In telecommunications, asynchronous communication is transmission of data, generally without the use of an external clock signal, where data can be transmitted intermittently rather than in a steady stream. Any timing required to recover data from the communication symbols is encoded within the symbols.
In telecommunications, RS-232, Recommended Standard 232 refers to a standard originally introduced in 1960 for serial communication transmission of data. It formally defines signals connecting between a DTE such as a computer terminal, and a DCE, such as a modem. The standard defines the electrical characteristics and timing of signals, the meaning of signals, and the physical size and pinout of connectors. The current version of the standard is TIA-232-F Interface Between Data Terminal Equipment and Data Circuit-Terminating Equipment Employing Serial Binary Data Interchange, issued in 1997. The RS-232 standard had been commonly used in computer serial ports.

Synchronous optical networking (SONET) and synchronous digital hierarchy (SDH) are standardized protocols that transfer multiple digital bit streams synchronously over optical fiber using lasers or highly coherent light from light-emitting diodes (LEDs). At low transmission rates data can also be transferred via an electrical interface. The method was developed to replace the plesiochronous digital hierarchy (PDH) system for transporting large amounts of telephone calls and data traffic over the same fiber without the problems of synchronization.
A universal asynchronous receiver-transmitter is a computer hardware device for asynchronous serial communication in which the data format and transmission speeds are configurable. The electric signaling levels and methods are handled by a driver circuit external to the UART. A UART is usually an individual integrated circuit (IC) used for serial communications over a computer or peripheral device serial port. One or more UART peripherals are commonly integrated in microcontroller chips. A related device, the universal synchronous and asynchronous receiver-transmitter (USART) also supports synchronous operation.
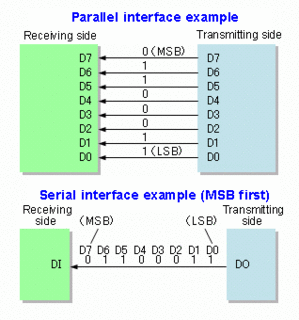
In telecommunication and data transmission, serial communication is the process of sending data one bit at a time, sequentially, over a communication channel or computer bus. This is in contrast to parallel communication, where several bits are sent as a whole, on a link with several parallel channels.
Asynchronous serial communication is a form of serial communication in which the communicating endpoints' interfaces are not continuously synchronized by a common clock signal. Instead of a common synchronization signal, the data stream contains synchronization information in form of start and stop signals, before and after each unit of transmission, respectively. The start signal prepares the receiver for arrival of data and the stop signal resets its state to enable triggering of a new sequence.
A Controller Area Network is a robust vehicle bus standard designed to allow microcontrollers and devices to communicate with each other in applications without a host computer. It is a message-based protocol, designed originally for multiplex electrical wiring within automobiles to save on copper, but is also used in many other contexts.
Source-Synchronous clocking refers to a technique used for timing symbols on a digital interface. Specifically, it refers to the technique of having the transmitting device send a clock signal along with the data signals. The timing of the unidirectional data signals is referenced to the clock sourced by the same device that generates those signals, and not to a global clock. Compared to other digital clocking topologies like system-synchronous clocks, where a global clock source is fed to all devices in the system, a source-synchronous clock topology can attain far higher speeds.
Synchronous and asynchronous transmissions are two different methods of transmission synchronization. Synchronous transmissions are synchronized by an external clock, while asynchronous transmissions are synchronized by special signals along the transmission medium.
Column Access Strobe (CAS) latency, or CL, is the delay time between the moment a memory controller tells the memory module to access a particular memory column on a RAM module, and the moment the data from the given array location is available on the module's output pins.
A universal synchronous and asynchronous receiver-transmitter (USART) is a type of a serial interface device that can be programmed to communicate asynchronously or synchronously. See universal asynchronous receiver-transmitter (UART) for a discussion of the asynchronous capabilities of these devices.

Parallel SCSI is the earliest of the interface implementations in the SCSI family. SPI is a parallel data bus; There is one set of electrical connections stretching from one end of the SCSI bus to the other. A SCSI device attaches to the bus but does not interrupt it. Both ends of the bus must be terminated.

Twinaxial cabling, or "Twinax", is a type of cable similar to coaxial cable, but with two inner conductors instead of one. Due to cost efficiency it is becoming common in modern (2013) very-short-range high-speed differential signaling applications.
Camera Link is a serial communication protocol standard designed for camera interface applications based on the National Semiconductor interface Channel-link. It was designed for the purpose of standardizing scientific and industrial video products including cameras, cables and frame grabbers. The standard is maintained and administered by the Automated Imaging Association or AIA, the global machine vision industry's trade group.
M-Modules are a mezzanine standard mainly used in industrial computers. Being mezzanines, they are always plugged on a carrier PCB that supports this format. The modules communicate with their carrier over a dedicated bus, and can have all kinds of special functions.
FASTBUS is a computer bus standard, originally intended to replace Computer Automated Measurement and Control (CAMAC) in high-speed, large-scale data acquisition. It is also a modular crate electronics standard commonly used in data acquisition systems in particle detectors.

Synchronous Serial Interface (SSI) is a widely used serial interface standard for industrial applications between a master and a slave. SSI is based on RS-422 standards and has a high protocol efficiency in addition to its implementation over various hardware platforms, making it very popular among sensor manufacturers. SSI was originally developed by Max Stegmann GmbH in 1984 for transmitting the position data of absolute encoders – for this reason, some servo/drive equipment manufacturers refer to their SSI port as a "Stegmann Interface". It was formerly covered by the German patent DE 34 45 617 which expired in 1990. It is very suitable for applications demanding reliability and robustness in measurements under varying industrial environments.
MOST is a high-speed multimedia network technology optimized by the automotive industry. It can be used for applications inside or outside the car. The serial MOST bus uses a daisy-chain topology or ring topology and synchronous data communication to transport audio, video, voice and data signals via plastic optical fiber (POF) or electrical conductor physical layers.

In electronics, a flip-flop or latch is a circuit that has two stable states and can be used to store state information. A flip-flop is a bistable multivibrator. The circuit can be made to change state by signals applied to one or more control inputs and will have one or two outputs. It is the basic storage element in sequential logic. Flip-flops and latches are fundamental building blocks of digital electronics systems used in computers, communications, and many other types of systems.










