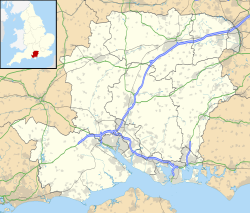
Joint Helicopter Command Flying Station Aldergrove or more simply JHC FS Aldergrove is located 4.4 miles (7.1 km) south of Antrim, Northern Ireland and 18 miles (29 km) northwest of Belfast and adjoins Belfast International Airport. It is sometimes referred to simply as Aldergrove which is the name of a nearby hamlet. The military flying units share the Aldergrove runways but have their own separate facilities and helipad.

Royal Air Force Abingdon or more simply RAF Abingdon was a Royal Air Force station near Abingdon, Oxfordshire. It is now known as Dalton Barracks and is used by the Royal Logistic Corps.

The Sembawang Air Base is a military airbase of the Republic of Singapore Air Force (RSAF) located at Sembawang, in the northern part of Singapore. The base motto is Swift and Resolute.

Tain Air Weapons Range is a Ministry of Defence air weapons range on the Dornoch Firth near Tain in Scotland. Royal Air Force aircrews from RAF Lossiemouth are trained in air weaponry on the range, along with NATO aircrew.

667 Squadron AAC is a squadron of the British Army's Army Air Corps (AAC).

848 Naval Air Squadron was a squadron of the Royal Navy Fleet Air Arm. It operated the Westland Sea King HC.4 helicopter and previously provided advanced flying training to pilots for the other squadrons in the Commando Helicopter Force. The squadron was based at RNAS Yeovilton in Somerset and was decommissioned on 24 March 2016.
No. 191 Squadron was a Royal Air Force squadron. During World War I it was a non-operational night training unit, while during World War II it was engaged in maritime reconnaissance.

Army Aviation Centre (AAC) Middle Wallop is a British Army airfield located near the Hampshire village of Middle Wallop, used for Army Air Corps training. The base hosts 2 (Training) Regiment AAC and 7 (Training) Regiment AAC under the umbrella of the Army Aviation Centre. 2 (Training) Regiment performs ground training; 7 (Training) Regiment trains aircrew on AAC aircraft after they complete basic training at RAF Shawbury.

Royal Air Force Detling or more simply RAF Detling is a former Royal Air Force station situated 600 feet (180 m) above sea level, located near Detling, a village about 4 miles (6.4 km) miles north-east of Maidstone, Kent.
No. 204 Squadron was a Royal Air Force unit first formed in March 1915 as No.4 Squadron Royal Naval Air Service.
810 Naval Air Squadron was a Royal Navy Fleet Air Arm carrier based squadron formed on 3 April 1933 with the amalgamation of the 12 Blackburn Dart aircraft from 463 and 44 Flight Flights Royal Air Force to the Fleet Air Arm. The squadron saw action during the Second World War, the Suez Crisis and the Korean War.
No. 661 Squadron was a Royal Air Force Air Observation Post squadron associated with the Canadian 1st Army and later part of the Royal Auxiliary Air Force. Numbers 651 to 663 Squadrons of the RAF were Air Observation Post units working closely with Army units in artillery spotting and liaison. A further three of these squadrons, 664–666, were manned with Canadian personnel. Their duties and squadron numbers were transferred to the Army with the formation of the Army Air Corps on 1 September 1957.

Netheravon Airfield is a Ministry of Defence grass strip airfield on Salisbury Plain, in Wiltshire, England. Established in 1913 by the Royal Flying Corps, it became RAF Netheravon from 1918 until 1963, then AAC Netheravon until 2012. Buildings from 1913 and 1914 survive on part of the site. The site forms part of the Tidworth, Netheravon and Bulford (TidNBul) Garrison.

813 Naval Air Squadron was an aircraft squadron of the Royal Navy's Fleet Air Arm during World War II and again post-war. It initially operated Swordfish Mk Is from the aircraft carrier Illustrious and took part in the successful raid on Taranto in November 1940.

No. 1300 (Meteorological) Flight was formed on 31 July 1943 at RAF Alipore, West Bengal, British India, by re-designating No. 1 Meteorological Flight RAF. The flight, strength of which had been reduced to three Hawker Hurricane Mk.IIs by this time, was disbanded on 30 May 1946 at RAF Kallang, Malaya, as No. 1300 Flight, THUM standing for Temperature and Humidity.
194 Squadron RAF, though formed as a training unit in Egypt and ended as a casualty evacuation unit in Malaya, was for most of its active service life a RAF transport squadron that flew in South East Asia.

HMS Gannet is a forward operating base of the Royal Navy's Fleet Air Arm located at Glasgow Prestwick Airport, South Ayrshire in Scotland.

703 Naval Air Squadron of the Fleet Air Arm of the Royal Navy was formed as a long-range catapult squadron on 3 March 1942 at RNAS Lee-on-Solent. During the Cold War, it was reformed as an experimental trials unit, and then as a helicopter training squadron. Since 2003, the squadron has formed the Royal Naval wing of the Defence Elementary Flying Training School at RAF Barkston Heath.

706 Naval Air Squadron was a Naval Air Squadron of the Royal Navy's Fleet Air Arm. Established as a fighter and torpedo-bomber training unit in Australia at the end of World War Two, it was briefly reformed as a helicopter squadron in the early 1950s, before becoming a helicopter training unit in 1962, and operating until 1998.
Royal Naval Air Station Crail or RNAS Crail is a former Fleet Air Arm base located 4.9 miles (7.9 km) of Anstruther, Fife and 8.8 miles (14.2 km) of St Andrews, Fife, Scotland. It was home to a site of the Joint Services School for Linguists from 1956 to 1960.