The cerebral cortex, also known as the cerebral mantle, is the outer layer of neural tissue of the cerebrum of the brain in humans and other mammals. It is the largest site of neural integration in the central nervous system, and plays a key role in attention, perception, awareness, thought, memory, language, and consciousness. The cerebral cortex is the part of the brain responsible for cognition.

The cingulate cortex is a part of the brain situated in the medial aspect of the cerebral cortex. The cingulate cortex includes the entire cingulate gyrus, which lies immediately above the corpus callosum, and the continuation of this in the cingulate sulcus. The cingulate cortex is usually considered part of the limbic lobe.

A Brodmann area is a region of the cerebral cortex, in the human or other primate brain, defined by its cytoarchitecture, or histological structure and organization of cells. The concept was first introduced by the German anatomist Korbinian Brodmann in the early 20th century. Brodmann mapped the human brain based on the varied cellular structure across the cortex and identified 52 distinct regions, which he numbered 1 to 52. These regions, or Brodmann areas, correspond with diverse functions including sensation, motor control, and cognition.

The parietal lobe is one of the four major lobes of the cerebral cortex in the brain of mammals. The parietal lobe is positioned above the temporal lobe and behind the frontal lobe and central sulcus.

In neuroanatomy, the precuneus is the portion of the superior parietal lobule on the medial surface of each brain hemisphere. It is located in front of the cuneus. The precuneus is bounded in front by the marginal branch of the cingulate sulcus, at the rear by the parieto-occipital sulcus, and underneath by the subparietal sulcus. It is involved with episodic memory, visuospatial processing, reflections upon self, and aspects of consciousness.
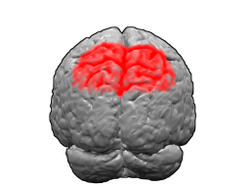
Brodmann area 6 (BA6) is part of the frontal cortex in the human brain. Situated just anterior to the primary motor cortex (BA4), it is composed of the premotor cortex and, medially, the supplementary motor area (SMA). This large area of the frontal cortex is believed to play a role in planning complex, coordinated movements.

Brodmann area 10 is the anterior-most portion of the prefrontal cortex in the human brain. BA10 was originally defined broadly in terms of its cytoarchitectonic traits as they were observed in the brains of cadavers, but because modern functional imaging cannot precisely identify these boundaries, the terms anterior prefrontal cortex, rostral prefrontal cortex and frontopolar prefrontal cortex are used to refer to the area in the most anterior part of the frontal cortex that approximately covers BA10—simply to emphasize the fact that BA10 does not include all parts of the prefrontal cortex.

Brodmann area 5 is one of Brodmann's cytoarchitectural defined regions of the brain. It is involved in somatosensory processing, movement and association, and is part of the posterior parietal cortex.

Brodmann area 19, or BA 19, is part of the occipital lobe cortex in the human brain. Along with area 18, it comprises the extrastriate cortex. In humans with normal sight, extrastriate cortex is a visual association area, with feature-extracting, shape recognition, attentional, and multimodal integrating functions.

Brodmann area 40 (BA40) is part of the parietal cortex in the human brain. The inferior part of BA40 is in the area of the supramarginal gyrus, which lies at the posterior end of the lateral fissure, in the inferior lateral part of the parietal lobe.

Brodmann area 11 is one of Brodmann's cytologically defined regions of the brain. It is in the orbitofrontal cortex which is above the eye sockets (orbitae). It is involved in decision making, processing rewards, and encoding new information into long-term memory.

In neuroanatomy, the postcentral gyrus is a prominent gyrus in the lateral parietal lobe of the human brain. It is the location of the primary somatosensory cortex, the main sensory receptive area for the sense of touch. Like other sensory areas, there is a map of sensory space in this location, called the sensory homunculus.

Brodmann area 4 refers to the primary motor cortex of the human brain. It is located in the posterior portion of the frontal lobe.

In neuroanatomy, the primary somatosensory cortex is located in the postcentral gyrus of the brain's parietal lobe, and is part of the somatosensory system. It was initially defined from surface stimulation studies of Wilder Penfield, and parallel surface potential studies of Bard, Woolsey, and Marshall. Although initially defined to be roughly the same as Brodmann areas 3, 1 and 2, more recent work by Kaas has suggested that for homogeny with other sensory fields only area 3 should be referred to as "primary somatosensory cortex", as it receives the bulk of the thalamocortical projections from the sensory input fields.

The supramarginal gyrus is a portion of the parietal lobe. This area of the brain is also known as Brodmann area 40 based on the brain map created by Korbinian Brodmann to define the structures in the cerebral cortex. It is probably involved with language perception and processing, and lesions in it may cause receptive aphasia.

The precentral gyrus is a prominent gyrus on the surface of the posterior frontal lobe of the brain. It is the site of the primary motor cortex that in humans is cytoarchitecturally defined as Brodmann area 4.

The lobes of the brain are the major identifiable zones of the human cerebral cortex, and they comprise the surface of each hemisphere of the cerebrum. The two hemispheres are roughly symmetrical in structure, and are connected by the corpus callosum. They traditionally have been divided into four lobes, but are today considered as having six lobes each. The lobes are large areas that are anatomically distinguishable, and are also functionally distinct to some degree. Each lobe of the brain has numerous ridges, or gyri, and furrows, the sulci that constitute further subzones of the cortex. The expression "lobes of the brain" usually refers only to those of the cerebrum, not to the distinct areas of the cerebellum.

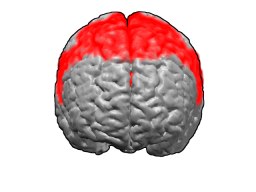
The superior parietal lobule is bounded in front by the upper part of the postcentral sulcus, but is usually connected with the postcentral gyrus above the end of the sulcus. The superior parietal lobule contains Brodmann's areas 5 and 7.

The superior longitudinal fasciculus (SLF) is an association tract in the brain that is composed of three separate components. It is present in both hemispheres and can be found lateral to the centrum semiovale and connects the frontal, occipital, parietal, and temporal lobes. This bundle of tracts (fasciculus) passes from the frontal lobe through the operculum to the posterior end of the lateral sulcus where they either radiate to and synapse on neurons in the occipital lobe, or turn downward and forward around the putamen and then radiate to and synapse on neurons in anterior portions of the temporal lobe.