
Broad Margin is the name given to the private residence originally commissioned by Gabrielle and Charlcey Austin. It is located in Greenville, South Carolina, United States, was designed by Frank Lloyd Wright and was built by local builder Harold T. Newton in 1954. It is one of two buildings designed by Wright in South Carolina.
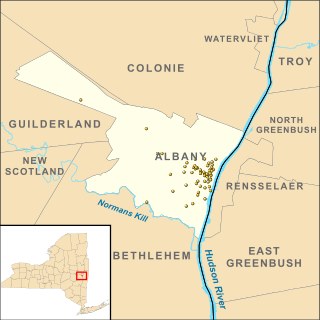
There are 75 properties listed on the National Register of Historic Places in Albany, New York, United States. Six are additionally designated as National Historic Landmarks (NHLs), the most of any city in the state after New York City. Another 14 are historic districts, for which 20 of the listings are also contributing properties. Two properties, both buildings, that had been listed in the past but have since been demolished have been delisted; one building that is also no longer extant remains listed.

This is a list of the National Register of Historic Places listings in Greenville, South Carolina.

Old Greenville City Hall is a former building in Greenville, South Carolina, originally built as the U.S. Courthouse and Post Office in 1889 on the corner of Main and Broad Streets. Transferred to the city of Greenville in 1938, it served as Greenville city hall. It was listed in the National Register of Historic Places on August 19, 1971, and was removed in 1973 after its demolition.

The Old Muhlenberg County Jail is a historic jail located on Court Row in Greenville, Kentucky. Built in 1912, the jail was the third used in Greenville. The stucco building was designed in the Mission Revival style. Its design features a red tile roof, a Mission-style dormer with a quatrefoil vent, and porches with hipped tile roofs over the entrances on three sides.

The Rice Tobacco Factory is a historic tobacco factory located at 112 N. Cherry St. in Greenville, Kentucky. The factory was built in 1922 by S.E. Rice, whose S.E. Rice Company was founded in 1904. Tobacco had been Muhlenberg County's largest cash crop throughout the 19th century, and the region became known for its variety, called "Greenville Tobacco". The Rice factory, however, was the last building built in Greenville for tobacco production. It is now the only surviving commercial building connected to the city's tobacco industry. The property was acquired in March, 2018, and the new owner is in the process of a historic rehabilitation of the building.

The Greenville Commercial Historic District is a historic district located on two blocks of N. Main St. and E. Main Cross St. in Greenville, Kentucky. The district consists of thirteen commercial buildings, ten of which are contributing buildings. The buildings in the district are commercial buildings constructed in the late 19th and early 20th centuries. The oldest of the buildings are two Italianate buildings built in the 1870s. The district includes the First National Bank Building, a Beaux-Arts building constructed in 1901; a building at 121-123 N. Main with a metal facade and engaged columns; the Greenville Record building at 115 N. Main; Greenville's Odd Fellows hall at 103 E. Main Cross; and the Palace Theater at 121 N. Main.

The North Main Street Historic District is a historic district located along the 100 and 200 blocks of North Main Street in Greenville, Kentucky. The district includes 22 buildings, 20 of which are contributing buildings to the district's historic status. The primarily residential district is located just north of downtown Greenville. The houses within the district were mainly built in the early 20th century and designed in the Colonial Revival, Bungalow, and Queen Anne styles; an exception to this pattern is the George Short House, which was built in 1841 and is the oldest surviving house in the city. The district also includes the United Methodist Church, a Neoclassical church built in 1921.

The City Hall of Rock Springs, Wyoming, located at 4th and B Sts. in Rock Springs, is a gray sandstone building that was built in 1894. It includes Richardsonian Romanesque architecture in a design by Salt Lake City architect M.D. Kern. It has an irregular plan within 90.9-by-71.9-foot dimensions. It was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1980.

Isaqueena, also known as the Gassaway Mansion, is a historic house in Greenville, South Carolina, and the largest private residence in the Upstate. In 1982 it was listed in the National Register of Historic Places.

