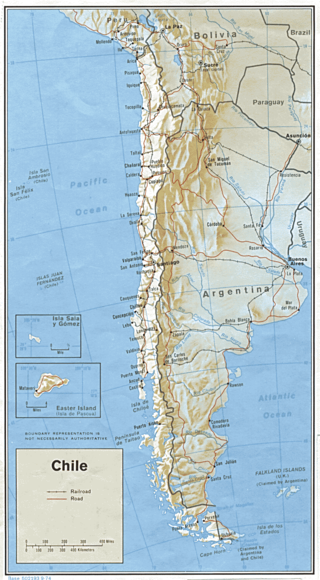
Transport in Chile is mostly by road. The far south of the country is not directly connected to central Chile by road without travelling through Argentina, and water transport also plays a part there. The railways were historically important in Chile, but now play a relatively small part in the country's transport system. Because of the country's geography and long distances between major cities, aviation is also important.

Transport in the Dominican Republic utilizes a system of roads, airports, ports, harbours, and an urban railway.
The vast territory of Kazakhstan spans across 2,700,000 km2 (1,000,000 sq mi). The population density is low in Kazakhstan, and the centers of industry and agriculture are spread out and remote from world markets.
This article describes the transport in Peru.
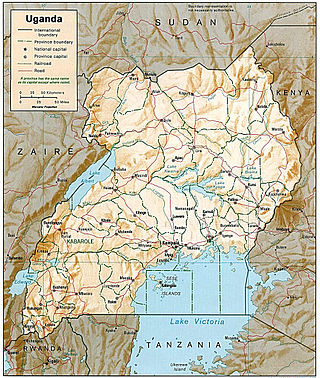
Transport in Uganda refers to the transportation structure in Uganda. The country has an extensive network of paved and unpaved roads.
Transport in Bolivia is mostly by road. The railways were historically important in Bolivia, but now play a relatively small part in the country's transport system. Because of the country's geography, aviation is also important.

Lake Titicaca is a large freshwater lake in the Andes mountains on the border of Bolivia and Peru. It is often called the highest navigable lake in the world. Titicaca is the largest lake in South America both in terms of the volume of water and surface area.

The Trans-Andean railways provide rail transport over the Andes. Several are either planned, built, defunct, or waiting to be restored. They are listed here in order from north to south.

Empresa de los Ferrocarriles del Estado is the national railway and the oldest state-run enterprise in Chile. It manages the infrastructure and operating rail services in the country.

PeruRail is a railway operator providing tourist, freight, and charter services in southern Peru. It was founded in 1999 by two Peruvian entrepreneurs and the British company Sea Containers.

Rail transport in Peru has a varied history. Peruvian rail transport has never formed a true network, primarily comprising separate lines running inland from the coast and built according to freight need rather than passenger need.
Pedro Cieza de León was a Spanish conquistador and chronicler of Peru and Popayán. He is known primarily for his extensive work, Crónicas del Perú, which has been a source of knowledge for centuries for different disciplines such as history, philology, geography, biology, anthropology, botany and zoology. He wrote this book in four parts, but only the first was published during his lifetime; the remaining sections were not published until the 19th and 20th centuries.

The Ferrocarril de Antofagasta a Bolivia is a private railway operating in the northern provinces of Chile. It is notable in that it was one of the earliest railways built to 2 ft 6 in narrow gauge, with a route that climbed from sea level to over 4,500 m (14,764 ft), while handling goods traffic totaling near 2 million tons per annum. It proved that a railway with such a narrow gauge could do the work of a standard gauge railway, and influenced the construction of other railways such as the Estrada de Ferro Oeste de Minas. It was later converted to 1,000 mmmetre gauge, and still operates today.
Following is a list of railway stations in Bolivia, categorized by eastern and western networks. The eastern and western networks do not directly connect, except via a roundabout route through Argentina.
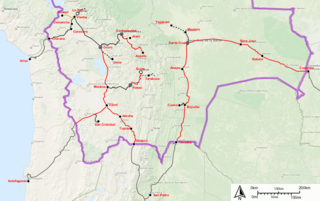
The Bolivian rail network has had a peculiar development throughout its history.

Benin has a total of 578 km (359 mi) of single track, 1,000 mm railway. Rail construction began around 1900, with regular services commencing in 1906; rail operation was taken into government control in 1930.

The history of rail transport in Chile has gone through several periods of boom and bust. It began in 1840, with the construction by William Wheelwright of the first branch in the north. Further construction proceeded apace linking cities from Pisagua all the way to Puerto Montt.

Chucuito is a village in the Chucuito District, Puno Province, Peru. It is 18 kilometres (11 mi) from the city of Puno. It sits at 3,875 metres (12,713 ft) above sea level. The population is 7,913.