Related Research Articles
The electoral system of Australia comprises the laws and processes used for the election of members of the Australian Parliament and is governed primarily by the Commonwealth Electoral Act 1918. The system presently has a number of distinctive features including compulsory enrolment; compulsory voting; majority-preferential instant-runoff voting in single-member seats to elect the lower house, the House of Representatives; and the use of the single transferable vote proportional representation system to elect the upper house, the Senate.

The Legislative Council, or upper house, is one of the two chambers of the Parliament of South Australia. Its central purpose is to act as a house of review for legislation passed through the lower house, the House of Assembly. It sits in Parliament House in the state capital, Adelaide.

The House of Assembly, or lower house; Is one of the two chambers of the Parliament of South Australia. The other is the Legislative Council. It sits in Parliament House in the state capital, Adelaide.

The Parliament of South Australia is the bicameral legislature of the Australian state of South Australia. It consists of the 47-seat House of Assembly and the 22-seat Legislative Council. General elections are held every 4 years, with all of the lower house and half of the upper house filled at each election. It follows a Westminster system of parliamentary government with the executive branch required to both sit in parliament and hold the confidence of the House of Assembly. The parliament is based at Parliament House on North Terrace in the state capital of Adelaide.
The Division of Angas was an Australian Electoral Division in South Australia. The division was created in 1903 and abolished in 1934. It was named for George Fife Angas, a South Australian pioneer politician, banker and pastoralist who played a significant part in the formation and establishment of the Province of South Australia.
Since 1970, the South Australian House of Assembly — the lower house of the Parliament of South Australia — has consisted of 47 single-member electoral districts consisting of approximately the same number of enrolled voters. The district boundaries are regulated by the State Electoral Office, according to the requirements of the South Australian Constitution and are subject to mandatory redistributions by the South Australian Electoral Districts Boundaries Commission in order to respond to changing demographics.

Michael Raphael O'Halloran was an Australian politician, representing the South Australian Branch of the Australian Labor Party. He served as Leader of the Opposition in the Parliament of South Australia and also in the Australian Senate.

Adelaide is a single-member electoral district for the South Australian House of Assembly. The 22.8 km² state seat of Adelaide currently consists of the Adelaide city centre including North Adelaide and suburbs to the inner north and inner north east: Collinswood, Fitzroy, Gilberton, Medindie, Medindie Gardens, Ovingham, Thorngate, Walkerville, most of Prospect, and part of Nailsworth. The federal division of Adelaide covers the state seat of Adelaide and additional suburbs in each direction.
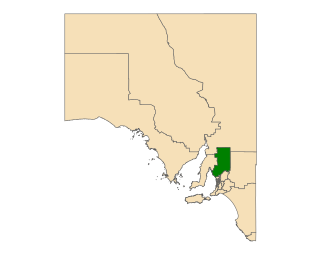
Frome is a single-member electoral district for the South Australian House of Assembly. It is named after Edward Charles Frome, the third surveyor-general of South Australia. The electorate stretches north-eastwards from the Gawler River and Gulf St Vincent in the south, and includes many of the agricultural areas of the Clare and Gilbert Valleys. It covers a total of 12,921 km2 (4,989 sq mi) and takes in the towns of Auburn, Clare, Mintaro, Port Broughton, Saddleworth, Snowtown and Riverton. Prior to the 2020 redistribution, its main population centre was Port Pirie, since transferred to Stuart.

Light is a single-member electoral district for the South Australian House of Assembly. Light is named after Colonel William Light, who was the first Surveyor-General of South Australia. The electorate was created in 1857, abolished at the 1902 election and recreated at the 1938 election. It is based on the semi-rural township of Gawler, and stretches southwards into the outermost northern suburbs of Adelaide.

Chaffey, created in 1936, is a single-member electoral district for the South Australian House of Assembly. It covers the Riverland region of South Australia including the towns of Renmark, Berri, Barmera, Loxton and Waikerie. The seat is named after brothers George and William Chaffey who established the irrigation area along the Murray River from 1886.

Collie-Preston is a Legislative Assembly electorate in the state of Western Australia. While the seat was known as Collie for just over a century of its existence as an electorate, the seat was known as South West Mining from 1901 to 1904, and Collie-Wellington from 2005 to 2008. It is named for the South West coal mining town of Collie. While historically a very safe seat for the Labor Party, redistributions in 1988 and 2007 due to increases in the quota for country seats which had historically been malapportioned resulted in the seat incorporating surrounding rural shires which were hostile to Labor and thereby becoming more marginal.

Tom Cleave Stott CBE spent 37 years as an independent member of the South Australian House of Assembly, from 1933 to 1970. He served as Speaker of the House from 1962 to 1965 for the Tom Playford LCL government and 1968 to 1970 for the Steele Hall LCL government, both times in exchange for his confidence and supply vote to form minority governments.
The Playmander was a pro-rural electoral malapportionment in the Australian state of South Australia, which was introduced by the incumbent Liberal and Country League (LCL) government in 1936, and remained in place for 32 years until 1968.

State elections were held in South Australia on 30 May 1970. All 47 seats in the South Australian House of Assembly were up for election. The incumbent Liberal and Country League led by Premier of South Australia Steele Hall was defeated by the Australian Labor Party led by Leader of the Opposition Don Dunstan.

The 1968South AustralianState election was held in South Australia on 2 March 1968. All 39 seats in the South Australian House of Assembly were up for election; 38 of the 39 contests were won by candidates from Australia's two major political parties. The incumbent Labor Party South Australia led by Premier of South Australia Don Dunstan and the Liberal and Country League led by Leader of the Opposition Steele Hall) both won 19 seats. The sole independent candidate to win a race, Tom Stott of the Ridley electorate, joined with the LCL's 19 seats to form a coalition government that held a 20 to 19 majority, thus defeating the Dunstan Labor government.

State elections were held in South Australia on 6 March 1965. All 39 seats in the South Australian House of Assembly were up for election. The incumbent Liberal and Country League led by Premier of South Australia Thomas Playford IV, in power since 1938, was defeated by the Australian Labor Party led by Leader of the Opposition Frank Walsh.

The principles of the current Constitution of South Australia, also known as the South Australian Constitution, which includes the rules and procedures for the government of the State of South Australia, are set out in the Constitution Act 1934. Its long title is "An Act to provide for the Constitution of the State; and for other purposes".

The South Australian Liberal Party, officially known as the Liberal Party of Australia (South Australian Division), and often shortened to SA Liberals, is the South Australian Division of the Liberal Party of Australia. It was formed as the Liberal and Country League (LCL) in 1932 and became the South Australian Division of the Liberal Party when the Liberal Party was formed in 1945. It retained its Liberal and Country League name before changing to its current name in 1974. It is one of two major parties in the bicameral Parliament of South Australia, the other being the Australian Labor Party (SA Branch). The party is led by Vincent Tarzia since 12 August 2024.

The 2022 South Australian state election was held on 19 March 2022 to elect members to the 55th Parliament of South Australia. All 47 seats in the House of Assembly, and half the seats in the Legislative Council were up for re-election.
References
- ↑ See Third Schedule, page 227 "ELECTORAL DISTRICT OF MURRAY" in An Act to amend the Constitution Act, 1934–1953 (SA).
- ↑ See section 11, pages 709-710 "ELECTORAL DISTRICT OF MURRAY" in An Act to amend the Constitution Act, 1934–1965 (SA).
- ↑ List of members is not directly navigable. Enter "Murray" in electorate drop-down menu to display list of members for the electorate. Former Members of the Parliament of South Australia – Parliament of South Australia.