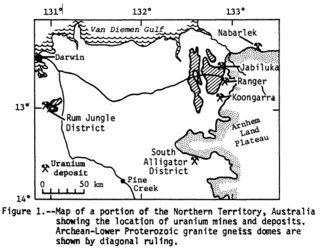
| Blackmore | |
| River | |
| Country | Australia |
|---|---|
| Territory | Northern Territory |
| Source | |
| - location | Wild Horse Plain, Australia |
| - elevation | 21 m (69 ft) |
| Mouth | |
| - location | Darwin Harbour, Australia |
| - elevation | 0 m (0 ft) |
| - coordinates | 12°38′27″S130°57′03″E / 12.64083°S 130.95083°E Coordinates: 12°38′27″S130°57′03″E / 12.64083°S 130.95083°E |
| Length | 25 km (16 mi) |
| Basin | 848 km2 (327 sq mi) |
Location of the Blackmore River mouth in the Northern Territory | |
| [1] | |
Blackmore River flows into Darwin Harbour close to Darwin in the Australian Northern Territory. [2]

Darwin Harbour is the body of water close to Darwin in the Northern Territory of Australia. It opens to the north at a line from Charles Point in the west to Lee Point in the east into the Beagle Gulf and connects via the Clarence Strait with the Van Diemen Gulf. It contains Port Darwin, which is flanked by Frances Bay to the east and Cullen Bay to the west.

Darwin is the capital city of the Northern Territory of Australia, situated on the Timor Sea. It is the largest city in the sparsely populated Northern Territory, with a population of 145,916. It is the smallest and most northerly of the Australian capital cities, and acts as the Top End's regional centre.

Australia, officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a sovereign country comprising the mainland of the Australian continent, the island of Tasmania and numerous smaller islands. It is the largest country in Oceania and the world's sixth-largest country by total area. The neighbouring countries are Papua New Guinea, Indonesia and East Timor to the north; the Solomon Islands and Vanuatu to the north-east; and New Zealand to the south-east. The population of 25 million is highly urbanised and heavily concentrated on the eastern seaboard. Australia's capital is Canberra, and its largest city is Sydney. The country's other major metropolitan areas are Melbourne, Brisbane, Perth and Adelaide.