Related Research Articles
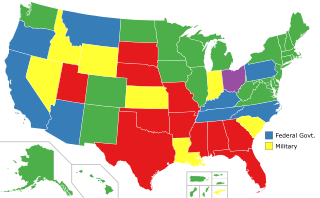
In the United States, capital punishment is a legal penalty in 27 states, throughout the country at the federal level, and in American Samoa. It is also a legal penalty for some military offenses. Capital punishment has been abolished in the other 23 states and in the federal capital, Washington, D.C. It is usually applied for only the most serious crimes, such as aggravated murder. Although it is a legal penalty in 27 states, 20 of them have authority to execute death sentences, with the other 7, as well as the federal government and military, subject to moratoriums.
The U.S. state of Washington enforced capital punishment until the state's capital punishment statute was declared null and void and abolished in practice by a state Supreme Court ruling on October 11, 2018. The court ruled that it was unconstitutional as applied due to racial bias; however, it did not render the wider institution of capital punishment unconstitutional and rather required the statute to be amended to eliminate racial biases. From 1904 to 2010, 78 people were executed by the state; the last was Cal Coburn Brown on September 10, 2010. In April 2023, Governor Jay Inslee signed SB5087 which formally abolished capital punishment in Washington State and removed provisions for capital punishment from state law.

Capital punishment was abolished via the legislative process on May 2, 2013, in the U.S. state of Maryland.
Capital punishment is a legal penalty in the U.S. state of Nebraska. In 2015, the state legislature voted to repeal the death penalty, overriding governor Pete Ricketts' veto. However, a petition drive secured enough signatures to suspend the repeal until a public vote. In the November 2016 general election, voters rejected the repeal measure, preserving capital punishment in the state. Nebraska currently has 11 inmates on death row.
Capital punishment is one of two possible penalties for aggravated murder in the U.S. state of Oregon, with it being required by the Constitution of Oregon.
An execution chamber, or death chamber, is a room or chamber in which capital punishment is carried out. Execution chambers are almost always inside the walls of a maximum-security prison, although not always at the same prison where the death row population is housed. Inside the chamber is the device used to carry out the death sentence.
Capital punishment was abolished in 2019 in New Hampshire for persons convicted of capital murder. It remains a legal penalty for crimes committed prior to May 30, 2019.
Capital punishment in Connecticut formerly existed as an available sanction for a criminal defendant upon conviction for the commission of a capital offense. Since the 1976 United States Supreme Court decision in Gregg v. Georgia until Connecticut repealed capital punishment in 2012, Connecticut had only executed one person, Michael Bruce Ross in 2005. Initially, the 2012 law allowed executions to proceed for those still on death row and convicted under the previous law, but on August 13, 2015, the Connecticut Supreme Court ruled that applying capital punishment only for past cases was unconstitutional.
Capital punishment is a legal penalty in the U.S. state of South Dakota.
Capital punishment was abolished in Colorado in 2020. It was legal from 1974 until 2020 prior to it being abolished in all future cases.
Ann Bilansky was an American housewife convicted in 1859 of poisoning her husband with arsenic. She is the only woman in Minnesota to receive the death penalty and the first white person in the state to be executed by hanging.

William Williams was a Cornish miner and the last person executed by the state of Minnesota in the United States. Williams was convicted for the 1905 murders of 16-year old John Keller and his mother, Mary Keller in Saint Paul, and his subsequent botched execution led to increased support for the abolition of capital punishment in Minnesota in 1911.

