Related Research Articles
Furman v. Georgia, 408 U.S. 238 (1972), was a landmark criminal case in which the United States Supreme Court invalidated all then existing legal constructions for the death penalty in the United States. It was a 5–4 decision, with each member of the majority writing a separate opinion. Following Furman, in order to reinstate the death penalty, states had to at least remove arbitrary and discriminatory effects in order to satisfy the Eighth Amendment to the U.S. Constitution.
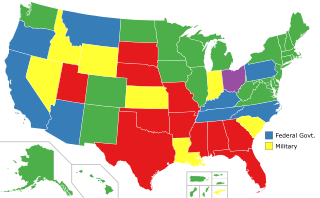
In the United States, capital punishment is a legal penalty throughout the country at the federal level, in 27 states, and in American Samoa. It is also a legal penalty for some military offenses. Capital punishment has been abolished in 23 states and in the federal capital, Washington, D.C. It is usually applied for only the most serious crimes, such as aggravated murder. Although it is a legal penalty in 27 states, 19 of them have authority to execute death sentences, with the other 8, as well as the federal government and military, subject to moratoriums.

In the U.S. state of California, capital punishment is not allowed to be carried out as of March 2019, because executions were halted by an official moratorium ordered by Governor Gavin Newsom. Before the moratorium, executions had been frozen by a federal court order since 2006, and the litigation resulting in the court order has been on hold since the promulgation of the moratorium. Thus, there will be a court-ordered moratorium on executions after the termination of Newsom's moratorium if capital punishment remains a legal penalty in California by then.
A hung jury, also called a deadlocked jury, is a judicial jury that cannot agree upon a verdict after extended deliberation and is unable to reach the required unanimity or supermajority. A hung jury may result in the case being tried again.
Gregg v. Georgia, Proffitt v. Florida, Jurek v. Texas, Woodson v. North Carolina, and Roberts v. Louisiana, 428 U.S. 153 (1976), is a landmark decision of the U.S. Supreme Court. It reaffirmed the Court's acceptance of the use of the death penalty in the United States, upholding, in particular, the death sentence imposed on Troy Leon Gregg. The set of cases is referred to by a leading scholar as the July 2 Cases, and elsewhere referred to by the lead case Gregg. The court set forth the two main features that capital sentencing procedures must employ in order to comply with the Eighth Amendment ban on "cruel and unusual punishments". The decision essentially ended the de facto moratorium on the death penalty imposed by the Court in its 1972 decision in Furman v. Georgia (1972). Justice Brennan's dissent famously argued that "The calculated killing of a human being by the State involves, by its very nature, a denial of the executed person's humanity ... An executed person has indeed 'lost the right to have rights.'"

Capital punishment in India is a legal penalty for some crimes under the country's main substantive penal legislation, the Indian Penal Code, as well as other laws. Executions are carried out by hanging as the primary method of execution per Section 354(5) of the Criminal Code of Procedure, 1973 is "Hanging by the neck until dead", and is imposed only in the 'rarest of cases'.
The People of the State of California v. Robert Page Anderson, 493 P.2d 880, 6 Cal. 3d 628, was a landmark case in the state of California that outlawed capital punishment for nine months until the enactment of a constitutional amendment reinstating it, Proposition 17.
People v. LaValle, 3 N.Y.3d 88 (2004), was a landmark decision by the New York Court of Appeals, the highest court in the U.S. state of New York, in which the court ruled that the state's death penalty statute was unconstitutional because of the statute's direction on how the jury was to be instructed in case of deadlock. New York has since then abandoned the death penalty, as the law has not been amended.
Morgan v. Illinois, 504 U.S. 719 (1992), is a case decided by the United States Supreme Court. The case established the right of defendants to challenge for cause any juror that would automatically impose the death penalty in all capital cases.
Witherspoon v. Illinois, 391 U.S. 510 (1968), was a U.S. Supreme Court case where the court ruled that a state statute providing the state unlimited challenge for cause of jurors who might have any objection to the death penalty gave too much bias in favor of the prosecution.

William Henry Hance was an American serial killer and soldier who is believed to have murdered four women and molested three in and around military bases before his arrest in 1978. He was convicted of murdering three of them, and not brought to trial on the fourth. He was executed by the state of Georgia in the electric chair.

Capital punishment is a legal penalty in the U.S. state of Florida.
Spaziano v. Florida was two United States Supreme Court cases dealing with the imposition of the death penalty. In the first case, 454 U.S. 1037 (1981), the Supreme Court, with two dissents, refused Spaziano's petition for certiorari. However, the Florida Supreme Court would reverse Spaziano's death sentence based on the judge's receipt of a confidential report which was not received by either party. On remand, the judge reimposed the death penalty and the Florida Supreme Court upheld the sentence. In the second case, 468 U.S. 447 (1984), the Court heard Spaziano's appeal of his death sentence.
Loss of rights due to criminal conviction refers to the practice in some countries of reducing the rights of individuals who have been convicted of a criminal offence. The restrictions are in addition to other penalties such as incarceration or fines. In addition to restrictions imposed directly upon conviction, there can also be collateral civil consequences resulting from a criminal conviction, but which are not imposed directly by the courts as a result of the conviction.
A citizen's right to a trial by jury is a central feature of the United States Constitution. It is considered a fundamental principle of the American legal system.
Wainwright vs. Witt, 469 U.S. 412 (1985), was a U.S. Supreme Court case concerning a criminal defendant, Johnny Paul Witt, who argued that his Sixth and Fourteenth Amendment rights were violated when he was sentenced to death for first degree murder by the state of Florida. He argued that the trial court had unconstitutionally hand-picked a jury during the voir dire process. This was because certain people were excused from the jury because they admitted pre-trial, that their decision of guilty or not guilty toward capital punishment would be swayed due to personal or religious beliefs.

The United States Constitution contains several provisions regarding the law of criminal procedure.
The United States Constitution contains several provisions related to criminal sentencing.
Capital punishment is a legal punishment in American Samoa, an unincorporated territory of the United States. The only crime punishable by death is first degree murder. American Samoa last executed a prisoner by hanging on 24 November 1939. The territory is de facto abolitionist.
Hurst v. Florida, 577 U.S. 92 (2016), was a United States Supreme Court case in which the Court, in an 8–1 ruling, applied the rule of Ring v. Arizona to the Florida capital sentencing scheme, holding that the Sixth Amendment requires a jury to find the aggravating factors necessary for imposing the death penalty. In Florida, under a 2013 statute, the jury made recommendations but the judge decided the facts.
References
- ↑ Witherspoon v. Illinois, 391 U.S. 510 (1968)
- ↑ Lockhart v. McCree, 476 U.S. 162 (1986)
- ↑ Dieter, Richard C. (2007-06-09). "A Crisis of Confidence: Americans' Doubts About the Death Penalty" (PDF). Death Penalty Information Center . Archived (PDF) from the original on 2021-11-29. Retrieved 2009-03-15.
- ↑ Salgado, Richard (2005). "Tribunals Organized To Convict: Searching for a Lesser Evil in the Capital Juror Death-Qualification Process in United States v. Green". Brigham Young University Law Review. Archived from the original on 2015-09-24. Retrieved 2006-08-12.
- ↑ Samuel Gross (1996), The Risks of Death: Why Erroneous Convictions Are Common in Capital Cases, 44 Buffalo L. Rev. 469, 494.