
Clivia is a genus of monocot flowering plants native to southern Africa. They are from the family Amaryllidaceae, subfamily Amaryllidoideae. Common names are Natal lily or bush lily.

Pancratium is a genus of African and Eurasian perennial, herbaceous and bulbous plants in the Amaryllis family, subfamily Amaryllidoideae

Eucrosia is a genus of herbaceous, perennial and bulbous plants in the Amaryllis family distributed from Ecuador to Peru. The name is derived from the Greek eu, beautiful, and krossos, a fringe, referring to the long stamens. As circumscribed in 2020, the genus contains six species. Phaedranassa and Rauhia are the genera most closely related to Eucrosia.

Pamianthe is a genus of South American bulbous perennials in the Amaryllis family, subfamily Amaryllidoideae. They can be found in sandy, but rocky areas in Colombia, Ecuador, Peru, and Bolivia.

Strumaria is a genus of African plants in Amaryllis family, subfamily Amaryllidoideae. The genus is known in nature only from South Africa, Lesotho and Namibia. Almost all species flower in the autumn and are cultivated as ornamental bulbous plants.

Scadoxus is a genus of African and Arabian plants in the Amaryllis family, subfamily Amaryllidoideae. The English names blood lily or blood flower are used for some of the species. The genus has close affinities with Haemanthus. Species of Scadoxus are grown as ornamental plants for their brilliantly coloured flowers, either in containers or in the ground in frost-free climates. Although some species have been used in traditional medicine, they contain poisonous alkaloids.

Proiphys is a genus of herbaceous, perennial and bulbous plants in the family Amaryllidaceae, subfamily Amaryllidoideae. It includes 5 accepted species that are native to Southeast Asia, Papuasia, and Australia.

Boophone is a small genus of herbaceous, perennial and bulbous plants in the Amaryllis family It consists of two confirmed species distributed across South Africa to Kenya and Uganda. It is closely related to Crossyne, a genus whose species have prostrate leaves. They are drought tolerant but not cold-hardy, and are very poisonous to livestock.
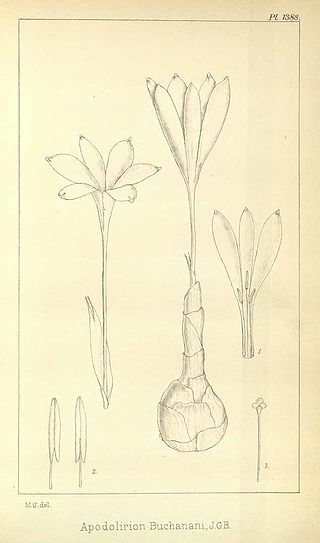
Apodolirion is a genus of herbaceous, perennial and bulbous plants in the Amaryllis family. It consists of 6 species distributed in South Africa. The name Apodolirion comes from the Greek and means "stemless flower" and describes the almost sessile flowers of these species.

The Griffineae is a tribe in the family Amaryllidaceae, subfamily Amaryllidoideae. It includes 3 genera with 22 species endemic to Brazil in South America. A typical character of the representatives of the tribe are the flowers - They are blue or lilac and collected into an umbel. Only the members of this tribe and the genus Lycoris are able to form flowers with such color in the whole subfamily Amaryllidoideae of Amaryllidaceae. The species in this group are typically perennial and produce bulbs. The leaves are green, with elliptical form in most of the cases but in some members, as in Worsleya, they are sword-shaped.

The Amaryllidaceae are a family of herbaceous, mainly perennial and bulbous flowering plants in the monocot order Asparagales. The family takes its name from the genus Amaryllis and is commonly known as the amaryllis family. The leaves are usually linear, and the flowers are usually bisexual and symmetrical, arranged in umbels on the stem. The petals and sepals are undifferentiated as tepals, which may be fused at the base into a floral tube. Some also display a corona. Allyl sulfide compounds produce the characteristic odour of the onion subfamily (Allioideae).

Amaryllidoideae is a subfamily of monocot flowering plants in the family Amaryllidaceae, order Asparagales. The most recent APG classification, APG III, takes a broad view of the Amaryllidaceae, which then has three subfamilies, one of which is Amaryllidoideae, and the others are Allioideae and Agapanthoideae. The subfamily consists of about seventy genera, with over eight hundred species, and a worldwide distribution.

Nerine masoniorum is a species of flowering plant in the family Amaryllidaceae, subfamily Amaryllidoideae, native to the eastern Cape Province of South Africa. It is a bulbous perennial belonging to the group of nerines that have narrow evergreen foliage. The thread-like leaves reach a length of 25 cm or more. The flowering stem is 15–25 cm tall, with up to 11 flowers arranged in an umbel. Each flower has six narrow pink tepals with wavy edges. It flowers in late summer in cultivation, the first of the nerines to do so. It has received the Royal Horticultural Society's Award of Garden Merit.

Pancratieae are a small European tribe of subfamily Amaryllidoideae, consisting of two genera including the type genus, Pancratium.

Hippeastrum mirum is a species of herbaceous perennial bulbous flowering plants in the amaryllis family, Amaryllidaceae, subfamily Amaryllidoideae. It was formerly treated as Tocantinia mira, the only species in the monotypic genus Tocantinia.

Eustephieae is a flowering plant tribe in the family Amaryllidaceae, subfamily Amaryllidoideae. It forms part of the Andean clade, one of two clades in The Americas.

Eucharideae is a tribe of plants within the family Amaryllidaceae. It was augmented in 2000 by Meerow et al. following a molecular phylogenetic study that revealed that many elements of the tribe Stenomesseae segregated with it, rather than separately, and were subsequently submerged in it. Further revisions were made in 2020, when three genera were merged. It forms one of the tribes of the Andean subclade of the American clade of the subfamily.

Clinantheae is a tribe, where it forms part of the Andean clade, one of two American clades. The tribe was described in 2000 by Alan Meerow et al. as a result of a molecular phylogenetic study of the American Amaryllidoideae. This demonstrated that the tribe Stenomesseae, including the type genus Stenomesson was polyphyletic. Part of the tribe segregated with the Eucharideae and were submerged into it, while the other part formed a unique subclade. Since the type species of Stenomesson was not part of the second subclade, it was necessary to form a new name for the remaining species together with the other genera that remained. This was Clinanthus, the oldest name for these species, and consequently the tribe Clinantheae.

Hymenocallideae is a tribe, where it forms part of the Andean clade, one of two American clades. The tribe was originally recognised by both Meerow (1995) and the Muller-Doblies' (1996). Its phylogenetic position within the Amaryllidoideae was established by Meerow et al. in 2000, while in-depth infratribal relationships were established in 2002.

Cyrtanthus obliquus, the Knysna lily, is a species of flowering plant in the amaryllis family. It has spiralling leaves and large pendulous flowers. It is native to coastal grasslands from KwaZulu-Natal to the Eastern Cape, South Africa.


















