
North Canaan is a town in Litchfield County, Connecticut, United States. The population was 3,211 at the 2020 census. The town is part of the Northwest Hills Planning Region. The town center is still called "Canaan", being the main town center of the old town of Canaan prior to North Canaan splitting off as its own town.

The New York, New Haven and Hartford Railroad, commonly known as The Consolidated, or simply as the New Haven, was a railroad that operated principally in the New England region of the United States from 1872 to December 31, 1968. Founded by the merger of the New York and New Haven and Hartford and New Haven railroads, the company had near-total dominance of railroad traffic in Southern New England for the first half of the 20th century.
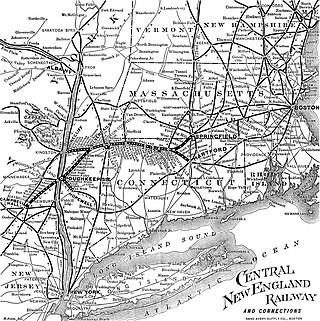
The Central New England Railway was a railroad from Hartford, Connecticut, and Springfield, Massachusetts, west across northern Connecticut and across the Hudson River on the Poughkeepsie Bridge to Maybrook, New York. It was part of the Poughkeepsie Bridge Route, an alliance between railroads for a passenger route from Washington to Boston, and was acquired by the New York, New Haven & Hartford Railroad in 1904. The New Haven ran the CNE as a separate company until finally merging it in 1927. The vast majority of the system was abandoned by the 1930s and 1940s. Surviving portions of the Central New England Railway are operated by the Central New England Railroad and the Housatonic Railroad.

The Newburgh, Dutchess and Connecticut Railroad was a railroad in Dutchess County, New York, United States. Its line ran 58.9 miles (94.8 km) northeast from the Hudson River in Fishkill to the Connecticut state line near Millerton. The Dutchess and Columbia Railroad (D&C), was chartered in 1866 to link rural villages with the Hudson River Railroad and New York and Harlem Railroad. The under-construction line was leased by the Boston, Hartford and Erie Railroad (BH&E) in 1868. The first segment opened in July 1869, and it reached Pine Plains the following February.

The Housatonic Railroad is a Class III railroad operating in southwestern New England and eastern New York. It was chartered in 1983 to operate a short section of ex-New York, New Haven and Hartford Railroad in northwestern Connecticut, and has since expanded north and south, as well as west into New York State.

The Danbury Branch is a diesel branch of the Metro-North Railroad's New Haven Line in the U.S. state of Connecticut, running from downtown Norwalk north to Danbury. It opened in 1852 as the Danbury and Norwalk Railroad. Until the early 1970s, passenger service continued north from Danbury to Canaan, Connecticut, and Pittsfield, Massachusetts. Metro-North took over operation of the line from Conrail in 1983, and the modern-day branch is mostly single-tracked.

The Danbury Railway Museum is a railway museum housed in the former Union Station on the east end of downtown Danbury, Connecticut, United States. It was established in the mid-1990s following the closure of the station by the Metro-North Railroad in favor of a new station nearby, and primarily focuses on the history of railroading in southern New England and neighboring New York. In addition to the former station building, the museum has a collection of heritage railcars in the neighboring rail yard it shares with Metro-North.

Falls Village is a village and census-designated place in the town of Canaan in Litchfield County, Connecticut, United States. As of the 2010 census it had a population of 538, out of 1,234 in the entire town of Canaan. Because Falls Village is the town center and principal constituent village in Canaan, the entire town is often referred to as "Falls Village". That usage also avoids confusion of the town with Canaan Village in the town of North Canaan, Connecticut, just to the north. Falls Village derives its name from a waterfall, known as Great Falls, on the Housatonic River within the village.

The Joseph Scelsi Intermodal Transportation Center is a transit facility located in downtown Pittsfield, Massachusetts, United States. The $11 million facility is named after Joseph Scelsi, a longtime State Representative who represented Pittsfield. Owned by the Berkshire Regional Transit Authority (BRTA), it is serviced by local BRTA bus services, Amtrak intercity rail service, and Peter Pan intercity bus service. The second floor of the building houses two classrooms used by Berkshire Community College and Massachusetts College of Liberal Arts.

