Related Research Articles

An actuary is a business professional with advanced statistical skills who deals with the measurement and management of risk and uncertainty. The name of the corresponding field is actuarial science. These risks can affect both sides of the balance sheet and require asset management, liability management, and valuation skills. Actuaries provide assessments of financial security systems, with a focus on their complexity, their mathematics, and their mechanisms.

Actuarial science is the discipline that applies mathematical and statistical methods to assess risk in insurance, pension, finance, investment and other industries and professions. More generally, actuaries apply rigorous mathematics to model matters of uncertainty.
The Canada Pension Plan is a contributory, earnings-related social insurance program. It forms one of the two major components of Canada's public retirement income system, the other component being Old Age Security (OAS). Other parts of Canada's retirement system are private pensions, either employer-sponsored or from tax-deferred individual savings. As of Jun 30, 2022, the CPP Investment Board manages over C$523 billion in investment assets for the Canada Pension Plan on behalf of 20 million Canadians. CPPIB is one of the world's biggest pension funds.
Unemployment benefits, also called unemployment insurance, unemployment payment, unemployment compensation, or simply unemployment, are payments made by authorized bodies to unemployed people. In the United States, benefits are funded by a compulsory governmental insurance system, not taxes on individual citizens. Depending on the jurisdiction and the status of the person, those sums may be small, covering only basic needs, or may compensate the lost time proportionally to the previous earned salary.

Life insurance is a contract between an insurance policy holder and an insurer or assurer, where the insurer promises to pay a designated beneficiary a sum of money upon the death of an insured person. Depending on the contract, other events such as terminal illness or critical illness can also trigger payment. The policyholder typically pays a premium, either regularly or as one lump sum. The benefits may include other expenses, such as funeral expenses.
The Canada Revenue Agency is the revenue service of the Canadian federal government, and most provincial and territorial governments. The CRA collects taxes, administers tax law and policy, and delivers benefit programs and tax credits. Legislation administered by the CRA includes the Income Tax Act, parts of the Excise Tax Act, and parts of laws relating to the Canada Pension Plan, employment insurance (EI), tariffs and duties. The agency also oversees the registration of charities in Canada, and enforces much of the country's tax laws.
Taxation in Canada is a prerogative shared between the federal government and the various provincial and territorial legislatures.
The Equitable Life Assurance Society, founded in 1762, is a life insurance company in the United Kingdom. The world's oldest mutual insurer, it pioneered age-based premiums based on mortality rate, laying "the framework for scientific insurance practice and development" and "the basis of modern life assurance upon which all life assurance schemes were subsequently based". After closing to new business in 2000, parts of the business were sold off and the remainder of the company became a subsidiary of Utmost Life and Pensions in January 2020.
Employment and Social Development Canada is a department of the Government of Canada responsible for social programs and the labour market at the federal level. The department delivers a number of federal government programs and services including Employment Insurance (EI), Service Canada centres, Canada Student Loan Program (CSLP), Canada Pension Plan (CPP), issuing social insurance numbers (SIN) and the federal Labour Program among others things.

The Canadian Institute of Actuaries (CIA) is the national organization of the actuarial profession in Canada. It was incorporated March 18, 1965. The FCIA designation stands for Fellow of the Canadian Institute of Actuaries. As the national organization of the Canadian actuarial profession, the CIA serves the public through the provision by the profession of actuarial services and advice by: representing the Canadian actuarial profession in the formulation of public policy; promoting the advancement of actuarial science; educating and qualifying CIA members; ensuring that actuarial services provided by its members meet accepted professional standards; and assisting actuaries in Canada in the discharge of their professional responsibilities.
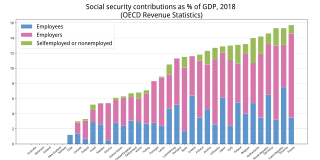
Social insurance is a form of social welfare that provides insurance against economic risks. The insurance may be provided publicly or through the subsidizing of private insurance. In contrast to other forms of social assistance, individuals' claims are partly dependent on their contributions, which can be considered insurance premiums to create a common fund out of which the individuals are then paid benefits in the future.

