Related Research Articles

Christ Church is an Episcopal church located at 118 North Washington Street, with an entrance at 141 North Columbus Street, in Alexandria, Virginia. Constructed as the main church in the Church of England's Fairfax Parish, the building was designed by Col. James Wren, a descendant of Sir Christopher Wren.

Saint Paul's Episcopal Church is a historic church in Norfolk, Virginia, United States. The Nave of the current church was built in 1739 and is the sole colonial-era building which survived the various wars that Norfolk has witnessed. The church has played host to several different denominations throughout its history. Originally a Church of England parish, the building was home to a Baptist parish in the early-19th century and was finally converted back into an Episcopal church.

Grace Episcopal Church is a historic Episcopal church located at 5607 Gordonsville Road in Keswick, Albemarle County, Virginia, United States. The Gothic Revival building was designed by architect William Strickland in 1847. It is the only known work of Strickland in Virginia. The interior was rebuilt after a fire in 1895.

Thomas Methodist Episcopal Chapel, also known as Thomas Chapel and Thomas Chapel United Methodist Church, is a historic Methodist Episcopal church located at Thaxton, Bedford County, Virginia. It was built in 1844, and is a small, rectangular-plan, one-story, one-room, brick structure in a vernacular Greek Revival style. It measures 30 feet wide and 40 feet long, and has a three-bay facade and a pedimented front gable roof.

Christ Episcopal Church, also known as Christ Church; Big Stone Gap, is a historic Episcopal church located at 100 Clinton Avenue in Big Stone Gap, Wise County, Virginia. It was built in 1892, and is a cruciform frame church. It is covered with weatherboard and the hipped roof has asphalt shingles. The interior features Gothic style details. Christ Church was organized as a congregation in October 1890 and is one of the oldest in this area.

St. John's Church is a historic Episcopal church located near Sweet Hall, King William County, Virginia, United States. It was constructed in 1734 and is a one-story, T-shaped brick building. It measures 50 feet, 3 inches, by 20 feet, 2 inches, with a 24 feet wide, 28 feet, 9 inch, wing. St. John's is the only surviving colonial church in King William County to remain in the Episcopal charge. This church is also important in that it is associated with Carter Braxton, Signer of the Declaration of Independence, who regularly attended worship there.

Wickliffe Church is a historic Episcopal church building located in Berryville, Clarke County, Virginia. The church has not been in active use since 1918, except for an annual homecoming service held in August and occasional special events.

Old Chapel is a historic Episcopal church building located near Millwood, Clarke County, Virginia. Old Chapel is now the oldest Episcopal church building still in use west of the Blue Ridge Mountains. It was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1973. In 2014, the Chapel Rural Historic District was recognized, and which encompasses both Cunningham parish churches, discussed below, as well as approximately 700 other structures and an area of nearly 10,500 acres.

St. Thomas Chapel, also known as St. Thomas Episcopal Church or St. Thomas Protestant Episcopal Chapel, is a historic building located at 7854 Church Street in Middletown, Frederick County, Virginia, United States. Built in the 1830s, regular services were held at the Episcopal church for almost 100 years. The building has been restored twice, once after being heavily damaged during the Civil War, and again in the 1960s. The church was added to the Virginia Landmarks Register (VLR) and the National Register of Historic Places (NRHP) in 1973.

Hickory Neck Church is a historic Episcopal church located just outside Toano, James City County, Virginia. The original section was built between 1733 and 1738, with an extension made to the main body of the church in 1773–1774. It was altered about 1825. It is a one-story, three bay deep, rectangular brick structure, measuring 36 feet, 6 inches, long by 28 feet, 6 inches, wide.
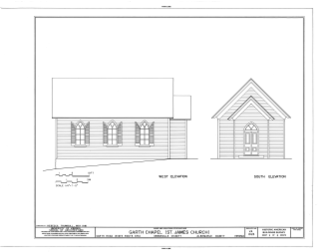
St. James Church is a historic church located northwest of Charlottesville near Owensville, Albemarle County, Virginia, United States on VA 614 east of VA 676. The vernacular Gothic Revival chapel was constructed in 1896 with the help of the Garth Family and the sponsorship of Christ Episcopal Church in Charlottesville. The church served a congregation of between 25–30 people at its construction. Regular worship services were held up until the 1940s, after which only graveside funeral services were held. Beginning in 1974 and continuing to the present day, christenings, weddings, and funerals were held in the church. Although there is no active congregation, St. James Church continues to be a consecrated Episcopal Church.

Christ Church is a historic Episcopal church located at Saluda, Middlesex County, Virginia. The present building was constructed in the 1720s, and is a one-story, rectangular brick building with a gable roof. It measures 60 feet by 33 feet, 6 inches.

