| Gao | |
|---|---|
| Cercle | |
 | |
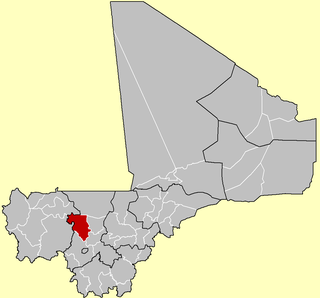
 Cercle of Gap in Mali | |
| Country | |
| Region | Gao Region |
| Capital | Gao |
| Area [1] | |
| • Total | 31,250 km2 (12,070 sq mi) |
| Population (2009 census) [2] | |
| • Total | 239,853 |
| • Density | 7.7/km2 (20/sq mi) |
| Time zone | GMT (UTC+0) |
Gao Cercle is an administrative subdivision of the Gao Region of north-eastern Mali. The administrative center ( chef-lieu ) is the town of Gao.
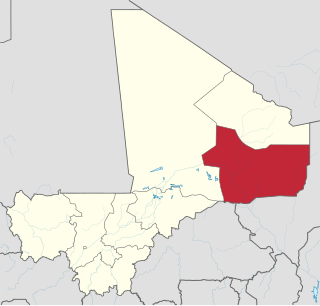
The Gao Region is in northeastern Mali. The capital city is Gao.

Mali, officially the Republic of Mali, is a landlocked country in West Africa, a region geologically identified with the West African Craton. Mali is the eighth-largest country in Africa, with an area of just over 1,240,000 square kilometres (480,000 sq mi). The population of Mali is 18 million. Its capital is Bamako. The sovereign state of Mali consists of eight regions and its borders on the north reach deep into the middle of the Sahara Desert, while the country's southern part, where the majority of inhabitants live, features the Niger and Senegal rivers. The country's economy centers on agriculture and mining. Some of Mali's prominent natural resources include gold, being the third largest producer of gold in the African continent, and salt.
During the Northern Mali conflict in 2012, the main Tuareg rebel group, the National Movement for the Liberation of Azawad (MNLA) lost the region to the Islamist groups Ansar Dine, Movement for Oneness and Jihad in West Africa (MOJWA) and Al-Qaeda in the Islamic Maghreb (AQIM). In 2013, the Islamists then lost most of the region to French and Malian soldiers.

The National Movement for the Liberation of Azawad or the Azawad National Liberation Movement, formerly the National Movement of Azawad, is a political and military organisation based in Azawad in northern Mali.

Ansar Dine also known as Ansar al-Din is a militant Islamist group led by Iyad Ag Ghaly, one of the most prominent leaders of the Tuareg Rebellion (1990–1995) who is suspected of having ties to Al-Qaeda in the Islamic Maghreb, which is led by his cousin Hamada Ag Hama. Ansar Dine seeks to impose strict Sharia law across Mali. The group's first action was in March 2012. The organization is not to be confused with the Sufi movement Ançar Dine, started in Southern Mali by Chérif Ousmane Haidara in the 1980s, which is fundamentally opposed to militant Islamism. Ansar Dine is opposed to Sufi shrines.
The Movement for Oneness and Jihad in West Africa or the Movement for Unity and Jihad in West Africa, was a militant Islamist organisation that broke off from Al-Qaeda in the Islamic Maghreb with the intended goal of spreading jihad across a larger section of West Africa.
The cercle is divided into seven communes: [2]
- Anchawadi
- Gabero
- Gao (an urban commune)
- Gounzoureye
- N'Tillit
- Sony Aliber
- Tilemsi
Anchawadi is a commune in the Cercle of Gao in the Gao Region of south-eastern Mali. The principal town lies at Djebock. As of 1998 the commune had a population of 7392.

Gabero is a rural commune in the Cercle of Gao in the Gao Region of south-eastern Mali. The commune covers an area of approximately 2,007 square kilometers and includes 15 villages. In the 2009 census the commune had a population of 25,688. The Niger River crosses the commune from north to south. The administrative center (chef-lieu) is Haoussa Foulane that lies on the left (east) bank of the Niger. The village is 45 km south of Gao, on the road, the N17, linking Gao and Ansongo.

Gounzoureye is a rural commune in the Cercle of Gao in the Gao Region of south-eastern Mali. The commune includes the villages of Koima, Tchirissoro, Sadou, Lobou, Sidibé, Kosseye, Gorom Gorom, Kadji, Wabaria, Arhabou, Tacharane, Bagoundjé I and Bagoundjé II, which are all located on the banks of the River Niger. The administrative center (chef-lieu) is at the village of Wabaria. In the 2009 census the commune had a population of 30,772.