Claude Castonguay, was a Canadian politician, educator, and businessman.
Whole life insurance, or whole of life assurance, sometimes called "straight life" or "ordinary life", is a life insurance policy which is guaranteed to remain in force for the insured's entire lifetime, provided required premiums are paid, or to the maturity date. As a life insurance policy it represents a contract between the insured and insurer that as long as the contract terms are met, the insurer will pay the death benefit of the policy to the policy's beneficiaries when the insured dies. Because whole life policies are guaranteed to remain in force as long as the required premiums are paid, the premiums are typically much higher than those of term life insurance where the premium is fixed only for a limited term. Whole life premiums are fixed, based on the age of issue, and usually do not increase with age. The insured party normally pays premiums until death, except for limited pay policies which may be paid up in 10 years, 20 years, or at age 65. Whole life insurance belongs to the cash value category of life insurance, which also includes universal life, variable life, and endowment policies.
An export credit agency or investment insurance agency is a private or quasi-governmental institution that acts as an intermediary between national governments and exporters to issue export insurance solutions and guarantees for financing. The financing can take the form of credits or credit insurance and guarantees or both, depending on the mandate the ECA has been given by its government. ECAs can also offer credit or cover on their own account. This does not differ from normal banking activities. Some agencies are government-sponsored, others private, and others a combination of the two.
Income taxes in Canada constitute the majority of the annual revenues of the Government of Canada, and of the governments of the Provinces of Canada. In the fiscal year ending 31 March 2018, the federal government collected just over three times more revenue from personal income taxes than it did from corporate income taxes.

The Insurance Corporation of British Columbia (ICBC) is a provincial Crown corporation in British Columbia providing insurance. ICBC was created in 1973 by the NDP government of Premier Dave Barrett.
Medical underwriting is a health insurance term referring to the use of medical or health information in the evaluation of an applicant for coverage, typically for life or health insurance. As part of the underwriting process, an individual's health information may be used in making two decisions: whether to offer or deny coverage and what premium rate to set for the policy. The two most common methods of medical underwriting are known as moratorium underwriting, a relatively simple process, and full medical underwriting, a more indepth analysis of a client's health information. The use of medical underwriting may be restricted by law in certain insurance markets. If allowed, the criteria used should be objective, clearly related to the likely cost of providing coverage, practical to administer, consistent with applicable law, and designed to protect the long-term viability of the insurance system.
The Canada Pension Plan Investment Board, operating as CPP Investments, is a Canadian Crown corporation established by way of the 1997 Canada Pension Plan Investment Board Act to oversee and invest the funds contributed to and held by the Canada Pension Plan (CPP).
Public auto insurance is a government-owned and -operated system of compulsory automobile insurance used in the Canadian provinces of British Columbia, Saskatchewan, Manitoba, and Quebec. It is based on the idea that if motorists are compelled to purchase auto insurance by the government, the government ought to ensure motorists pay fair premiums and receive high-quality coverage. Governments across the country have used various insurance schemes from full tort to full no-fault in pursuit of that goal.
Unemployment insurance in France was first established in 1958. Benefits and contributions are set by the independent body called UNEDIC which is controlled equally by Trade Unions and Employer associations. Unemployment benefits are paid only to those persons who fulfill certain requirements.
References
- ↑ "Canada Employment Insurance Financing Board - l'Office de financement de l'assurance-emploi du Canada". Archived from the original on 2011-01-21. Retrieved 2011-03-05.
- ↑ "Canada Employment Insurance Financing Board - l'Office de financement de l'assurance-emploi du Canada". Archived from the original on 2011-01-21. Retrieved 2011-03-05.
- ↑ Institutions, Office of the Superintendent of Financial (2022-08-30). "2023 Actuarial Report on the Employment Insurance Premium Rate". www.osfi-bsif.gc.ca. Retrieved 2023-05-04.
- ↑ "Canada Employment Insurance Financing Board - l'Office de financement de l'assurance-emploi du Canada". Archived from the original on 2011-01-21. Retrieved 2011-03-05.
- ↑ "Archived copy" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 2013-10-17. Retrieved 2013-10-17.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link) - ↑ "The government quietly deep-sixes an EI embarrassment | iPolitics". Archived from the original on 2013-10-17. Retrieved 2013-10-17.
- ↑ Weston, Greg (January 19, 2012). "EI financing agency spends millions doing nothing". CBC News . Archived from the original on 2012-01-26.