
An automatic transmission, also called auto, self-shifting transmission, n-speed automatic, or AT, is a type of motor vehicle transmission that automatically changes the gear ratio as the vehicle moves, meaning that the driver does not have to shift the gears manually. Like other transmission systems on vehicles, it allows an internal combustion engine, best suited to run at a relatively high rotational speed, to provide a range of speed and torque outputs necessary for vehicular travel. The number of forward gear ratios is often expressed for manual transmissions as well.

A transmission is a machine in a power transmission system, which provides controlled application of the power. Often the term 5 speed transmission refers simply to the gearbox that uses gears and gear trains to provide speed and torque conversions from a rotating power source to another device.

A manual transmission, also known as a manual gearbox, a standard transmission, stick shift, or simply stick, or gearbox, is a type of transmission used in motor vehicle applications. It uses a driver-operated clutch, usually engaged and disengaged by a foot pedal or hand lever, for regulating torque transfer from the engine to the transmission; and a gear selector that can be operated by hands.
A semi-automatic transmission is an automobile transmission that combines manual transmission and automatic transmission. It's a partially automatic transmission.

The fifth generation of the BMW 5 Series consists of the BMW E60 and BMW E61 executive cars. The E60/E61 generation was produced from 2003 to 2010 and is often collectively referred to as the E60.
Magna PT, known until 2018 as GETRAG, is the world's largest supplier of transmission systems for passenger cars and commercial vehicles. The company was founded on 1 May 1935, in Ludwigsburg, Germany, by Hermann Hagenmeyer; as the Getriebe und Zahnradfabrik Hermann Hagenmeyer GmbH & Cie KG.

The BMW M5 is a high performance variant of the BMW 5 Series marketed under the BMW M sub-brand. It is considered an iconic vehicle in the sports sedan category. The majority of M5s have been produced in the sedan (saloon) body style, but in some countries the M5 was also available as a wagon (estate) from 1992 to 1995 and from 2006 to 2010.
Manumatic, a portmanteau of the words manual and automatic, is a term referring to a class of automotive transmission.

[[Image:Cambio a doppia frizione.svg|thumb|right|Schematic diagram of a dual-clutch gearbox:{{unbulleted list | M: Motor | A: Primary drive and driving shaft | B: Dual clutch | C: Driven shaft | D: Layshaft, hollow, even gears | E: Layshaft, odd gears | F: Output } ]]

A preselector gearbox is a type of manual transmission mostly used on passenger cars and racing cars in the 1930s, in buses from 1940-1960 and in armoured vehicles from the 1930s to the 1970s. The defining characteristic of a preselector gearbox is that the gear shift lever allowed the driver to "pre-select" the next gear, usually with the transmission remaining in the current gear until the driver pressed the "gear change pedal" at the desired time.
Shift time refers to the time interval between gear changes in a transmission. This interval is the time in which power delivery is interrupted and engine speed is reduced or increased to synchronize speed for the next selected gear. Shift time is usually in reference to motor vehicles but can apply to any gearbox. Reducing shift time is important in performance vehicles or race cars because the shifting process generally interrupts power delivery to the wheels. Shift time in a manual gearbox is dependent on the driver, but in automatic or automated manual cars the electronic or hydraulic control mechanism must be calibrated and tuned to deliver a fast gear change.
Easytronic is the Opel tradename for a type of transaxle-based automated manual transmission or gearbox, as used in some Opel/Vauxhall cars.

A sequential manual transmission is a type of manual transmission used mostly for motorcycles and racing cars. It produces faster shift times than traditional synchronized manual transmissions and restricts the driver to selecting either the next or previous gear.

Selespeed is the name of an automated manual transmission used in Alfa Romeo cars, developed by Italian company Magneti Marelli and made by Graziano Trasmissioni.
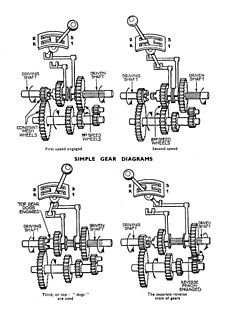
A non-synchronous transmission— also called a crash gearbox— is a form of manual transmission based on gears that do not use synchronizing mechanisms. They require the driver to manually synchronise the transmission's input speed and output speed.

The Can-Am Spyder ("Spyder") is a three-wheeled motorcycle manufactured by Can-Am motorcycles, itself a division of Bombardier Recreational Products. The vehicle has a single rear drive wheel and two wheels in front for steering, similar in layout to a modern snowmobile. The Spyder uses an ATV-like chassis. The manufacturer refers to it as a "roadster," but in technical terms, it is more of what has been traditionally called a trike.

A dual-clutch transmission (DCT) is a type of transmission that uses two separate clutches for odd and even gear sets. The design is often similar to two separate manual transmissions with their respective clutches contained within one housing, and working as one unit. In car and truck applications, the DCT functions as an automatic transmission, requiring no driver input to change gears.
Dana Graziano is an Italian company based in Turin manufacturing gearboxes, drivelines and their mechatronics components. It makes the "Pre-Cog" seven-speed Seamless-Shift gearbox (SSG) dual-clutch transmission used in the McLaren 12C.

Shift by wire is the system by which the transmission modes are engaged/changed in an automobile through electronic controls without any mechanical linkage between the gear shifting lever and the transmission. The transmission shifting was traditionally accomplished by mechanical links to put the vehicle in Park, Reverse, Neutral and Drive positions through a lever mounted on the steering column or a gear shifter near the center console.
Automatic Manual Transmission (AMT) is a type of automated manual transmission. Offered by Renault Group's Dacia under the "Easy-R" name, it is founded on electro-mechanical rather than hydraulic technology. The Easy-R automated transmission uses a traditional manual gearbox with an electronically controlled clutch; the gear shifts are automatic, and the need for a clutch pedal is eliminated.





