Capital punishment was outlawed in the State of New York after the New York Court of Appeals declared that the statute as written was not valid under the state's constitution in 2004. However certain crimes occurring in the state that fall under the jurisdiction of the federal government are subject to the federal death penalty.
Capital punishment in New Jersey is currently abolished, after Governor of New Jersey Jon Corzine signed a law repealing it in 2007. Before this, capital punishment was used and at least 361 people have been executed.
Hanging has been practiced legally in the United States of America from before the nation's birth, up to 1972 when the United States Supreme Court found capital punishment to be in violation of the Eighth Amendment to the United States Constitution. Four years later, the Supreme Court overturned its previous ruling, and in 1976, capital punishment was again legalized in the United States. Currently, only New Hampshire has a law specifying hanging as an available secondary method of execution, now only applicable to one person, who was sentenced to capital punishment by the state prior to its repeal in 2019.
Capital punishment is currently a legal penalty in the U.S. state of Kansas, although it has not been used since 1965.
Capital punishment in Delaware was formally abolished in 2024, however it has not been enforced after Delaware’s capital punishment statues were declared unconstitutional by the Delaware Supreme Court on August 2, 2016. The ruling retroactively applies to earlier death sentences, and remaining Delaware death row inmates had their sentences commuted to life imprisonment. The capital statute for first-degree murder under Title 11, Chapter 42, Section 09, of the Delaware Code was fully repealed on September 26, 2024.
Capital punishment has been repealed in the U.S. state of Illinois since 2011.
Capital punishment is a legal punishment in Tennessee.
References
- 1 2 "Capital Punishment in Minnesota". Minnesota State Law Library. Retrieved July 26, 2021.
- ↑ "Index by State - MINNESOTA". deathpenaltyusa.org. Retrieved March 5, 2024.
- ↑ Woltman, Nick (February 12, 2016). "This bungled St. Paul hanging caused Minnesota to abolish the death penalty". Twin Cities. Archived from the original on February 13, 2016. Retrieved July 26, 2021.
- ↑ "Minnesota - Death Penalty Information Center". Deathpenaltyinfo.org. Retrieved November 15, 2018.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 "Minnesota: History of the Death Penalty". Death Penalty Information Center . Archived from the original on January 8, 2025. Retrieved January 8, 2025.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Bessler, John D. (1996). "The "Midnight Assassination Law" and Minnesota's Anti-Death Penalty Movement, 1849–1911". William Mitchell Law Review. 22 (2): 577–730.
- 1 2 3 "Governor Walz makes historic apology for 1862 mass hanging in Mankato". ICT News. Indian Country Today. January 7, 2020. Archived from the original on January 8, 2025. Retrieved January 8, 2025.
- 1 2 "The Trials & Hanging". The US-Dakota War of 1862. Archived from the original on January 9, 2025. Retrieved January 9, 2025.
- ↑ Elder, Robert K. (December 14, 2010). "Execution 150 Years Ago Spurs Calls for Pardon". The New York Times . ISSN 0362-4331. Archived from the original on January 8, 2025. Retrieved January 8, 2025.
- ↑ Brown, Curt (April 2, 2015). "Minnesota History: Caught in the middle of the Dakota War". Star Tribune. Minneapolis. Retrieved May 7, 2016.
- ↑ "How Fair Were the Dakota Conflict Trials?". Famous Trials. Archived from the original on January 9, 2025. Retrieved January 9, 2025.
- 1 2 3 4 Cartwright, R. L. (January 30, 2023). "Execution of William Williams". MNopedia. Archived from the original on January 8, 2025. Retrieved January 8, 2025.
- ↑ Woltman, Nick (February 12, 2016). "This bungled St. Paul hanging caused Minnesota to abolish the death penalty" . Retrieved October 16, 2018.
- ↑ "This bungled St. Paul hanging caused Minnesota to abolish the death penalty". Twin Cities Pioneer Press. February 12, 2016. Archived from the original on January 9, 2025. Retrieved January 9, 2025.
- 1 2 Bessler, John (March 2004). "The Botched Hanging of William Williams: How Too Much Rope and Minnesota's Newspapers Brought an End to the Death Penalty in Minnesota". University of Baltimore School of Law Journal– via ScholarWorks.
- ↑ "NEW VOICES: Former Supporter Will Oppose Any Measure to Restore Minnesota Death Penalty". Death Penalty Information Center . April 21, 2011. Archived from the original on January 9, 2025. Retrieved January 8, 2025.