
Doom is a 1993 first-person shooter (FPS) game developed by id Software for MS-DOS. Players assume the role of a space marine, popularly known as Doomguy, fighting his way through hordes of invading demons from Hell. The first episode, comprising nine levels, was distributed freely as shareware and played by an estimated 15–20 million people within two years; the full game, with two further episodes, was sold via mail order. An updated version with an additional episode and more difficult levels, Ultimate Doom, was released in 1995 and sold at retail.

Duke Nukem 3D is a first-person shooter video game developed by 3D Realms. It is a sequel to the platform games Duke Nukem and Duke Nukem II, published by 3D Realms.

Heretic is a dark fantasy first-person shooter video game released in 1994. It was developed by Raven Software and published by id Software through GT Interactive. The game was released on Steam on August 3, 2007.

Hexen: Beyond Heretic is a dark fantasy first-person shooter video game developed by Raven Software and published by id Software through GT Interactive Software on October 30, 1995. It is the sequel to 1994's Heretic, and the second game in Raven Software's "Serpent Riders" trilogy, which culminated with Hexen II. The title comes from the German noun Hexen, which means "witches", and/or the verb hexen, which means "to cast a spell". Game producer John Romero stated that a third, unreleased game in this series was to be called Hecatomb.

Heretic II is a dark fantasy action-adventure game developed by Raven Software and published by Activision in 1998 continuing the story of Corvus, the main character from its predecessor, Heretic. It is the fourth game in the Hexen: Beyond Heretic series and comes after the "Serpent Rider" trilogy.

id Software LLC is an American video game developer based in Richardson, Texas. The company was founded on February 1, 1991, by four members of the computer company Softdisk, programmers John Carmack and John Romero, game designer Tom Hall, and artist Adrian Carmack. Business manager Jay Wilbur was also involved. id Software made important technological developments in video game technologies for the PC, including work done for the Wolfenstein, Doom, and Quake franchises. id's work was particularly important in 3D computer graphics technology and in game engines that are used throughout the video game industry. The company was involved in the creation of the first-person shooter (FPS) genre. Wolfenstein 3D is often considered to be the first true FPS, Doom is a game that popularized the genre and PC gaming in general, and Quake was id's first true 3D FPS.

Quake III Arena is a 1999 multiplayer-focused first-person shooter developed by id Software. It is the third game in the Quake series; it differs from previous games by excluding a story-based single-player mode and highly focusing on multiplayer gameplay. The single-player mode is played against computer-controlled bots. It features music composed by Sonic Mayhem and Front Line Assembly founder Bill Leeb.

Quake is a first-person shooter video game developed by id Software and published by GT Interactive in 1996. It is the first game in the Quake series. In the game, players must find their way through various maze-like, medieval environments while battling a variety of monsters using an array of weaponry. The overall atmosphere is dark and gritty, with much stone textures and a rusty, capitalized font.

Unreal is a first-person shooter video game developed by Epic MegaGames and Digital Extremes and published by GT Interactive in May 1998. It was powered by Unreal Engine, an original game engine. The game reached sales of 1.5 million units by 2002.

Wolfenstein 3D is a first-person shooter video game developed by id Software and published by Apogee Software and FormGen. Originally released on May 5, 1992 for DOS, it was inspired by the 1981 Muse Software video game Castle Wolfenstein, and is the third installment in the Wolfenstein series. In Wolfenstein 3D, the player assumes the role of Allied spy William "B.J." Blazkowicz during World War II as he escapes from the Nazi German prison Castle Wolfenstein and carries out a series of crucial missions against the Nazis. The player traverses each of the game's levels to find an elevator to the next level or kill a final boss, fighting Nazi soldiers, dogs, and other enemies with knives and a variety of guns.
id Tech 1, also known as Doom engine, is the game engine that powers the id Software games Doom and Doom II: Hell on Earth. It is also used in Heretic, Hexen: Beyond Heretic, Strife: Quest for the Sigil, Hacx: Twitch 'n Kill, Freedoom, and other games produced by licensees. It was created by John Carmack, with auxiliary functions written by Mike Abrash, John Romero, Dave Taylor, and Paul Radek. Originally developed on NeXT computers, it was ported to DOS for Doom's initial release and was later ported to several game consoles and operating systems.

Unreal Tournament is a first-person shooter video game developed by Epic Games and Digital Extremes. The second installment in the Unreal series, it was first published by GT Interactive in 1999 for Microsoft Windows, and later released on the PlayStation 2 and Dreamcast by Infogrames in 2000 and 2001, respectively. Players compete in a series of matches of various types, with the general aim of out-killing opponents. The PC version supports multiplayer online or over a local area network. Free expansion packs were released, some of which were bundled with a 2000 re-release: Unreal Tournament: Game of the Year Edition.
A first-person shooter engine is a video game engine specialized for simulating 3D environments for use in a first-person shooter video game. First-person refers to the view where the players see the world from the eyes of their characters. Shooter refers to games which revolve primarily around wielding firearms and killing other entities in the game world, either non-player characters or other players.

Digital Extremes is a Canadian video game developer founded in 1993 by James Schmalz. They are best known for creating Warframe, a free-to-play cooperative online action game, and co-creating Epic Games' Unreal series of games. Digital Extremes is headquartered in London, Ontario. In 2014, 61% of the company was sold to Chinese holding company Multi Dynamic, now Leyou, for $73 million. President Michael Schmalz and two partners retained 39% of Digital Extremes, and will continue to manage it. On May 22, 2016 Leyou exercised a call option and now owns 97% of Digital Extremes for a total consideration of $138.2 million US.
Extreme Paintbrawl is a paintball video game released for DOS/Microsoft Windows on October 31, 1998. The game uses a modified version of the Duke Nukem 3D: Atomic Edition v1.5 executable. The game is considered to be one of the worst video games ever made. Extreme Paintbrawl was developed in two weeks, with a soundtrack by musician Todd Duane, who sent his demo tracks to Head Games. The game was followed by Extreme Paintbrawl 2 in 1999, Ultimate Paintbrawl 3 in 2000, and Extreme Paintbrawl 4 in 2002, all of which were met with negative reviews.
Linux gaming refers to playing video games developed for the Linux operating system.

id Tech is a series of separate game engines designed and developed by id Software. Prior to the presentation of the id Tech 5-based game Rage in 2011, the engines lacked official designation and as such were simply referred to as the Doom and Quake engines, from the name of the main game series the engines had been developed for. "id Tech" numbers 1, 2, 3, and 4 have been released as free software under the GNU General Public License, along with the source code to Wolfenstein 3D, Doom, and Quake. id Tech 7 is currently the latest utilized engine.

Doom is a video game series and media franchise created by John Carmack, John Romero, Adrian Carmack, Kevin Cloud, and Tom Hall. The series focuses on the exploits of an unnamed space marine operating under the auspices of the Union Aerospace Corporation (UAC), who fights hordes of demons and the undead.
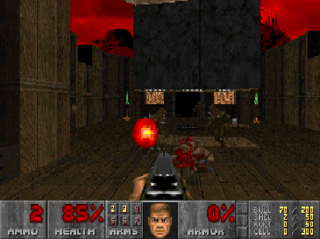
First-person shooter (FPS) is a video game genre centered on gun and other weapon-based combat in a first-person perspective; that is, the player experiences the action through the eyes of the protagonist. The genre shares common traits with other shooter games, which in turn makes it fall under the heading action game. Since the genre's inception, advanced 3D and pseudo-3D graphics have challenged hardware development, and multiplayer gaming has been integral.














