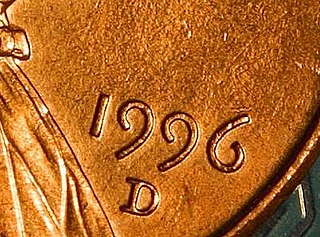The ten Arabic numerals 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, and 9 are the most commonly used symbols for writing numbers. The term often also implies a positional notation using the numerals, as well as the use of a decimal base, in particular when contrasted with other systems such as Roman numerals. However, the symbols are also used to write numbers in other bases such as octal, as well as for writing non-numerical information such as trademarks or license plate identifiers.
Chinese numerals are words and characters used to denote numbers in written Chinese.

Roman numerals are a numeral system that originated in ancient Rome and remained the usual way of writing numbers throughout Europe well into the Late Middle Ages. Numbers are written with combinations of letters from the Latin alphabet, each letter with a fixed integer value. Modern style uses only these seven:
0 (zero) is a number representing an empty quantity. Adding 0 to any number leaves that number unchanged. In mathematical terminology, 0 is the additive identity of the integers, rational numbers, real numbers, and complex numbers, as well as other algebraic structures. Multiplying any number by 0 has the result 0, and consequently, division by zero has no meaning in arithmetic.
Greek numerals, also known as Ionic, Ionian, Milesian, or Alexandrian numerals, are a system of writing numbers using the letters of the Greek alphabet. In modern Greece, they are still used for ordinal numbers and in contexts similar to those in which Roman numerals are still used in the Western world. For ordinary cardinal numbers, however, modern Greece uses Arabic numerals.
CV, Cv, or cv may refer to:

Volga Bulgaria or Volga–Kama Bulgaria was a historical Bulgar state that existed between the 9th and 13th centuries around the confluence of the Volga and Kama River, in what is now European Russia. Volga Bulgaria was a multi-ethnic state with large numbers of Bulgars, Finno-Ugrians, Varangians and East Slavs. Its strategic position allowed it to create a local trade monopoly with Norse, Cumans, and Pannonian Avars.

Chuvashia, officially the Chuvash Republic — Chuvashia, is a republic of Russia located in Eastern Europe. It is the homeland of the Chuvash people, a Turkic ethnic group. Its capital is the city of Cheboksary. As of the 2010 Census, its population was 1,251,619.

Cheboksary is the capital city of Chuvashia, Russia, and a port on the Volga River.

The Chuvash people, plural: чӑвашсем, çăvaşsem; Russian: чува́ши ) are a Turkic ethnic group, a branch of the Ogurs, native to an area stretching from the Idel-Ural (Volga-Ural) region to Siberia.
Bulgar is an extinct Oghuric Turkic language spoken by the Bulgars.
Chuvash is a Turkic language spoken in European Russia, primarily in the Chuvash Republic and adjacent areas. It is the only surviving member of the Oghur branch of Turkic languages, one of the two principal branches of the Turkic family.

U is a letter of the Cyrillic script. It commonly represents the close back rounded vowel, somewhat like the pronunciation of ⟨oo⟩ in "boot" or "rule". The forms of the Cyrillic letter U are similar to the lowercase of the Latin letter Y, with the lowercase Cyrillic letter U's form being identical to that of small Latin letter Y.
Text figures are numerals designed with varying heights in a fashion that resembles a typical line of running text, hence the name. They are contrasted with lining figures, which are the same height as upper-case letters. Georgia is an example of a popular typeface that employs text figures by default.
The Onoghurs, Onoğurs, or Oğurs were Turkic nomadic equestrians who flourished in the Pontic–Caspian steppe and the Volga region between 5th and 7th century, and spoke the Oghuric language.
In linguistics, ordinal numerals or ordinal number words are words representing position or rank in a sequential order; the order may be of size, importance, chronology, and so on. They differ from cardinal numerals, which represent quantity and other types of numerals.

Counting in prehistory was first assisted by using body parts, primarily the fingers. This is reflected in the etymology of certain number names, such as in the names of ten and hundred in the Proto-Indo-European numerals, both containing the root *dḱ also seen in the word for "finger".

The Chuvash Wikipedia is the Chuvash language edition of Wikipedia. It was founded on November 22, 2004. Its 50,000th article was created in October 2022.

Vattisen Yaly is a contemporary revival of the ethnic religion of the Chuvash people, a Turkic ethnicity of Bulgar ancestry mostly settled in the republic of Chuvashia and surrounding federal subjects of Russia.

Tally marks, also called hash marks, are a form of numeral used for counting. They can be thought of as a unary numeral system.