West Concord station is an MBTA Commuter Rail station located in West Concord, Massachusetts. It is served by the Fitchburg Line. The station has two side platforms serving the line's two tracks, with mini-high platforms for accessibility. The adjacent station building, now a restaurant, is not used for railroad purposes.

The Shepaug, Litchfield and Northern Railroad was a short independent railroad in western Connecticut that was chartered as the Shepaug Valley Railroad in 1868 and operated from 1872 to 1891 when it was taken over by the Housatonic Railroad. In 1898, the Housatonic operation was assumed by the New York, New Haven & Hartford Railroad (NH). As the Litchfield Division of the NH, the line was operated until abandonment in 1948. Much of the line remains as a rail trail.

Lenox station is a former Housatonic Railroad train station in Lenox, Massachusetts. Built in 1902, it served as the town's railroad station, on a line of the New York, New Haven and Hartford Railroad, until 1970. Now home to the Berkshire Scenic Railway Museum, it serves as a stop on the heritage railroad service provided by the museum. It was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1989 as Lenox Railroad Station.

The Housatonic Railroad was a railroad in the U.S. states of Connecticut and Massachusetts, chartered in 1836. Opened between Bridgeport, Connecticut, and New Milford, Connecticut, in 1840, it was completed to a connection with the Western Railroad in West Stockbridge, Massachusetts, in 1842. Branches were later built to Pittsfield, Massachusetts, Danbury, Connecticut, and Derby, Connecticut, the latter as part of the Housatonic Railroad's purchase of the New Haven and Derby Railroad in 1887.
The Maybrook Line was a line of the New York, New Haven and Hartford Railroad which connected with its Waterbury Branch in Derby, Connecticut, and its Maybrook Yard in Maybrook, New York, where it interchanged with other carriers. It was the main east-west freight route of the New Haven until its merger with the Penn Central in 1969.

Newington Junction is a bus rapid transit station on the CTfastrak line opened in 2015 located off Willard Avenue (CT-173) in the Newington Junction neighborhood of Newington, Connecticut.

New Milford station is a former railroad station on Railroad Street in New Milford, Connecticut. Built in 1886 by the Housatonic Railroad Company, it cemented the town's importance as a regional tourist and business center. It served passenger service until 1971, and is now home to the Greater New Milford chamber of commerce. It was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1984.

Canaan is a village and census-designated place (CDP) within the town of North Canaan in Litchfield County, Connecticut, United States. Formerly known as Canaan Depot, the village is more commonly known as Canaan Village to distinguish it from the town of Canaan located to the south of North Canaan. The Canaan Village Historic District is listed on the National Register of Historic Places. As of the 2010 census, the CDP had a population of 1,212, out of a total population of 3,315 in the town of North Canaan.

Lee station is a former railroad station in Lee, Massachusetts. It was built in 1893 to serve passenger traffic on the Housatonic Railroad, which operated the tracks that run through the town between Pittsfield to the north and Connecticut to the south. It served as the town's main passenger station until passenger service was terminated in 1971 by the Penn Central Railroad, the NYNH&H's successor. In 1976 the building was converted to office use, and in 1981 it was rehabilitated and opened as a restaurant. It also serves excursions of the Berkshire Scenic Railway Museum. It was added to the National Register of Historic Places in 2010 as Lee Station.

Great Barrington station is a former railroad station in Great Barrington, Massachusetts along the Housatonic Railroad Berkshire Line.
The Berkshire was a New York, New Haven and Hartford Railroad named train running from New York City's Grand Central Terminal to Pittsfield, Massachusetts. It was the longest-running north–south train in Litchfield Hills of western Connecticut and the Berkshires of Massachusetts. From New York City it followed the New Haven Line to South Norwalk, the Danbury Line to Danbury and the Berkshire Division to Pittsfield. It began in the 1940s and ran until 1968. The train was preceded by the Berkshire Express, of c.1938-c.1943. It terminated at Pittsfield Union Station until 1960, when the New Haven moved it to another station in the city.



















