| |
 | |
Location within Mesoamerica | |
| Location | San Ignacio, Cayo District, Belize |
|---|---|
| Region | Cayo District |
| History | |
| Founded | 1200 BCE |
| Abandoned | 900 CE |
| Periods | Classic |
| Cultures | Maya |
| Site notes | |
| Excavation dates | 1988 - 2000 |
| Archaeologists | Jaime Awe National Institute of Archaeology (NICH) |
| Architecture | |
| Architectural styles | Classic |
| Responsible body: Belize Department of Archaeology | |
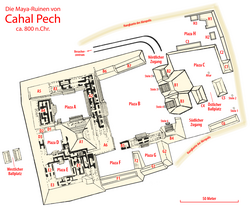
Cahal Pech is a Maya site located near the town of San Ignacio in the Cayo District of Belize. The site was a palatial, hilltop home for an elite Maya family, and though the most major construction dates to the Classic period, evidence of continuous habitation has been dated to as far back as 1200 BCE during the Early Middle Formative period (Early Middle Preclassic), making Cahal Pech one of the oldest recognizably Maya sites in Western Belize. [1] [2]