular cortices.

The lobes of the brain are the four major identifiable regions of the human cerebral cortex, and they comprise the surface of each hemisphere of the cerebrum. The two hemispheres are roughly symmetrical in structure, and are connected by the corpus callosum. Some sources include the insula and limbic lobe but the limbic lobe incorporates parts of the other lobes. The lobes are large areas that are anatomically distinguishable, and are also functionally distinct. Each lobe of the brain has numerous ridges, or gyri, and furrows, sulci that constitute further subzones of the cortex. The expression "lobes of the brain" usually refers only to those of the cerebrum, not to the distinct areas of the cerebellum.

The posterior cerebral artery (PCA) is one of a pair of cerebral arteries that supply oxygenated blood to the occipital lobe, part of the back of the human brain. The two arteries originate from the distal end of the basilar artery, where it bifurcates into the left and right posterior cerebral arteries. These anastomose with the middle cerebral arteries and internal carotid arteries via the posterior communicating arteries.

The inferior temporal gyrus is one of three gyri of the temporal lobe and is located below the middle temporal gyrus, connected behind with the inferior occipital gyrus; it also extends around the infero-lateral border on to the inferior surface of the temporal lobe, where it is limited by the inferior sulcus. This region is one of the higher levels of the ventral stream of visual processing, associated with the representation of objects, places, faces, and colors. It may also be involved in face perception, and in the recognition of numbers and words.

In neuroanatomy, the parieto-occipital sulcus is a deep sulcus in the cerebral cortex that marks the boundary between the cuneus and precuneus, and also between the parietal and occipital lobes. Only a small part can be seen on the lateral surface of the hemisphere, its chief part being on the medial surface.

The occipitomastoid suture, or occipitotemporal suture, is the cranial suture between the occipital bone and the mastoid portion of the temporal bone.

In neuroanatomy, a sulcus is a shallow depression or groove in the cerebral cortex. One or more sulci surround a gyrus, a ridge on the surface of the cortex, creating the characteristic folded appearance of the brain in humans and most other mammals. The larger sulci are also called fissures. The cortex develops in the fetal stage of corticogenesis, preceding the cortical folding stage known as gyrification. The large fissures and main sulci are the first to develop.
The sensory cortex can refer sometimes to the primary somatosensory cortex, or it can be used as a term for the primary and secondary cortices of the different senses : the visual cortex on the occipital lobes, the auditory cortex on the temporal lobes, the primary olfactory cortex on the uncus of the piriform region of the temporal lobes, the gustatory cortex on the insular lobe, and the primary somatosensory cortex on the anterior parietal lobes. Just posterior to the primary somatosensory cortex lies the somatosensory association cortex or area, which integrates sensory information from the primary somatosensory cortex to construct an understanding of the object being felt. Inferior to the frontal lobes are found the olfactory bulbs, which receive sensory input from the olfactory nerves and route those signals throughout the brain. Not all olfactory information is routed to the olfactory cortex: some neural fibers are routed to the supraorbital region of the frontal lobe, while others are routed directly to limbic structures. The direct limbic connection makes the olfactory sense unique.

The collateral fissure is a large sulcus on the tentorial surface of the cerebral hemisphere and extends from near the occipital pole to within a short distance of the temporal pole. It is also known as the medial occipitotemporal sulcus.

In the occipital lobe, the lateral occipital sulcus, where present, divides the lateral, or middle occipital gyrus into a superior and an inferior part, which are then continuous in front with the parietal and temporal lobes. The anterior portion is often incomplete, but in some individuals it may encounter the superior temporal sulcus whilst the posterior portion originates from the middle of the curved lunate sulcus, or from a curved portion of the transverse occipital sulcus if absent.

The occipital gyri (OcG) are three gyri in parallel, along the lateral portion of the occipital lobe, also referred to as a composite structure in the brain. The gyri are the superior occipital gyrus, the middle occipital gyrus, and the inferior occipital gyrus, and these are also known as the occipital face area. The superior and inferior occipital sulci separates the three occipital gyri.