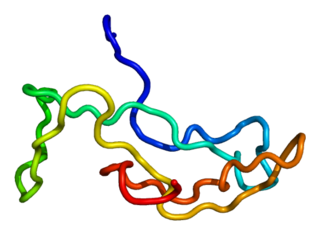
Luteinizing hormone is a hormone produced by gonadotropic cells in the anterior pituitary gland. The production of LH is regulated by gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) from the hypothalamus. In females, an acute rise of LH known as an LH surge, triggers ovulation and development of the corpus luteum. In males, where LH had also been called interstitial cell–stimulating hormone (ICSH), it stimulates Leydig cell production of testosterone. It acts synergistically with follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH).

Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) is a gonadotropin, a glycoprotein polypeptide hormone. FSH is synthesized and secreted by the gonadotropic cells of the anterior pituitary gland and regulates the development, growth, pubertal maturation, and reproductive processes of the body. FSH and luteinizing hormone (LH) work together in the reproductive system.
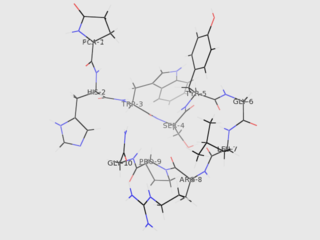
Gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) is a releasing hormone responsible for the release of follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinizing hormone (LH) from the anterior pituitary. GnRH is a tropic peptide hormone synthesized and released from GnRH neurons within the hypothalamus. The peptide belongs to gonadotropin-releasing hormone family. It constitutes the initial step in the hypothalamic–pituitary–gonadal axis.
Gonadotropins are glycoprotein hormones secreted by gonadotropic cells of the anterior pituitary of vertebrates. This family includes the mammalian hormones follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinizing hormone (LH), the placental/chorionic gonadotropins, human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) and equine chorionic gonadotropin (eCG), as well as at least two forms of fish gonadotropins. These hormones are central to the complex endocrine system that regulates normal growth, sexual development, and reproductive function. LH and FSH are secreted by the anterior pituitary gland, while hCG and eCG are secreted by the placenta in pregnant humans and mares, respectively. The gonadotropins act on the gonads, controlling gamete and sex hormone production.
Fertility medications, also known as fertility drugs, are medications which enhance reproductive fertility. For women, fertility medication is used to stimulate follicle development of the ovary. There are very few fertility medication options available for men.
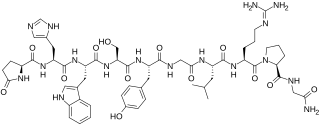
Gonadorelin is a gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonist which is used in fertility medicine and to treat amenorrhea and hypogonadism. It is also used in veterinary medicine. The medication is a form of the endogenous GnRH and is identical to it in chemical structure. It is given by injection into a blood vessel or fat or as a nasal spray.
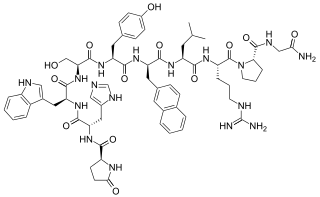
Nafarelin, sold under the brand name Synarel among others, is a gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonist medication which is used in the treatment of endometriosis and early puberty. It is also used to treat uterine fibroids, to control ovarian stimulation in in vitro fertilization (IVF), and as part of transgender hormone therapy. The medication is used as a nasal spray two to three times per day.
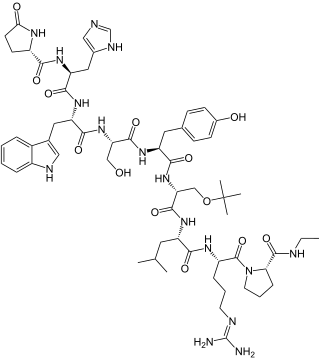
Buserelin, sold under the brand name Suprefact among others, is a medication which is used primarily in the treatment of prostate cancer and endometriosis. It is also used for other indications such as the treatment of premenopausal breast cancer, uterine fibroids, and early puberty, in assisted reproduction for female infertility, and as a part of transgender hormone therapy. In addition, buserelin is used in veterinary medicine. The medication is typically used as a nasal spray three times per day, but is also available for use as a solution or implant for injection into fat.

Triptorelin, sold under the brand name Decapeptyl among others, is a medication that acts as an agonist analog of gonadotropin-releasing hormone, repressing expression of luteinizing hormone (LH) and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH).

A gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonist is a type of medication which affects gonadotropins and sex hormones. They are used for a variety of indications including in fertility medicine and to lower sex hormone levels in the treatment of hormone-sensitive cancers such as prostate cancer and breast cancer, certain gynecological disorders like heavy periods and endometriosis, high testosterone levels in women, early puberty in children, as a part of transgender hormone therapy, and to delay puberty in transgender youth among other uses. It is also used in the suppression of spontaneous ovulation as part of controlled ovarian hyperstimulation, an essential component in IVF. GnRH agonists are given by injections into fat, as implants placed into fat, and as nasal sprays.

