Related Research Articles

The European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts (ECMWF) is an independent intergovernmental organisation supported by most of the nations of Europe. It is based at three sites: Shinfield Park, Reading, United Kingdom; Bologna, Italy; and Bonn, Germany. It operates one of the largest supercomputer complexes in Europe and the world's largest archive of numerical weather prediction data.

The Rapid Update Cycle (RUC) was an American atmospheric prediction system that consisted primarily of a numerical forecast model and an analysis system to initialize the model. The first operational implementation was created in 1994, with 60km resolution and a 3-hour cycle.

The Weather Prediction Center (WPC), located in College Park, Maryland, is one of nine service centers under the umbrella of the National Centers for Environmental Prediction (NCEP), a part of the National Weather Service (NWS), which in turn is part of the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) of the U.S. Government. Until March 5, 2013 the Weather Prediction Center was known as the Hydrometeorological Prediction Center (HPC). The Weather Prediction Center serves as a center for quantitative precipitation forecasting, medium range forecasting, and the interpretation of numerical weather prediction computer models.
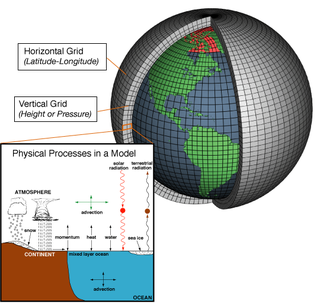
Numerical weather prediction (NWP) uses mathematical models of the atmosphere and oceans to predict the weather based on current weather conditions. Though first attempted in the 1920s, it was not until the advent of computer simulation in the 1950s that numerical weather predictions produced realistic results. A number of global and regional forecast models are run in different countries worldwide, using current weather observations relayed from radiosondes, weather satellites and other observing systems as inputs.

The Environmental Modeling Center (EMC) is a United States Government agency, which improves numerical weather, marine and climate predictions at the National Centers for Environmental Prediction (NCEP), through a broad program of research in data assimilation and modeling. In support of the NCEP operational forecasting mission, the EMC develops, improves and monitors data assimilation systems and models of the atmosphere, ocean and coupled system, using advanced methods developed internally as well as cooperatively with scientists from universities, NOAA laboratories and other government agencies, and the international scientific community.

Ensemble forecasting is a method used in or within numerical weather prediction. Instead of making a single forecast of the most likely weather, a set of forecasts is produced. This set of forecasts aims to give an indication of the range of possible future states of the atmosphere. Ensemble forecasting is a form of Monte Carlo analysis. The multiple simulations are conducted to account for the two usual sources of uncertainty in forecast models: (1) the errors introduced by the use of imperfect initial conditions, amplified by the chaotic nature of the evolution equations of the atmosphere, which is often referred to as sensitive dependence on initial conditions; and (2) errors introduced because of imperfections in the model formulation, such as the approximate mathematical methods to solve the equations. Ideally, the verified future atmospheric state should fall within the predicted ensemble spread, and the amount of spread should be related to the uncertainty (error) of the forecast. In general, this approach can be used to make probabilistic forecasts of any dynamical system, and not just for weather prediction.

The Global Forecast System (GFS) is a global numerical weather prediction system containing a global computer model and variational analysis run by the United States' National Weather Service (NWS).

A tropical cyclone forecast model is a computer program that uses meteorological data to forecast aspects of the future state of tropical cyclones. There are three types of models: statistical, dynamical, or combined statistical-dynamic. Dynamical models utilize powerful supercomputers with sophisticated mathematical modeling software and meteorological data to calculate future weather conditions. Statistical models forecast the evolution of a tropical cyclone in a simpler manner, by extrapolating from historical datasets, and thus can be run quickly on platforms such as personal computers. Statistical-dynamical models use aspects of both types of forecasting. Four primary types of forecasts exist for tropical cyclones: track, intensity, storm surge, and rainfall. Dynamical models were not developed until the 1970s and the 1980s, with earlier efforts focused on the storm surge problem.

In atmospheric science, an atmospheric model is a mathematical model constructed around the full set of primitive, dynamical equations which govern atmospheric motions. It can supplement these equations with parameterizations for turbulent diffusion, radiation, moist processes, heat exchange, soil, vegetation, surface water, the kinematic effects of terrain, and convection. Most atmospheric models are numerical, i.e. they discretize equations of motion. They can predict microscale phenomena such as tornadoes and boundary layer eddies, sub-microscale turbulent flow over buildings, as well as synoptic and global flows. The horizontal domain of a model is either global, covering the entire Earth, or regional (limited-area), covering only part of the Earth. The different types of models run are thermotropic, barotropic, hydrostatic, and nonhydrostatic. Some of the model types make assumptions about the atmosphere which lengthens the time steps used and increases computational speed.

