
Eurocard is an IEEE standard format for printed circuit board (PCB) cards that can be plugged together into a standard chassis which, in turn, can be mounted in a 19-inch rack. The chassis consists of a series of slotted card guides on the top and bottom, into which the cards are slid so they stand on end, like books on a shelf. At the spine of each card is one or more connectors which plug into mating connectors on a backplane that closes the rear of the chassis.
Myrinet, ANSI/VITA 26-1998, is a high-speed local area networking system designed by the company Myricom to be used as an interconnect between multiple machines to form computer clusters.
Fibre Channel (FC) is a high-speed data transfer protocol providing in-order, lossless delivery of raw block data. Fibre Channel is primarily used to connect computer data storage to servers in storage area networks (SAN) in commercial data centers.

VMEbus is a computer bus standard physically based on Eurocard sizes.
A PCI Mezzanine Card or PMC is a printed circuit board assembly manufactured to the IEEE P1386.1 standard. This standard combines the electrical characteristics of the PCI bus with the mechanical dimensions of the Common Mezzanine Card or CMC format.

Electronic test equipment is used to create signals and capture responses from electronic devices under test (DUTs). In this way, the proper operation of the DUT can be proven or faults in the device can be traced. Use of electronic test equipment is essential to any serious work on electronics systems.

Automatic test equipment or automated test equipment (ATE) is any apparatus that performs tests on a device, known as the device under test (DUT), equipment under test (EUT) or unit under test (UUT), using automation to quickly perform measurements and evaluate the test results. An ATE can be a simple computer-controlled digital multimeter, or a complicated system containing dozens of complex test instruments capable of automatically testing and diagnosing faults in sophisticated electronic packaged parts or on wafer testing, including system on chips and integrated circuits.

The RapidIO architecture is a high-performance packet-switched electrical connection technology. It supports messaging, read/write and cache coherency semantics. Based on industry-standard electrical specifications such as those for Ethernet, RapidIO can be used as a chip-to-chip, board-to-board, and chassis-to-chassis interconnect.
A fieldbus is a member of a family of industrial digital communication networks used for real-time distributed control. Fieldbus profiles are standardized by the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) as IEC 61784/61158.

IEC 62056 is a set of standards for electricity metering data exchange by International Electrotechnical Commission. The IEC 62056 standards are the international standard versions of the DLMS/COSEM specification.
The Storage Management Initiative Specification, commonly called SMI-S, is a computer data storage management standard developed and maintained by the Storage Networking Industry Association (SNIA). It has also been ratified as an ISO standard. SMI-S is based upon the Common Information Model and the Web-Based Enterprise Management standards defined by the Distributed Management Task Force, which define management functionality via HTTP. The most recent approved version of SMI-S is available on the SNIA website.

Computer-Aided Measurement And Control (CAMAC) is a standard bus and modular-crate electronics standard for data acquisition and control used in particle detectors for nuclear and particle physics and in industry. The bus allows data exchange between plug-in modules and a crate controller, which then interfaces to a PC or to a VME-CAMAC interface.
Instrument control consists of connecting a desktop instrument to a computer and taking measurements.

A system on a module (SoM) is a board-level circuit that integrates a system function in a single module. It may integrate digital and analog functions on a single board. A typical application is in the area of embedded systems. Unlike a single-board computer, a SoM serves a special function like a system on a chip (SoC). The devices integrated in the SoM typically requires a high level of interconnection for reasons such as speed, timing, bus width etc.. There are benefits in building a SoM, as for SoC; one notable result is to reduce the cost of the base board or the main PCB. Two other major advantages of SoMs are design-reuse and that they can be integrated into many embedded computer applications.

VPX, also known as VITA 46, is a set of standards for connecting components of a computer, commonly used by defense contractors. Some are ANSI standards such as ANSI/VITA 46.0–2019. VPX provides VMEbus-based systems with support for switched fabrics over a new high speed connector. Defined by the VMEbus International Trade Association (VITA) working group starting in 2003, it was first demonstrated in 2004, and became an ANSI standard in 2007.
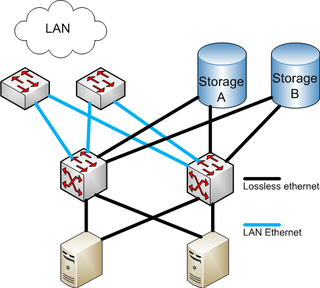
Fibre Channel over Ethernet (FCoE) is a computer network technology that encapsulates Fibre Channel frames over Ethernet networks. This allows Fibre Channel to use 10 Gigabit Ethernet networks while preserving the Fibre Channel protocol. The specification was part of the International Committee for Information Technology Standards T11 FC-BB-5 standard published in 2009. FCoE did not see widespread adoption.
M-Modules are a mezzanine standard mainly used in industrial computers. Being mezzanines, they are always plugged on a carrier printed circuit board (PCB) that supports this format. The modules communicate with their carrier over a dedicated bus, and can have all kinds of special functions.
The front panel data port (FPDP) is a bus that provides high speed data transfer between two or more VMEbus boards at up to 160 Mbit/s with low latency. The FPDP bus uses a 32-bit parallel synchronous bus wired with an 80-conductor ribbon cable.
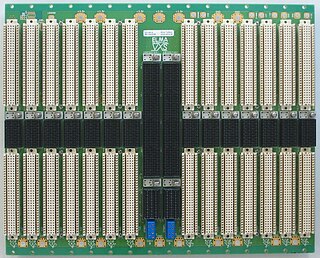
Elma Electronic is a publicly traded Swiss electronics company founded in 1960 and based in Wetzikon, Switzerland. The company has 5 product divisions: Systems Platforms, Backplanes, Enclosures & Components, Rotary Switches, and Cabinet Enclosures. The largest segment is systems packaging serving the military, aerospace, homeland security, medical and industrial markets. The Elma Bustronic division develops backplanes, including VME320, which was the world's fastest VME backplane in 1997. Elma Bustronic also develops backplanes in OpenVPX, VMEbus, VME64X, CompactPCI, MicroTCA, and custom bus structures. Elma is an executive member of the PCI Industrial Computer Manufacturers Group (PICMG), VME International Trade Association, and member of the OpenVPX Industry Working Standards Group.

FPGA Mezzanine Card (FMC) is an ANSI/VITA 57.1 standard that defines I/O mezzanine modules with connection to an FPGA or other device with re-configurable I/O capability. It specifies a low profile connector and compact board size for compatibility with several industry standard slot card, blade, low profile motherboard, and mezzanine form factors.