Greenville City Hall in Greenville, Alabama is a historic city hall. The building was designed by Montgomery architect Moreland Griffith Smith, and built in 1936–37 by workers from the Works Progress Administration. The building is designed in a Colonial Revival style with Palladian influences, a popular style in the 1930s due to the recent restoration of Colonial Williamsburg. It was built on the site of a grammar school that was originally built in the 1890s, but burned in the early 1920s and again in 1927. The building is constructed of brick, with a full-height portico around the main entry. Each window on the first floor is topped with an ashlar keystone. The corners of the main block are adorned with stone quoins. The building was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1986.

Woodside Cotton Mill Village Historic District is a national historic district located in Greenville County, South Carolina. The district encompasses 278 contributing buildings and 2 contributing sites in an early 20th century urban South Carolina textile mill village. Centered on a mill founded by John T. Woodside in 1902, the district is located just west of the city limits of Greenville and is largely intact despite modernizations made by a succession of mill and home owners. The mill itself is a rectangular, brick, four-story building designed by J.E. Sirrine and built between 1902 and 1912. Eventually the mill became the largest cotton mill under one roof in the United States and one of the largest in the world.

Greenville County Courthouse, also known as Greenville Family Courts Building, is a historic courthouse located at Greenville, South Carolina. It was built in 1918, and is a Beaux-Arts style brick and concrete building with terra cotta trim. The building consists of a three-story front section, with an eight-story tower behind. The building served as the courthouse for Greenville County until 1950 when the court was moved to a new building. The Family Court of Greenville County was located then in the building and remained there until 1991.

Hampton–Pinckney Historic District is a national historic district located at Greenville, South Carolina. It encompasses 70 contributing buildings in a residential section of Greenville. The houses date from about 1890 to 1930, and include Italianate, Greek Revival, Queen Anne, various bungalows, and examples of Gothic Revival and Colonial Revival design, as well as vernacular forms. The oldest house in the district is the McBee House.

West End Commercial Historic District is a national historic district located at Greenville, South Carolina. It encompasses 15 contributing buildings in Greenville's second "downtown." The commercial buildings primarily date from about 1880 to 1920, and include examples of Victorian commercial architecture. Notable buildings include the American Bank, Alliance and Mills & McBayer Cotton Warehouses, Indian River Fruit Store, Pete's Place, Bacot's West End Drug Store/Stringer's Drug, Furman Lunch, and Greer Thompson Building.

The First National Bank of Greenville is a historic building in Greenville, Mississippi.

Greenville Commercial Historic District is a national historic district located at Greenville, Pitt County, North Carolina. The district encompasses 51 contributing buildings in the central business district of Greenville. It includes buildings dated from about 1914 to 1952 and notable examples of Greek Revival and Queen Anne style architecture. Located in the district and listed separately are the Pitt County Courthouse (1911) by Milburn, Heister & Company and U.S. Post Office (1913). Other notable buildings include the Proctor Hotel (1911), Montgomery Ward Department Store (1929), Dail-Hodges Building (1919), Blount Building (1924), Greenville Bank and Trust, Smith Electric Building, Greenville Municipal Building (1929) designed by Benton & Benton, Blount-Harvey Department Store (1923), White's Theater (1914), Charles Greene House (1860), and the Robert Lee Humber House (1895).

The Bank of Washington is a historic building in Greenville, Mississippi, USA.

The American Spinning Company Mill No. 2 is a historic mill complex at 300 Hammett Street, in a pocket of unincorporated Greenville County, South Carolina surrounded on three sides by the city of Greenville. It is a five-story brick building, to which a number of warehouse buildings and other additions were made. It was built in 1901-02, as part of a major expansion to the American Spinning Company's Mill No. 1, which originally stood just south of Hammett Street. It was built by Oscar Sampson, a Boston textile manufacturer to a design by the industrial design firm Lockwood and Greene, and is one of thirteen early 20th-century mills surviving in the Greenville area. It was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 2016. Its major tenant now is the Victor Mill Company, a furniture maker.




