Lower Church is a historic Methodist church, formerly an Episcopal church, located near Hartfield, Middlesex County, Virginia. It was constructed in 1717, and is a one-story, rectangular brick building with a clipped gable roof. It measures 56 by 34 feet.

Blacksburg Historic District is a national historic district located at Blacksburg, Montgomery County, Virginia. The district encompasses 137 contributing buildings and 2 contributing sites in the central business district and surrounding residential areas of the town of Blacksburg. The district includes commercial, residential, and institutional buildings in a variety of popular architectural styles including Greek Revival, Gothic Revival, and Colonial Revival. Notable buildings include the Johnson House, Blacksburg Presbyterian Church #1 (1847), Smith-Montgomery House, Croy House, Spout Spring House, Deyerle's Store (1875-1877), W. B. Conway Building, Presbyterian manse (1907), Sheriff Camper House, Christ Episcopal Church, African Methodist Episcopal Church of Blacksburg, Blacksburg Presbyterian Church (1904), Blacksburg Methodist Church (1910), St. Mary's Catholic Church, Hunter's Lodge Masonic Building (1928), Martin-Logan Store, Lyric Theater (1922), and Ellett's Drug Store (1900).

St. Thomas Church is a historic Episcopal church located at Orange, Virginia, United States. It is a rectangular brick structure measuring 40 feet wide and 105 feet deep. The front facade features a recessed portico with two Doric columns flanked by two Doric pilasters. Atop the gable roof is a three-stage tower topped by an octagonal cupola. The original church building was built in 1833–1834, and measured approximately 40 feet wide and 65 feet deep. It was built by William B. Philips, a master mason employed by Thomas Jefferson during the construction of the University of Virginia. It was enlarged and improved in 1853, and enlarged again in 1912. In 1928, the rear addition was raised to a full two stories and a parish hall constructed. The original church is believed to have been based on the plans by Thomas Jefferson for Christ Church in Charlottesville, Virginia. That church was demolished in 1895.

Farnham Church is a historic Episcopal church located at Farnham, Richmond County, Virginia. It was built in 1737, and is a one-story, cruciform shaped brick Colonial era church building. It measures 63 feet, 8 inches, feet by 58 feet, 2 inches, and is topped by a gable roof. Two years into the War of 1812, bullet holes were left in the walls during a conflict between the Virginia militia and the British fleet, led by Admiral George Cockburn. This event was called the Skirmish at Farnham Church. During the Civil War the church was used by Union soldiers as a stable. The church was last renovated in 1921 in the Georgian Revival style.

Christ and St. Luke's Church is a historic Episcopal church located at Norfolk, Virginia. It was built in 1909–1910, and is a long, narrow building of rough-faced random ashlar in the English Perpendicular Gothic Revival style. It features a tall, four-stage corner tower crowned with battlements and pinnacles.

St. John's AME Church is a historic congregation of the African Methodist Episcopal Church in Norfolk, Virginia, United States. Founded in 1840, it was the first African American Episcopal Church in Virginia. It moved to its present location on East Bute Street in what is now Downtown Norfolk in 1848.

St. Peter's Episcopal Church, now known as The New Saint James Holiness Church of Christ Disciples, is a historic Episcopal church in Norfolk, Virginia, United States. It is a frame, gable-roofed building with two contiguous sections: 1) the sanctuary built in 1886; 2) and the fellowship hall built in 1912. The church building is in the Gothic Revival style. The building features a small gable-roofed arched entrance door and large and small arched stained-glass windows. St. Peter's is one of six mission churches that descended from St. Paul's. St. Peter's Episcopal Church operated at this location until 1959, when it was transferred to the African-American trustees of Garretts Independent Community Church. In 1967, St. Peter's was transferred to the trustees of what come to be known as Saint James Holiness Church of Christ Disciples.

Trinity Episcopal Church is a historic Episcopal church located in Portsmouth, Virginia. It was built between 1828 and 1830, and is a stuccoed brick building. It has an attached bell tower. Also on the property is the contributing parish house, built in 1887. During the American Civil War, the church was used as a hospital.
References
- 1 2 "National Register Information System". National Register of Historic Places . National Park Service. July 9, 2010.
- ↑ "Virginia Landmarks Register". Virginia Department of Historic Resources. Archived from the original on September 21, 2013. Retrieved March 19, 2013.
- ↑ Virginia Historic Landmarks Commission Staff (March 1971). "National Register of Historic Places Inventory/Nomination: Christ Church" (PDF). Virginia Department of Historic Resources.

