
The Hume Highway, inclusive of the sections now known as the Hume Freeway and Hume Motorway, is one of Australia's major inter-city national highways, running for 840 kilometres (520 mi) between Melbourne in the southwest and Sydney in the northeast. Upgrading of the route from Sydney's outskirts to Melbourne's outskirts to dual carriageway was completed on 7 August 2013.

The A38, part of which is also known as the Devon Expressway, is a major A-class trunk road in England.

The Pacific Highway is a 790-kilometre-long (490 mi) national highway and major transport route along the central east coast of Australia, with the majority of it being part of Australia's national route 1.

The Sturt Highway is an Australian national highway in New South Wales, Victoria, and South Australia. The Sturt Highway is an important road link for the transport of passengers and freight between Sydney and Adelaide and the regions situated adjacent to the route.

The Midland Highway is one of Tasmania's major inter-city highways, running for 176 kilometres (109 mi) between Hobart and Launceston. It is part of the AusLink National Network and is a vital link for road freight to transport goods to and from the two cities. It represents a major north–south transportation corridor in Tasmania and has the route 1 designation as part of the National Highway. The highway consists of various traffic lane arrangements, the most common being two lanes – one in each direction, with overtaking options and at-grade intersections. At both the Launceston and Hobart sections of the highway there are small portions of grade-separated dual carriageway.

Albany Highway links Western Australia's capital city Perth with its oldest settlement, Albany, on the state's south coast. The 405-kilometre-long (252 mi) highway travels through the southern Wheatbelt and Great Southern regions, and is designated State Route 30 for most of its length. Outside of Perth the highway is predominately a sealed, single carriageway with regular overtaking lanes in some undulating areas. Albany Highway commences at The Causeway, a river crossing that connects to Perth's central business district. The highway heads south-east through Perth's metropolitan region, bypassed in part by Shepparton Road and Kenwick Link, and continues south-eastwards through to Albany. It intersects several major roads in Perth, including the Leach, Tonkin, Brookton, and South Western highways. The rural section of Albany Highway connects to important regional roads at the few towns and roadhouses along the route, including Coalfields Highway at Arthur River, Great Southern Highway at Cranbrook, and Muirs Highway at Mount Barker.
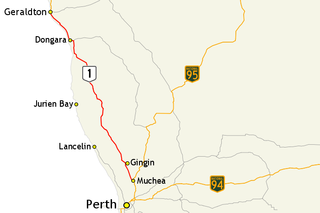
Brand Highway is a 370-kilometre (230 mi) main highway linking the northern outskirts of Perth, the capital of Western Australia, to the port city of Geraldton in Western Australia's Mid West region. Together with North West Coastal Highway, it forms part of the Western Australian coastal link to the Northern Territory. The highway is a part of Australia's Highway 1, and is for the most part a single carriageway with one lane in each direction.

North West Coastal Highway is a generally north-south Western Australian highway which links the coastal city of Geraldton with the town of Port Hedland. The 1,300-kilometre-long (808 mi) road, constructed as a sealed two-lane single carriageway, travels through remote and largely arid landscapes. Carnarvon is the only large settlement on the highway, and is an oasis within the harsh surrounding environment. The entire highway is allocated National Route 1, part of Australia's Highway 1, and parts of the highway are included in tourist routes Batavia Coast Tourist Way and Cossack Tourist Way. Economically, North West Coastal Highway is an important link to the Mid West, Gascoyne and Pilbara regions, supporting the agricultural, pastoral, fishing, and tourism industries, as well as mining and offshore oil and gas production.

