
In neuroscience and psychology, the term language center refers collectively to the areas of the brain which serve a particular function for speech processing and production. Language is a core system that gives humans the capacity to solve difficult problems and provides them with a unique type of social interaction. Language allows individuals to attribute symbols to specific concepts, and utilize them through sentences and phrases that follow proper grammatical rules. Finally, speech is the mechanism by which language is orally expressed.

The cingulate cortex is a part of the brain situated in the medial aspect of the cerebral cortex. The cingulate cortex includes the entire cingulate gyrus, which lies immediately above the corpus callosum, and the continuation of this in the cingulate sulcus. The cingulate cortex is usually considered part of the limbic lobe.

A Brodmann area is a region of the cerebral cortex, in the human or other primate brain, defined by its cytoarchitecture, or histological structure and organization of cells. The concept was first introduced by the German anatomist Korbinian Brodmann in the early 20th century. Brodmann mapped the human brain based on the varied cellular structure across the cortex and identified 52 distinct regions, which he numbered 1 to 52. These regions, or Brodmann areas, correspond with diverse functions including sensation, motor control, and cognition.

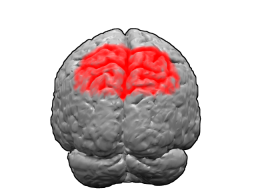
The parietal lobe is one of the four major lobes of the cerebral cortex in the brain of mammals. The parietal lobe is positioned above the temporal lobe and behind the frontal lobe and central sulcus.
Brodmann area 7 is one of Brodmann's cytologically defined regions of the brain corresponding to precuneus and superior parietal lobule (SPL). It is involved in locating objects in space. It serves as a point of convergence between vision and proprioception to determine where objects are in relation to parts of the body.
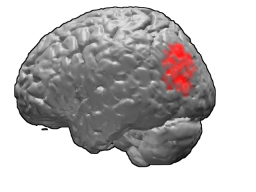
Brodmann area 39, or BA39, is part of the parietal cortex in the human brain. BA39 encompasses the angular gyrus, lying near to the junction of temporal, occipital and parietal lobes.

Brodmann area 40 (BA40) is part of the parietal cortex in the human brain. The inferior part of BA40 is in the area of the supramarginal gyrus, which lies at the posterior end of the lateral fissure, in the inferior lateral part of the parietal lobe.

In neuroanatomy, the postcentral gyrus is a prominent gyrus in the lateral parietal lobe of the human brain. It is the location of the primary somatosensory cortex, the main sensory receptive area for the sense of touch. Like other sensory areas, there is a map of sensory space in this location, called the sensory homunculus.

In neuroanatomy, the primary somatosensory cortex is located in the postcentral gyrus of the brain's parietal lobe, and is part of the somatosensory system. It was initially defined from surface stimulation studies of Wilder Penfield, and parallel surface potential studies of Bard, Woolsey, and Marshall. Although initially defined to be roughly the same as Brodmann areas 3, 1 and 2, more recent work by Kaas has suggested that for homogeny with other sensory fields only area 3 should be referred to as "primary somatosensory cortex", as it receives the bulk of the thalamocortical projections from the sensory input fields.

In neuroanatomy, the arcuate fasciculus is a bundle of axons that generally connects the Broca's area and the Wernicke's area in the brain. It is an association fiber tract connecting caudal temporal cortex and inferior frontal lobe.

The angular gyrus is a region of the brain lying mainly in the posteroinferior region of the parietal lobe, occupying the posterior part of the inferior parietal lobule. It represents the Brodmann area 39.

In neuroanatomy, a gyrus is a ridge on the cerebral cortex. It is generally surrounded by one or more sulci. Gyri and sulci create the folded appearance of the brain in humans and other mammals.

The human secondary somatosensory cortex is a region of cortex in the parietal operculum on the ceiling of the lateral sulcus.

The middle cerebral artery (MCA) is one of the three major paired cerebral arteries that supply blood to the cerebrum. The MCA arises from the internal carotid artery and continues into the lateral sulcus where it then branches and projects to many parts of the lateral cerebral cortex. It also supplies blood to the anterior temporal lobes and the insular cortices.

The lobes of the brain are the major identifiable zones of the human cerebral cortex, and they comprise the surface of each hemisphere of the cerebrum. The two hemispheres are roughly symmetrical in structure, and are connected by the corpus callosum. They traditionally have been divided into four lobes, but are today considered as having six lobes each. The lobes are large areas that are anatomically distinguishable, and are also functionally distinct to some degree. Each lobe of the brain has numerous ridges, or gyri, and furrows, the sulci that constitute further subzones of the cortex. The expression "lobes of the brain" usually refers only to those of the cerebrum, not to the distinct areas of the cerebellum.

The inferior parietal lobule lies below the horizontal portion of the intraparietal sulcus, and behind the lower part of the postcentral sulcus. Also known as Geschwind's territory after Norman Geschwind, an American neurologist, who in the early 1960s recognised its importance. It is a part of the parietal lobe.

The superior longitudinal fasciculus (SLF) is an association tract in the brain that is composed of three separate components. It is present in both hemispheres and can be found lateral to the centrum semiovale and connects the frontal, occipital, parietal, and temporal lobes. This bundle of tracts (fasciculus) passes from the frontal lobe through the operculum to the posterior end of the lateral sulcus where they either radiate to and synapse on neurons in the occipital lobe, or turn downward and forward around the putamen and then radiate to and synapse on neurons in anterior portions of the temporal lobe.

The posterior parietal cortex plays an important role in planned movements, spatial reasoning, and attention.
Extinction is a neurological disorder that impairs the ability to perceive multiple stimuli of the same type simultaneously. Extinction is usually caused by damage resulting in lesions on one side of the brain. Those who are affected by extinction have a lack of awareness in the contralesional side of space and a loss of exploratory search and other actions normally directed toward that side.

Gerstmann syndrome is a neuropsychological disorder that is characterized by a constellation of symptoms that suggests the presence of a lesion usually near the junction of the temporal and parietal lobes at or near the angular gyrus. Gerstmann syndrome is typically associated with damage to the inferior parietal lobule of the dominant hemisphere. It is classically considered a left-hemisphere disorder, although right-hemisphere damage has also been associated with components of the syndrome.


