The Weather Research and Forecasting (WRF) Model is a numerical weather prediction (NWP) system designed to serve both atmospheric research and operational forecasting needs. NWP refers to the simulation and prediction of the atmosphere with a computer model, and WRF is a set of software for this. WRF features two dynamical (computational) cores, a data assimilation system, and a software architecture allowing for parallel computation and system extensibility. The model serves a wide range of meteorological applications across scales ranging from meters to thousands of kilometers.
The Global Environmental Multiscale Model (GEM), often known as the CMC model in North America, is an integrated forecasting and data assimilation system developed in the Recherche en Prévision Numérique (RPN), Meteorological Research Branch (MRB), and the Canadian Meteorological Centre (CMC). Along with the NWS's Global Forecast System (GFS), which runs out to 16 days, the ECMWF's Integrated Forecast System (IFS), which runs out 10 days, the Naval Research Laboratory Navy Global Environmental Model (NAVGEM), which runs out eight days, the UK Met Office's Unified Model, which runs out to seven days, and Deutscher Wetterdienst's ICON, which runs out to 7.5 days, it is one of the global medium-range models in general use.
The NCEP/NCAR Reanalysis is an atmospheric reanalysis produced by the National Centers for Environmental Prediction (NCEP) and the National Center for Atmospheric Research (NCAR). It is a continually updated globally gridded data set that represents the state of the Earth's atmosphere, incorporating observations and numerical weather prediction (NWP) model output from 1948 to present.
The Unified Model is a numerical weather prediction and climate modeling software suite originally developed by the United Kingdom Met Office, and now both used and further developed by many weather-forecasting agencies around the world. The Unified Model gets its name because a single model is used across a range of both timescales and spatial scales. The models are grid-point based, rather than wave based, and are run on a variety of supercomputers around the world. The Unified Model atmosphere can be coupled to a number of ocean models. At the Met Office it is used for the main suite of Global Model, North Atlantic and Europe model (NAE) and a high-resolution UK model (UKV), in addition to a variety of Crisis Area Models and other models that can be run on demand. Similar Unified Model suites with global and regional domains are used by many other national or military weather agencies around the world for operational forecasting.
The Integrated Forecasting System (IFS) is a global numerical weather prediction system jointly developed and maintained by the European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts (ECMWF) based in Reading, England, and Météo-France based in Toulouse. The version of the IFS run at ECMWF is often referred to as the "ECMWF" or the "European model" in North America, to distinguish it from the American Global Forecast System.
An atmospheric reanalysis is a meteorological and climate data assimilation project which aims to assimilate historical atmospheric observational data spanning an extended period, using a single consistent assimilation scheme throughout.

The history of numerical weather prediction considers how current weather conditions as input into mathematical models of the atmosphere and oceans to predict the weather and future sea state has changed over the years. Though first attempted manually in the 1920s, it was not until the advent of the computer and computer simulation that computation time was reduced to less than the forecast period itself. ENIAC was used to create the first forecasts via computer in 1950, and over the years more powerful computers have been used to increase the size of initial datasets as well as include more complicated versions of the equations of motion. The development of global forecasting models led to the first climate models. The development of limited area (regional) models facilitated advances in forecasting the tracks of tropical cyclone as well as air quality in the 1970s and 1980s.
The NOAA National Operational Model Archive and Distribution System (NOMADS) is a Web-services based project providing both real-time and retrospective format independent access to climate and weather model data.
The Flow-following, finite-volume Icosahedral Model (FIM) is an experimental numerical weather prediction model that was developed at the Earth System Research Laboratory in the United States from 2008 to 2016.
The THORPEX Interactive Grand Global Ensemble (TIGGE) is an implementation of ensemble forecasting for global weather forecasting and is part of THORPEX, an international research programme established in 2003 by the World Meteorological Organization to accelerate improvements in the utility and accuracy of weather forecasts up to two weeks ahead.
The North American Ensemble Forecast System (NAEFS) is a joint project involving the Meteorological Service of Canada (MSC) in Canada, the National Weather Service (NWS) in the United States, and the National Meteorological Service of Mexico (NMSM) in Mexico providing numerical weather prediction ensemble guidance for the 1- to 16-day forecast period. The NAEFS combines the Canadian MSC and the US NWS global ensemble prediction systems, improving probabilistic operational guidance over what can be built from any individual country's ensemble. Model guidance from the NAEFS is incorporated into the forecasts of the respective national agencies.
References
- ↑ Climate Forecast System Introduction
- ↑ Saha, Suranjana; et al. (2014). "The NCEP Climate Forecast System Version 2". J. Climate. 27 (6): 2185–208. Bibcode:2014JCli...27.2185S. doi:10.1175/JCLI-D-12-00823.1. hdl: 2027.42/113112 .