Great Eastern Highway is a 590-kilometre-long (370 mi) road that links the Western Australian capital of Perth with the city of Kalgoorlie. A key route for road vehicles accessing the eastern Wheatbelt and the Goldfields, it is the western portion of the main road link between Perth and the eastern states of Australia. The highway forms the majority of National Highway 94, although the alignment through the Perth suburbs of Guildford and Midland, and the eastern section between Coolgardie and Kalgoorlie are not included. Various segments form parts of other road routes, including National Route 1, Alternative National Route 94, and State Route 51.
The Kwinana Freeway is a 72-kilometre (45 mi) freeway in and beyond the southern suburbs of Perth, Western Australia, linking central Perth with Mandurah to the south. It is the central section of State Route 2, which continues north as Mitchell Freeway to Clarkson, and south as Forrest Highway towards Bunbury. A 4-kilometre (2.5 mi) section between Canning and Leach highways is also part of National Route 1. Along its route are interchanges with several major roads, including Roe Highway and Mandjoogoordap Drive. The northern terminus of the Kwinana Freeway is at the Narrows Bridge, which crosses the Swan River, and the southern terminus is at Pinjarra Road, east of Mandurah.
Mitchell Freeway is a 30-kilometre-long (19 mi) freeway in the northern suburbs of Perth, Western Australia, linking central Perth with the satellite city of Joondalup. It is the northern section of State Route 2, which continues south as Kwinana Freeway and Forrest Highway. Along its length are interchanges with several major roads, including Graham Farmer Freeway and Reid Highway. The southern terminus of the Mitchell Freeway is at the Narrows Bridge, which crosses the Swan River, and the northern terminus is at Hester Avenue, Clarkson, a suburb within the City of Wanneroo.
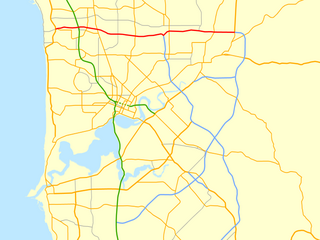
Reid Highway is a 23 kilometre east-west highway and partial freeway in the northern suburbs of Perth, Western Australia, linking North Beach with Middle Swan. As part of State Route 3, it forms half of Perth's outer ring road along with Roe Highway, which it joins onto at its eastern terminus.

Tonkin Highway is a 51-kilometre-long (32 mi) north-south highway and partial freeway in Perth, Western Australia, linking Perth Airport and Kewdale with the city's north-eastern and south-eastern suburbs. The northern terminus is at Gnangara Road in Cullacabardee, and the southern terminus is at Thomas Road in Oakford. It forms the entire length of State Route 4, and connects to several major roads, including Reid Highway, Great Eastern Highway, Leach Highway, Roe Highway, and Albany Highway.

Canning Highway is a 17 kilometre arterial road in Perth, Western Australia, linking the inner Perth suburb of Victoria Park in the north-east, to the port city of Fremantle in the south-west.

Marmion Avenue is a 40 kilometre arterial road in the northern coastal suburbs of Perth, Western Australia, linking Trigg in the south with Yanchep in the north. It forms part of State Route 71 along with West Coast Highway, which it joins onto at its southern terminus.

State Highway 1 is the longest and most significant road in the New Zealand road network, running the length of both main islands. It appears on road maps as SH 1 and on road signs as a white number 1 on a red shield, but it has the official designations SH 1N in the North Island, SH 1S in the South Island.
Geraldton–Mount Magnet Road is a 335-kilometre-long (208 mi) major regional road in the Mid West region of Western Australia, starting in Utakarra in Geraldton's eastern suburbs, and terminating 333 kilometres (207 mi) east-northeast at Great Northern Highway near the mining town of Mount Magnet. The road is signed as State Route 123, is a two-lane single carriageway for its entire length, and is a major traffic route which is regularly used by heavy vehicles and mine/grain road trains.
Main Roads Western Australia controls the major roads in the state's Pilbara region. There are two main highways in the region: Great Northern Highway, which travels north through the region to Port Hedland and then north-west along the coast, as well as North West Coastal Highway, which heads south-west from Port Hedland. A series of main roads connects towns to the highways, and local roads provide additional links. The majority of these roads service the western half of the region, with few located in the various deserts east of the Oakover River. Roads are often named after the towns or areas they connect.
Main Roads Western Australia controls the major roads in the state's Kimberley region. Great Northern Highway is the major road connection through the region, with sealed roads spurring off it to connect to population centres, and unsealed roads offering an alternative route between Derby and Wyndham.



