Gonadotropin-releasing hormone antagonists are a class of medications that antagonize the gonadotropin-releasing hormone receptor and thus the action of gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH). They are used in the treatment of prostate cancer, endometriosis, uterine fibroids, female infertility in assisted reproduction, and for other indications.
The gonadotropin-releasing hormone receptor (GnRHR), also known as the luteinizing hormone releasing hormone receptor (LHRHR), is a member of the seven-transmembrane, G-protein coupled receptor (GPCR) family. It is the receptor of gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH). The GnRHR is expressed on the surface of pituitary gonadotrope cells as well as lymphocytes, breast, ovary, and prostate.

Kisspeptins are proteins encoded by the KISS1 gene in humans. Kisspeptins are ligands of the G-protein coupled receptor, GPR54. Kiss1 was originally identified as a human metastasis suppressor gene that has the ability to suppress melanoma and breast cancer metastasis. Kisspeptin-GPR54 signaling has an important role in initiating secretion of gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) at puberty, the extent of which is an area of ongoing research. Gonadotropin-releasing hormone is released from the hypothalamus to act on the anterior pituitary triggering the release of luteinizing hormone (LH), and follicle stimulating hormone (FSH). These gonadotropic hormones lead to sexual maturation and gametogenesis. Disrupting GPR54 signaling can cause hypogonadotrophic hypogonadism in rodents and humans. The Kiss1 gene is located on chromosome 1. It is transcribed in the brain, adrenal gland, and pancreas.

Cetrorelix, or cetrorelix acetate, sold under the brand name Cetrotide, is an injectable gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) antagonist. A synthetic decapeptide, it is used in assisted reproduction to inhibit premature luteinizing hormone surges The drug works by blocking the action of GnRH upon the pituitary, thus rapidly suppressing the production and action of luteinizing hormone (LH) and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH). In addition, cetrorelix can be used to treat hormone-sensitive cancers of the prostate and breast and some benign gynaecological disorders. It is administered as either multiple 0.25 mg daily subcutaneous injections or as a single-dose 3 mg subcutaneous injection. The duration of the 3 mg single dose is four days; if human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) is not administered within four days, a daily 0.25 mg dose is started and continued until hCG is administered.
Controlled ovarian hyperstimulation is a technique used in assisted reproduction involving the use of fertility medications to induce ovulation by multiple ovarian follicles. These multiple follicles can be taken out by oocyte retrieval for use in in vitro fertilisation (IVF), or be given time to ovulate, resulting in superovulation which is the ovulation of a larger-than-normal number of eggs, generally in the sense of at least two. When ovulated follicles are fertilised in vivo, whether by natural or artificial insemination, there is a very high risk of a multiple pregnancy.
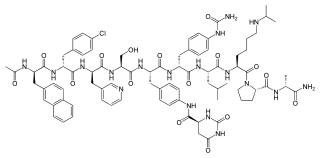
Degarelix, sold under the brand name Firmagon among others, is a hormonal therapy used in the treatment of prostate cancer.

Elagolix, sold under the brand name Orilissa, is a gonadotropin-releasing hormone antagonist medication which is used in the treatment of pain associated with endometriosis in women. It is also under development for the treatment of uterine fibroids and heavy menstrual bleeding in women. The medication was under investigation for the treatment of prostate cancer and enlarged prostate in men as well, but development for these conditions was discontinued. Elagolix is taken by mouth once or twice per day. It can be taken for up to 6 to 24 months, depending on the dosage.

Relugolix, sold under the brand names Orgovyx and Relumina among others, is a gonadotropin-releasing hormone antagonist medication which is used in the treatment of prostate cancer in men and uterine fibroids in women. It is taken by mouth.
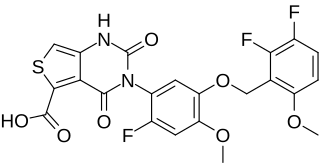
Linzagolix, sold under the brand name Yselty, is a medication used in the treatment of uterine fibroids. Linzagolix is a small-molecule, non-peptide, orally active gonadotropin-releasing hormone antagonist developed by Kissei Pharmaceutical and ObsEva.
Gonadotropin surge-attenuating factor (GnSAF) is a nonsteroidal ovarian hormone produced by the granulosa cells of small antral ovarian follicles in females. GnSAF is involved in regulating the secretion of luteinizing hormone (LH) from the anterior pituitary and the ovarian cycle. During the early to mid-follicular phase of the ovarian cycle, GnSAF acts on the anterior pituitary to attenuate LH release, limiting the secretion of LH to only basal levels. At the transition between follicular and luteal phase, GnSAF bioactivity declines sufficiently to permit LH secretion above basal levels, resulting in the mid-cycle LH surge that initiates ovulation. In normally ovulating women, the LH surge only occurs when the oocyte is mature and ready for extrusion. GnSAF bioactivity is responsible for the synchronised, biphasic nature of LH secretion.















